- Soulèvement
-
Liste de révolutions et de rébellions
Demande de traduction --- List of revolutions and rebellions →
List of revolutions and rebellions →  Liste de révolutions et de rébellions --- (+)
Liste de révolutions et de rébellions --- (+) Le Soulèvement, peinture d'Honoré Daumier
Le Soulèvement, peinture d'Honoré Daumier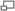
La France connaît de nombreuses révoltes populaires, parfois des révolutions et des crises de régimes, au cours du XIXe siècle.Cette liste présente une chronologie, non exhaustive, de différentes révolutions et rébellions dans le monde. Pour une liste de coups d'États et de tentatives de coups d'États voir : Liste de coups d'États.
Sommaire
Antiquité
- -499--493 : révolte de l'Ionie. La plupart des cités grecques occupées par les Perses en Asie mineure et à Chypre se révoltent contre la domination perse suite à l'échec de l'expédition contre les Scythes.
- -460 : révolte d'Inaros. Inaros, fils d'un chef libyen, prend la tête d'un mouvement d'insurrection contre les Perses. Il demande l'aide des Athéniens, qui, déjà en guerre contre la Perse, dépêchent des troupes en Égypte.
- -206 : Ziying, dernier dirigeant de la dynastie Qin (en Chine) capitule devant Liu Bang, dirigeant d'une révolte populaire et fondateur de la dynastie Han.
- -181--174 : révoltes celtibères dans la péninsule ibérique, face aux Romains.
- -154 : échec de la rébellion des sept États menée par des membres de la famille royale de la dynastie Han.
- -153--133 : nouvelle révolte celtibère dans la péninsule ibérique contre les Romains, qui s'achève avec la chute de Numance.
- -147--139 : durant la conquête romaine de l'Hispanie, le berger lusitanien Viriathe organise une résistance efficace, et bat plusieurs armées romaines. Les Romains ne peuvent en venir à bout qu’en le faisant assassiner par ses partisans.
- -73--71 : la troisième guerre servile est la dernière d’une série de rébellions d’esclaves contre la République Romaine, connues collectivement sous le nom de guerres serviles. Elle est dirigée par le gladiateur Spartacus.
- -52--51 : révoltes gauloises dirigées par Vercingetorix, vaincu par Jules César.
1 - 1000
- 6-9 : des tribus illyriennes et d'autres en provenance de Pannonie et de Dalmatie se révoltent et sont vaincues par Tiberius et Germanicus, après une rude campagne qui dura trois ans.
- 9 : révolte d'Arminius contre l'Empire romain; alliance des tribus germaniques dirigées par Arminius tendirent une embuscade et détruisirent ainsi trois légions romaines dirigées par Publius Quinctilius Varus lors de la bataille de Teutobourg.
- 18 : révolte des Sourcils Rouges en Chine
- 60-61 : Boudica, reine des Iceni, Celtes du Norfolk, conduit une rébellion des tribus bretonnes contre l'occupant romain[1].
- 66-70 : Première Guerre judéo-romaine, la première des trois guerres judéo-romaines qui ont eu lieu en Judée contre l’Empire romain.[2]
- 69-70 : rébellion des Bataves dans la province romaine de Germanie inférieure.
- 115-117 : guerre de Kitos, deuxième des guerres judéo-romaines.
- 132-135 : révolte de Bar Kokhba, troisième et dernière des guerres judéo-romaines.
- 184 : Zhang Jiao conduit la rébellion des Turbans jaunes contre la dynastie Han.
- 532 : Sédition Nika à Constantinople.
- 613 : la révolte de Yang Xuangan est écrasée par la dynastie Sui.
- 623 : soulèvement des Slaves menés par Samo de Bohême contre les Avars.
- 685-699 : révolte kharidjite en Iran et en Irak contre les Omeyyades.
- 740 : révolte zaïdite contre les Omeyyades.
- 740-743 : révolte berbère dans le Maghreb contre les Omeyyades.
- 747-750 : renversement de la dynastie omeyyade par les Abbassides révoltés.
- 755-763 : révolte d'An Lushan contre la dynastie Tang.
- 782-785 : révolte saxonne contre Charlemagne.
- 814 : Al-Hakam Ier écrase une révolte des musulmans espagnols à al-Ribad, sur la rive sud du Guadalquivir.
- 817-837 : révoltes des Iraniens khurramites conduite par Babak Khorramdin.
- 824-836 : révolte des troupes arabes de Tunisie contre les Aghlabides, qui n'est matée qu'avec l'aide des Berbères.
- 828 : échec de la révolte de Kim Heon-chang contre le Silla, en Corée.
- 845 : révolte du capitaine Jang Bogo contre le Silla, qui ne cesse qu'avec l'assassinat de Jang Bogo.
- 861-1003 : fondation de la dynastie des Saffarides par Ya`qûb bin Layth as-Saffâr dans l'est de l'Iran.
- 869-883 : révolte des Zanj, esclaves noirs, en Irak, écrasée par les Abbassides[3].
- 875-884 : rébellion du contrebandier Huang Chao contre la dynastie Tang, qui contribue à son effondrement.
- 884 : Omar Ben Hafsun conduit une révolte contre les Omeyyades dans le sud de l'Espagne.
- 899-906 : révolte de la secte des Qarmates contre les Abbassides dans l'est de l'Arabie.
- 934 : révolte des Normands de l'Ouest principalement (Rébellion de Riouf) dénonçant la francisation de la Normandie
- 943-947 : révolte du berbère kharidjite Abu Yazid contre les Fatimides.
- 982 : révolte des Slaves païens du bas Elbe (fleuve) contre le Saint-Empire.
1000-1600
- 1095 : en Angleterre, rébellion de nobles du Nord contre William Rufus
- 1125 : les Almohades commencent une rébellion dans les montagnes de l'Atlas
- 1156 : rébellion hogen qui réussit à établir la domination de clans samourai et finalement le premier gouvernement mené par des samouraïs du Japon
- 1185 : rébellion Vlach des Bulgares contre l'Empire byzantin.
- 1233-1234 : révolte stedingen revolt in Frise qui amène le Pape Grégoire IX à appeler à la croisade.
- 1242-1249 : premier soulèvement de la Prusse contre les Chevaliers Teutoniques, lors des croisades baltes.
- 1250 : les Mamelouks tuent le dernier sultan de la dynastie des Ayyoubides et fondent la dynastie des Baharites.
- 1296-1328 : première guerre d'indépendance de l'Écosse entre les Écossais et l'Angleterre, conduisant à une reconnaissance de l'indépendance en 1328 avec la signature du traité d’Édimbourg-Northampton.
- 1332-1357 : seconde guerre d'indépendance de l'Écosse, conduisant à une nouvelle reconnaissance de l'indépendance de l'Écosse par l'Angleterre lors de la signature du traité de Berwick.
- 1302 : bataille de Courtrai en Flandre, qui aboutit au départ de la France.
- 1323-1328 : début d'une série d'escarmouches rurales fin 1323, la révolte des Karls qui s'aggravera progressivement en une rébellion de plus en plus importante amenant la bataille de Cassel.
- 1343-1345 : révolte de la Saint-Georges en Estonie.
- 1354 : révolte de Cola di Rienzo.
- 1358 : la Jacquerie, en Île-de-France
 Fin sanglante de la révolte des paysans de 1381 en Angleterre. Wat Tyler, le chef des rebelles, est exécuté sous les yeux de Richard II. Une seconde image dans le tableau montre Richard parlant à la foule
Fin sanglante de la révolte des paysans de 1381 en Angleterre. Wat Tyler, le chef des rebelles, est exécuté sous les yeux de Richard II. Une seconde image dans le tableau montre Richard parlant à la foule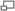
- 1368 : Ming Hongwu dirige les paysans han dans une rébellion contre la dynastie Yuan mongole établissant ainsi la dynastie Ming.
- 1378 : révolte des Ciompi.
- 1378-1384 : révolte des Tuchins en Languedoc
- 1381 : révolte des paysans en Angleterre
- 1382 : révolte de la Harelle à Rouen
- 1382 : révolte des Maillotins à Paris
- 1382 : révolte des tisserands gantois
- 1400-1415 : révolte galloise menée par Owain Glyndŵr.
- 1418-1427 : des Vietnamiens dirigés par Le Loi se révoltent contre l'occupation chinoise.
- 1420 : début de la révolte des hussites de Bohème contre l'Église catholique et le Saint Empire Romain Germanique. Cela débouche sur les croisades contre les Hussites.
- 1434 : rébellion de la paysannerie suédoise contre les Danois.
- 1437 : révolte Bobâlna en Transylvanie, utilisant des tactiques militaires issues des croisades contre les Hussites.
- 1444-1468 : rébellion de Skenderbeg dans lAlbanie sous le joug ottoman.
- 1450 : rébellion du Kent dirigée par Jack Cade.
- 1462-1485 : rébellion des Remença en Catalogne.
- 1490 : révolte de Plouyé, en Cornouailles
- 1497 : rébellion de 1497 en Cornouailles.
- 1501-1509 : Ismail Ier fonde la dynastie des Séfévides en Azerbaïdjan et en Iran, et joue également un rôle clé dans le soulèvement de la branche des Douze du chiisme dans ces deux régions jusqu'alors dominées par l'ismaélisme et le sunnisme.
- 1514 : révolte des paysans sicules conduite par György Dózsa dans le Royaume de Hongrie.
- 1515 : révolte des paysans slovènes
- 1515 : Frisian-rebellion of the Arumer Black Heap, lead by Pier Gerlofs Donia.
- 1519-1523 : the first Revolta de les Germanies in Valencia, an anti-monarchist, anti-feudal autonomist movement inspired by the Italian republics
- 1519-1610 : Jelali revolts in Anatolia against the authority of the Ottoman Empire.
- 1520-1522 : Revolt of the Comuneros against the rule of Spanish king and Holy Roman Emperor Charles V.
- 1524-1525 : Peasants' War of in the Holy Roman Empire.
- 1542 : Dacke Feud en Suède.
- 1548 : Jacquerie des pitauds, en Bordelais
- 1549 : Prayer Book Rebellion en Cornwall et Devon, Royaume-Uni.
- 1549 : Kett's Rebellion
- 1566-1648 : Eighty Years' War; revolt of the Low Countries against Spain.
- 1568-1571 : Morisco Revolt by the remnants of the Morisco community (Spanish Christian converts from Islam ["crypto-Muslims"] in Granada, Spain.
- 1573 : Croatian and Slovenian peasant revolt.
- 1579 : Jacquerie des gautiers en Normandie
- 1588 : La Ligue à Paris : Journée des barricades
- 1593-1599 : Soulévement des Tard-Avisés en Limousin et Périgord
- 1594-1603 : The Nine Years War or Tyrone's Rebellion in Ulster, Ireland against English rule in Ireland
- 1596 : Club War uprising in Finland.
1600-1900
- 1606-1607 : Bolotnikov rebellion for the abolition of serfdom, which was part of the Time of Troubles in Russia.
- 1618-1625 : Bohemian Revolt against the Habsburgs. Rebellion was part of Thirty Years' War.
- 1637-1638 : Shimabara Rebellion of Japanese Christians.[4]
- 1639 : Révolte des Nu-Pieds en Normandie.
- 1640 : Portuguese Revolt against Spanish Empire.
- 1640-1652 : Catalan Revolt.
- 1640-1644 : Vlach uprising against Habsburg rule in Moravia.
- 1641 : Irish Rebellion of 1641
- 1642-1653 : Première révolution anglaise
- 1644 : Li Zicheng rebellion against the Ming Dynasty.
- 1647 : Naples Revolt.
- 1648 : Khmelnytsky Uprising of Cossacks in Ukraine against Polish nobility in the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth.
- 1648-1653 : ** la Fronde contre Mazarin
- 1662 : Révolte des Lustucru en Boulonnais
- 1668 : Sikhs in the Anandpur revolted against the Mughal Empire.
- 1668-1676 : Solovetsky Monastery Uprising
- 1669 : Jat uprising under Gokula. The Hindu Jats in the Agra district revolted against the Mughal Emperor Aurangzeb.
- 1672 : Pasthun rebellion against the Mughals.
- 1672-1674 : Lipka Rebellion, an uprising of Polish Tatars against the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth.
- 1672-1678 : Messina Revolt. The Sicilian revolt against Spanish rule took place during the Franco-Dutch War of Louis XIV; the rebels were supported by France.
- 1675-1676 : King Philip's War between Indians and English settlers, sometimes called Metacom's Rebellion. One in ten soldiers on both sides was injured or killed.
- 1676 : Bashkir Rebellion against Russian rule.
- 1680 : Pueblo Revolt against Spanish settlers in New Mexico.
- 1682 : Révolte de Moscou de 1682.
- 1688 : Glorieuse Révolution en Angleterre
- 1688-1746 : The 'Jacobite Risings were a series of uprisings, rebellions, and wars in the British Isles occurring between 1688 and 1746.
- 1689 : Karposh's Rebellion against Ottoman Empire.
- 1693 : the second Revolta de les Germanies in Valencia, prompted by feudal taxation.
- 1698 : Streltsy Uprising in Russia.
- 1702-1715 : Camisard Rebellion in France.
- 1703-1711 : The Rákóczi Uprising against the Habsburgs.
- 1707-1709 : Bulavin Rebellion in Imperial Russia.
- 1709 : Mir Wais Hotak, an Afghani tribal leader, led a successful rebellion against Gurgin Khan, the Persian governor of Kandahar.
- 1722 : Afghan rebels defeated Shah Sultan Hossein and ended the Safavid dynasty.
- 1745-1746 : Bataille de Culloden en Ecosse, lors du soulevement jacobite
- 1763-1766 : Pontiac's Rebellion by numerous North American Indian tribes who joined the uprising in an effort to drive British soldiers and settlers out of the Great Lakes region.
- 1768 : Rebellion of 1768 by Creole and German settlers objecting to the turnover of the Louisiana Territory from New France to New Spain
- 1770 : Orlov Revolt in Peloponnese
- 1773-1775 :Pugachev's Rebellion was the largest peasant revolt in Russia's history. Between the end of the Pugachev rebellion and the beginning of the 19th century, there were hundreds of outbreaks across Russia.[5]
- 1774-1783 : Révolution américaine establishes independence of the thirteen North American colonies from Great Britain, creating the republic of the United States of America. A war of independence in that it created one nation from another, it was also a revolution in that it overthrew an existing societal and governmental order: the Colonial government in the Colonies. The American Revolution heavily influenced the French Revolution that followed it and led to the creation of a Constitutional form of government (see U.S. Constitution).
- 1675 : Révolte du papier timbré en Basse-Bretagne.
- 1780-1782 : José Gabriel Condorcanqui, known as Túpac Amaru II, raises an indigenous peasant army in revolt against Spanish control of Peru. Julián Apasa, known as Tupac Katari allied with Tupac Amaru and lead an indigenous revolt in Alto Peru (preset day Bolivia) nearly destroying the city of La Paz in a siege.
- 1789 : Révolution française is associated with the rise of the bourgeoisie and the downfall of the aristocracy.
 Hanging of suspected United Irishmen by Government troops. Irish Rebellion of 1798
Hanging of suspected United Irishmen by Government troops. Irish Rebellion of 1798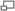
- 1791-1804 : the successful slave rebellion led by Toussaint Louverture establishes Haiti as the first free, black republic.
- 1793-1796 : Revolt in the Vendée was popular uprising against the Republican government during the French Revolution.
- 1794 : Polish revolt
- 1795-1796 : rebels in Grenada led by Julien Fédon execute the governor and wrest control of most of the island from Britain, which maintains a stronghold in St. George's, the capital. The goal was to incorporate Grenada into revolutionary France, but Fédon soon disappeared and was never heard from again.
- 1796-1804 : The White Lotus Rebellion against the Manchu Dynasty in China.
- 1797 : Spithead and Nore mutinies were two major mutinies by sailors of the British Royal Navy.
- 1798 : The Irish Rebellion of 1798 failed to overthrow British rule in Ireland.
- 1803 : The rebellion of Robert Emmet in Dublin, Ireland against British rule
- 1804-1813 : The First Serbian Uprising against Ottoman rule.
- 1808 : Dos de Mayo Uprising against the occupation of Madrid by French troops.
- 1808-1814 : The Peninsula war.
- 1809-1810 : The Rebellion of Velu Thampi Dalawa of Travancore.
- 1810-1821 : the Mexican War of Independence, a revolution against Spanish colonialism
- 1810 : the Viceroy of the Río de la Plata is deposed by local officers in Argentina
- 1810-1840 : the dictatorship of José Gaspar Rodriguez de Francia in Paraguay is dubbed the "autonomous revolution" by Paraguay specialist Richard Alan White.[6] Influenced by the Jacobins of the French Revolution and the meritocratic theory of socialism propounded by Henri de Saint-Simon, Francia led his country on an isolationist path, emphasizing self-sufficiency and breaking the power of the traditional colonial elite with harsh, autocratic repression. His rule was know as tyrannical, anticlerical, and xenophobic. Paraguay remained one of South America's most advanced countries until the War of the Triple Alliance.
- 1812 : Peasant rebellion of Hong Gyeong-nae against Joseon Dynasty of Korea
- 1817 : The Pernambucan Revolution, a republican separatist movement which resulted in the creation of the short-lived Republic of Pernambuco (7 mars 1817 - 20 mai 1817).
- 1817 : The Pentrich Revolution, Derbyshire; an ill-fated attempt to overthrow the Government, unknowingly it was instigated by William Oliver, aka Oliver the Spy. Three men were executed in Nov 1817 & 14 men were transported to NSW. The event is known as 'England's Last Revolution' (9-10 juin 1817).
- 1820 : revolutions in Spain and Portugal.
- 1820-1824 : revolutionary war of independence in Peru led by José de San Martín
- 1821-1829 : Greek War of Independence
- 1822-1823 : republican revolution in Mexico overthrows Emperor Agustín de Iturbide
- 1825 : Révolte des Décembristes in Russian Empire
- 1825-1830 : The Java War or Dipanegara Revolution, when the prince of Mataram Islam against the tax and land rent dommination from Dutch.
- 1826 : Janissary revolt in Ottoman Empire
- 1827-1828 : failed conservative rebellion in Mexico led by Nicolás Bravo
- 1830 : Les Trois Glorieuses (ou révolution de juillet) à Paris.
- 1830 : Révolution belge
- 1830 1831 - Révolution polonaise
- 1831 : Révolte des Canuts à Lyon
- 1832-1843 : Abdelkader's rebellion in French-occupied Algeria
- 1834-1859 : Imam Shamil's rebellion in Russian-occupied Caucasus.
- 1835-1836 : Texas secedes from Mexico in the Texas Revolution
- 1835-1845 : War of Tatters, Separatists gauchos revolutionaries declared the independence of the Rio Grande do Sul from Brazil.
- 1837-1838 : Rebellions of 1837 - failed republican revolutions against British rule in Canada.
- 1841-1842 : Afghan uprising. Hostile Afghan tribes massacred Elphinstone's British army including some 12,000 civilian dependents and camp followers.[7]
- 1847 : Maya Rebellion in Yucatán.
- 1847 : Taos Revolt in New Mexico against the United States
- 1848 : the Revolutions of 1848 are a wave of failed liberal and republican revolutions that swept Europe.
- 1848 : Révolution autrichienne
- 1848 : Révolution française de 1848
- 1848 : rebellion in British-ruled Ceylon
- 1851-1864 : révolte des Taïpings against the Qing Dynasty and Manchu domination in China. In total between 20 and 30 million lives had been lost, making it the second deadliest war in human history.
- 1854 : Revolution in Spain against the Moderate Party Government.
- 1854-1873 : The Miao Rebellion in China.
- 1854-1855 : Revolution of Ayutla in Mexico
- 1857 : failed Indian rebellion against British East India Company, marking the end of Mughal rule in India. Also known as the 1857 War of Independence and, particularly in the West, the Révolte des Cipayes.
- 1858 : Mahtra War in Estonia.
- 1858-1861 : War of the Reform in Mexico
- 1859 : The Second Italian War of Independence
- 1861-1865 : American Civil War in the United States, between the United States and the Confederate States of America, which was formed out of eleven southern states.
- 1861-1866 : Quantrill's Raiders in Missouri.
- 1862 : Sioux Uprising in Minnesota.[8]
- 1862-1877 : Muslim Rebellion against the Qing Dynasty.
- 1863 : New York Draft Riots.[9]
- 1863-1865 : January Uprising was the Polish uprising against the Russian Empire.
- 1865 : Morant Bay rebellion
- 1866-1868 : Meiji Restoration and modernization revolution in Japan. Samurai uprising leads to overthrow of shogunate and establishment of "modern" parliamentary, Western-style system.
- 1867 : Fenian Rising An attempt at a nationwide rebellion by the Irish Republican Brotherhood against British rule.
- 1868 : the Glorious Revolution in Spain deposes Queen Isabella II
- 1868 : in the Grito de Lares, rebels proclaim the independence of Puerto Rico from Spain.
- 1869 - 1870 : Red River Rebellion, the events surrounding the actions of a provisional government established by Métis leader Louis Riel at the Red River Settlement, Manitoba, Canada.
- 1871 : Commune de Paris
- 1871-1872 : Porfirio Díaz rebels against President Benito Juárez of Mexico
- 1871 : liberal revolution in Guatemala
- 1875 : Deccan Riots
- 1875 : Herzegovinian rebellion, the most famous of the rebellions against the Ottoman Empire in Herzegovina; unrest soon spread to other areas of Ottoman Bosnia.
- 1876 : a second rebellion by Porfirio Díaz against President Sebastián Lerdo de Tejada of Mexico
- 1876 : the April uprising, a revolt by the Bulgarian population against Ottoman rule.
- 1877 : Satsuma Rebellion of Satsuma ex-samurai against the Meiji government.
- 1882 : Urabi Revolt : an uprising in Egypt on 11 juin 1882 against the Khedive and European influence in the country. It was led by and named after Colonel Ahmed Urabi.
- 1885 : a peasant revolt in the Ancash region of Peru led by Pedro Pablo Atusparía succeeds in occupying the Callejón de Huaylas for several months
- 1885 : North-West Rebellion of Métis in Saskatchewan
- 1888 : the Rebellion of Peasant in Banten, Indonesia.
- 1893 : a liberal revolt brings José Santos Zelaya to power in Nicaragua
- 1894-1895 : Donghak Peasant Revolution : Korean peasants led by Jeon Bong-jun revolted against Joseon Dynasty; the revolt was crushed by Japanese and Chinese intervention, leading to First Sino-Japanese War
- 1895 : revolution against President Andrés Avelino Cáceres in Peru ushers in a period of stable constitutional rule
- 1896-1898 : the Philippine Revolution, a war of independence against Spanish rule directed by the Katipunan society
- 1899-1901 : guerre des Boxers against foreign influence in areas such as trade, politics, religion and technology that occurred in China during the final years of the Qing Dynasty.
1900-1950
- 1903 : the Ilinden Uprising of the Macedonians in the Ottoman Empire breaks out.
- 1904 : révolution libérale au Paraguay
- 1905 : échec de la bourgeoisie libérale lors de la Révolution russe contre le Tsar Nicholas II en Russie.
- 1905-1906 : Révolution constitutionnelle de l'Iran
- 1905-1906 : Maji Maji Rebellion in German east Africa
- 1907 : Romanian Peasants' Revolt
- 1908 : Young Turk Revolution, Young Turks force the autocratic ruler Abdul Hamid II to restore parliament and constitution in the Ottoman Empire.
Fichier:Constantinople settings and traits (1926)- public demonstration.pngPublic demonstration in the Sultanahmet district of Istanbul, during the Young Turk Revolution of 1908- 1910 : the Mexican Revolution overthrows the dictator Porfirio Díaz; seizure of power by Institutional Revolutionary Party.
- 1910 : republican revolution in Portugal
- 1910-1911 : the Sokehs Rebellion erupts in German-ruled Micronesia. Its primary leader, Somatau, is executed soon after being captured.
- 1911 : Révolution chinoise de 1911, établissement de la République de Chine
- 1914 : the Ten Days War was a shooting war involving irregular forces of coal miners using dynamite and rifles on one side, opposed to the Colorado National Guard, Baldwin Felts detectives, and mine guards deploying machine guns, cannon and aircraft on the other, occurring in the aftermath of the Ludlow Massacre. The Ten Days War ended when federal troops intervened.
- 1914 : Boer Revolt against the British in South Africa.
- 1916 : Easter Rising in Dublin, Ireland during which the Irish Republic was proclaimed.
- 1916 : an anti-French uprising in Algeria.
- 1916 : Central Asian Revolt started when the Russian Empire government ended its exemption of Muslims from military service.
- 1916-1918 : Arab Revolt with the aim of securing independence from the Ottoman Empire.
- 1916-1923 : Irish War of Independence, the period of nationalist rebellion, guerrilla warfare, political change and civil war which brought about the establishment of the independent nation, the Irish Free State.
- 1916-1947 : Gandhi's Struggle for Indian Independence.
- 1917 : Mutineries de 1917 dans les armées françaises
- 1917 : la révolution de Février conduit à l'abdication du tsar Nicolas II de Russie.
- 1917 : the Green Corn Rebellion takes place in rural Oklahoma.
- 1917 : Révolution d'Octobre en Russie - prise du pouvoir par les bolcheviks conduisant à la création de l'URSS.
- 1918 : Christmas Uprising in Montenegro - Montenegrins (Zelenaši) rebelled against unification of Kingdom of Montenegro with Kingdom of Serbia.
- 1918 : Wilhelmshaven mutiny
- 1918 : Révolution allemande. Renversement du Kaiser, établissement de la République de Weimar.
- 1918-1919 : a wave of strikes and student unrest shakes Peru. These events influence two of the dominant figures of Peruvian politics in the 20th century: Víctor Raúl Haya de la Torre and José Carlos Mariátegui.
- 1918-1919 : Greater Poland Uprising (1918-1919) Polish uprising against German authorities
- 1918-1921 : Ukrainian Revolution
- 1918-1922 : Third Russian Revolution, a failed anarchist revolution against both Bolshevism and the White movement.
- 1918-1931 : Basmachi Revolt against Soviet Russia rule in Central Asia.
- 1919-1921 : Tambov Rebellion
- 1919-1922 : Turkish War of Independence commanded by Mustafa Kemal Atatürk.
- 1919 : German Revolution
- 1919 : revolution in Hungary results in the short-lived Hungarian Soviet Republic
- 1920 : Pitchfork Uprising was a peasant uprising against the Soviet policy of the war communism in what is today Tatarstan.
- 1920-1922 : Gandhi led Non-cooperation movement.
- 1921 : Battle of Blair Mountain ten to fifteen thousand coal miners rebel in West Virginia, assaulting mountain-top lines of trenches established by the coal companies and local sheriff's forces in the largest armed, organized uprising in American labor history.
- 1921 : Kronstadt rebellion of Soviet sailors against the government of the early Russian SFSR.
- 1921-1923 : Yakut Revolt
- 1921-1924 : une révolution en Mongolie ré-établit l'indépendance du pays et décide de construire un état socialiste de type Soviétique
- 1922-1923 : Irish Civil War, between supporters of the Anglo-Irish Treaty and the government of the Irish Free State and more radical members of the original Irish Republican Army who opposed the treaty and the new government.
- 1923 : Founding of Republic of Turkey by overthrowing the Ottoman Empire, introduction of Atatürk's Reforms.
- 1923 : Klaipėda Revolt in the Memel territory that had been detached from Germany after World War I.
- 1924-1927 : Sheikh Said Rebellion
- 1925 : July Revolution in Ecuador
- 1925-1927 : The Syrian Revolution, a revolt initiated by the Druze and led by Sultan al-Atrash against French Mandate.
- 1926 : the so-called "National Revolution" in Portugal initiates a period known as the "National Dictatorship"
- 1926-1929 : the Cristero War in Mexico, an uprising against anti-clerical government policy
- 1926-1927 : the frist PKI - or Indonesian Communist Party - rebellion againts collonialism and imperialism of Dutch Hindie.
- 1927-1931 : Kurdish Rebellion against Turkey.
- 1927-1933 : rebellion led by Augusto César Sandino against the United States presence in Nicaragua
- 1930 : Brazilian Revolution of 1930 led by Getúlio Vargas.
- 1930 : Salt Satyagraha, a campaign of non-violent protest against the Britishsalt tax in colonial India .
- 1932 : a Constitutionalist Revolution against the provisional president Getúlio Vargas led Brazil to a short civil war.
- 1932 : an Aprista revolt in Trujillo, Peru. After about 60 officers are executed, the army responds with the killing of at least 1,000 people. The repression includes the first aerial bombing in South American history.
- 1932 : the Siamese coup d'état of 1932, sometimes called the "Promoters Revolution", ends absolute monarchy in Thailand
- 1933 : popular revolution against Cuban dictator Gerardo Machado
- 1934 : In October, workers including radical socialists and anarchists stage coups in the Spanish regions of Asturias and Catalonia. The immediate cause was the entrance of a right-wing Catholic party into the government of the unstable Second Spanish Republic. The Asturian uprising was put down by General Francisco Franco.
- 1936 : the Febrerista Revolution, oligarchic Liberal Party rule in Paraguay ended by Rafael Franco.
- 1936 : General Francisco Franco leds a coup and starts the Spanish Civil War.
- 1936 : Révolution espagnole
- 1936-1939 : a period of so-called "military socialism" in Bolivia follows a revolution in which celebrated war hero David Toro takes power. A constitution establishing a corporative state is promulgated in 1938, following the nationalization of Standard Oil and the passage of progressive labor laws.
- 1937-1938 : Dersim Rebellion was the most important Kurdish rebellion in modern Turkey.
- 1937 : the "Jornadas de Mayo", a workers' revolution in Catalonia
- 1938-1948 : The Zionist Revolution - the period of Jewish nationalist rebellion and guerrilla warfare against the British Empire in Palestine which brought about the establishment of the State of Israel. Mainly fought by the Lehi and Irgun underground organizations but periodically joined by the Jewish Agency's official Haganah militia.
- 1941 : June Uprising against the Soviet Union en Lituanie
- 1941-1945 : Yugoslav People's Liberation War against the Axis Powers in World War II.
- 1942 : Sri Lankan soldiers ignite the Cocos Islands Mutiny in an unsuccessful attempt to transfer the islands to Japanese control
- 1942 : The destruction of the German garrison in Lenin
- 1943 : soulèvement du ghetto de Varsovie
- 1943 : Uprising at Treblinka extermination camp
- 1943 : Uprising at Sobibór extermination camp
- 1944 : Guatemalan Revolution overthrows the dictator Jorge Ubico by liberal military officers.
- 1944 : Warsaw Uprising was an armed struggle during the Second World War by the Polish Home Army (Armia Krajowa) to liberate Warsaw from German occupation and Nazi rule. It started on 1er août 1944.
- 1944 : Paris Uprising staged by the French Resistance against the German Paris garrison.
- 1944 : Slovak National Uprising against Nazi Germany
- 1944 : Uprising at Auschwitz extermination camp
- 1944-1947 : a Communist-friendly government is installed in Bulgaria following a coup d'état and the Soviet invasion. The government was nominally a coalition called the Fatherland Front, but the Communist Party faction consolidated its power with Soviet support until 1947, when Soviet troops withdrew. Many royalist and fascist leaders from the previous Axis regime were given summary trials and executed.
- 1944 : Following the liberation of Albania completed on 29 novembre, the Communist Party of Albania under Enver Hoxha consolidates its control, moves forward with industrialization and modernization, and declares the People's Republic of Albania in January 1946.
- 1944-1949 : Greek Civil War.
- 1944-1965 : Forest Brothers Rebellion in Baltic states against Soviet Union.
- 1945-1949 : Indonesian National Revolution against Dutch after them independence from Japan. who lead by Soekarno, Hatta, Tan Malaka, etc. and the Dutch lead by Van Mook.
- 1945 : Prague uprising against German occupation during World War II.
- 1945 : August Revolution led by Ho Chi Minh declares the independence of the Democratic Republic of Vietnam from French rule
- 1945 : democratic revolution in Venezuela led by Rómulo Betancourt
- 1947 : Three months after an abortive coup, civil war breaks out in Paraguay. Led by Rafael Franco, the former head of the Febrerista (see above) government displaced in 1937, the rebellion was crushed by the government of dictator Higinio Morínigo. A local commander, Lt. Col. Alfredo Stroessner, seized the presidency in 1954 and ruled until 1989.
- 1946-1951 : Telengana Rebellion a Communist led peasant revolt that took place in the Hyderabad State, India.
- 1947-1952 : In the Albanian Subversion, the intelligence services of the United States and Britain deploy exiled fascists, Nazis, and monarchists (especially members of Balli Kombëtar and the Legaliteti) in a failed attempt to foment a counterrevolution in Communist-ruled Albania. The exiles carried out some sabotage but found little popular support. Some exiles were captured and executed, along with some ordinary Albanians suspected of assisting them.
- 1947 Indian Revolution ends with the British withdrawing all of its troops, governers and anyone else under its command from India, due to the extreme pressure being adminstered upon them, by the Indian populace, and their leaders, such as M.K. Gandhi.
- 1948 : following the liberation of Korea, Marxist former guerrillas under Kim Il Sung work to rapidly industrialize the country and rid it of the last vestiges of "feudalism."
- 1948-1960 : Malayan Emergency
- 1949 : the Communist-led Chinese Revolution under chairman Mao overthrows the ruling Nationalist Party and establishes the People's Republic of China.
- 1950 : Jayuya revolt in Puerto Rico, explosion in the Blair House, and shooting at Congress, all looking for Puerto Rican independence.
- 1954-1962 : Algerian War of Independence - revolutionary war of independence against French colonialism
1950-2000
- 1950s : Mau Mau Uprising
- 1952 : a popular revolution in Bolivia led by Víctor Paz Estenssoro and the Revolutionary Nationalist Movement (MNR) initiates a period of multiparty democracy lasting until a 1964 military coup.
- 1952 : Rosewater Revolution in Lebanon
- 1953 : Vorkuta uprising was a major uprising of the Gulag inmates in Vorkuta in the summer of 1953. Like other camp uprisings it was bloodily quelled by the Red Army and the NKVD.[10]
- 1954 : Kengir uprising in the Soviet prison labor camp Kengir.
- 1954 : Uyghur uprising against Chinese rule in Hotan.
- 1955-1960 : Guerrilla war against British colonial rule of Cyprus lead by the EOKA (National Organisation of Cypriot Fighters)
- 1955-1970 : The Union of the Peoples of Cameroon (UPC) engages in a guerrilla struggle against French colonialism in the French Cameroons. In 1955 the UPC was for all practical purposes banned, and in 1960 Cameroon achieved independence under the conservative government of President Ahmadou Ahidjo. After the gradual assassinations of many of its top leaders and the proclamation of a one-party state in 1966, the last significant remnants of the insurgency were extinguished in 1970. The UPC, unlike many other guerrilla organizations throughout Africa, never achieved state power.
- 1956-1962 : Border Campaign led by the Irish Republican Army against the British, along the border of the independent Republic of Ireland and British Northern Ireland.
Fichier:FidelGuerilla.JPGCuban guerilla fighters led by Fidel Castro in the Sierra Maestra mountains during the Cuban Revolution 1956-59- 1956 : Insurrection de Budapest, a failed workers' and peasants' revolution against the Soviet-supported communist state in Hungary.
- 1956 : Tibetan rebellions against Chinese rule broke out in Amdo and Kham.
- 1958 : popular revolt in Venezuela against military dictator Marcos Pérez Jiménez culminates in a civic-military coup d'état
- 1958 : the Iraqi Revolution led by nationalist soldiers abolishes the British-backed monarchy, executes many of its top officials, and begins to assert the country's independence from both Cold War power blocs.
- 1959 : The failed Tibetan uprising against Chinese rule led to the flight of the Dalai Lama.
- 1959 : Cuban Revolution led by Fidel Castro removes the government of General Fulgencio Batista. By 1962 Cuba had been transformed into a declared socialist republic.
- 1959 : the Tutsi king of Rwanda is forced into exile by Hutu extremists; racial pogroms follow an assassination attempt on Hutu leader Grégoire Kayibanda
- 1960-1973 : Counterculture of the 1960s was a social revolution that originated in the United States and United Kingdom and eventually spread to other westernized nations. Themes of this movement included the anti-war movement, rebellion towards conservative norms, increase of drug use, and the sexual revolution.
- 1961-1991 : Eritrean War of Independence led by Isaias Afewerki against Ethiopia.
- 1961-1975 : Angolan Marxists and other radicals grouped in the Popular Movement for the Liberation of Angola (MPLA) begin guerrilla attacks on Portuguese infrastructure. With extensive military assistance from Cuba, the MPLA is able to outmaneuver two rival organizations and establish control of Luanda in time for independence on 11 novembre 1975. Civil war between the MPLA government and the anti-communist UNITA continued on-and-off until 2002, when UNITA leader Jonas Savimbi was killed.
- 1962-1974 : The leftist African Party for the Independence of Guinea and Cape Verde (PAIGC) wages a revolutionary war of independence in Portuguese Guinea. In 1973, the independent Republic of Guinea-Bissau is proclaimed, and the next year the republic's independence is recognized by the reformist military junta in Lisbon.
- 1962 : revolution in northern Yemen overthrows the imam and establishes the Yemen Arab Republic
- 1963-1967 : Aden Emergency : nationalists in British-ruled Aden, with an eye on recent events in North Yemen and in Palestine, declare war on the British under the umbrella of the National Liberation Front (NLF). The UK hands over control to an independent South Yemen in novembre 1967. In 1969, moderate President Qahtan Muhammad al-Shaabi is edged out in favor of more radical socialists, who convoke a constituent assembly and begin to develop the state along Marxist-Leninist lines. The result is the only Communist state in the Arab world and the first in a Muslim country.
- 1964 : following an American school's provocative decision to raise only the flag of the United States, Panamanian students march into the Panama Canal Zone with the flag of Panama. After the latter flag is torn, thousands more become involved, starting huge riots that lasted three days. About 20 people were killed and hundreds more injured.
- 1964 : the Zanzibar Revolution overthrows the 157-year-old Arab monarchy, declares the People's Republic of Zanzibar, and begins the process of unification with Julius Nyerere's Tanganyika
- 1964 -1979 : Rhodesian Bush War also known as the Second Chimurenga or the Liberation Struggle, was a guerrilla war which lasted from July 1964 to 1979 and led to universal suffrage, the end of white-rule in Zimbabwe Rhodesia, and the creation of the Republic of Zimbabwe.
- 1964 : the October Revolution in Sudan, driven by a general strike and rioting, forces President Ibrahim Abboud to transfer executive power to a transitional civilian government and eventually resign.
- 1964-1975 : the Mozambican Liberation Front (FRELIMO), formed in 1962, commences a guerrilla war against Portuguese colonialism. Independence is granted on June 25, 1975; however, the Mozambican Civil War complicated the political situation and frustrated FRELIMO's attempts at radical change. The war continued into the early 1990s after the government dropped Marxism as the state ideology.]
- 1964-present: Colombian Armed Conflict.
- 1965 : March Intifada in Bahrain - A Leftist uprising demanding an end to the British presence in Bahrain
- 1966 : Kwame Nkrumah is removed from power in Ghana by coup d'état.
- 1966-1976: Révolution culturelle, une répression maoïste en République populaire de Chine
- 1966-1993 : A guerrilla warfare is conducted against the repressive government of François Tombalbaye from the Sudan-based group FROLINAT. After the killing of field commander Ibrahim Abatcha in 1968, the movement jettisoned its socialist rhetoric and split into irreconcilable factions that often fought among themselves. Tombalbaye was brought down and executed in a 1975 military coup, and in 1979 the FROLINAT factions established the Transitional Government of National Unity (GUNT). This experiment lasted until 1982, when a FROLINAT splinter, led by Hissène Habré, took control of N'Djamena. Supporters of marginalized GUNT president Goukouni Oueddei held out for a few years at Bardaï, but the group eventually dissolved; but a new formation, the MPS, continued the civil war and brought to power in 1990 Idriss Déby.
- 1966-1998 : The Ulster Volunteer Force is recreated by militant Protestant British Loyalistes in Northern Ireland to wage war against the Irish Republican Army, and the Roman Catholic community at large.
- 1967-1970 : Biafra; The former eastern Nigeria unsuccessfully fought for a breakaway republic of Biafra.After the mainly Ibo people of the region suffered pogroms in northern Nigeria the previous year.
- 1967 : Naxalite Movement begins in India, led by the AICCCR.
- 1967 : Anguillans resentful of Kittitian domination of the island expel the Kittitian police and declare independence from the British colony of Saint Christopher-Nevis-Anguilla. British forces retake the island in 1969 and make Anguilla a separate dependency in 1980. There was no bloodshed in the entire episode.
- 1967 : Cultural Revolution declared in Mali by President Modibo Keita.
- 1968 : revolution in Republic of Congo
- 1968 : Student protests and riots in Egypt in the wake of the Six-Day War lead to the ratification of the March 30 Program to deepen democratic processes.
- 1968 : May 1968 revolt - students' and workers' revolt against the government of Charles de Gaulle in France.
- 1968 : Socialist Cultural Revolution in Guinea launched by the government of President Ahmed Sékou Touré.
- 1968 : coup by Juan Velasco Alvarado in Peru, followed by radical social and economic reforms
- 1968 : a failed attempt by leader Alexander Dubček to liberalise Czechoslovakia in defiance of the Soviet-supported communist state culminates in the Prague Spring.
- 1969-1998 : Armée républicaine irlandaise provisoire and other Republican Paramilitaries wage an armed campaign against British Security forces and Loyalistes paramilitaires in an attempt to bring about a United Ireland in what is known as The Troubles.
- 1969 : a mass movement of workers, students, and peasants in Pakistan forces the resignation of President Muhammad Ayub Khan
- 1969 : overthrow of the pro-Western monarchy by Arab nationalist military officers in Libya
- 1969 : multiparty system supplanted by a military socialist government under Siad Barre in Somalia
- 1970 : Rebellion in Guinea by what its government identified as Portuguese agents.
- 1971 : the Bangladesh Liberation War led by the Mukti Bahini establishes the independent People's Republic of Bangladesh
- 1972 : revolution in Benin
- 1972 : military-led revolution against the civilian government of President Philibert Tsiranana in the Malagasy Republic; a Marxist faction takes power in 1975 under Didier Ratsiraka, modeled on the North Korean juche theory developed by Kim Il Sung.
- 1973 : Mohammad Daud overthrows the monarchy and establishes a republic in Afghanistan.
- 1973 : worker-student demonstrations in Thailand force dictator Thanom Kittikachorn and two close associates to flee the country, beginning a short period of democratic constitutional rule
- 1974 : revolution in Ethiopia
- 1974 : Carnation Revolution overthrows of right-wing dictatorship in Portugal
- 1975 : revolution in Cambodia
- 1975 : revolution in Laos overthrows the monarchy by guerrilla forces of the Pathet Lao
- 1975 : revolution in Cape Verde
- 1976 : student demonstrations and election-related violence in Thailand lead police to open fire on a sit-in at Thammasat University, killing hundreds. The military seizes power the next day, ending constitutional rule.
- 1977 : Market Women's Revolt in Guinea leads to a lessening of the state's role in the economy.
- 1977-1978 : Révolution iranienne
- 1978 : the Saur Revolution led by the Khalq faction of the People's Democratic Party of Afghanistan deposes and kills President Mohammad Daud.
- 1979 : the dictatorship of Eric Gairy overthrown by the New Jewel Movement in Grenada.
- 1979 : the popular overthrow of the Somoza dictatorship by progressive/Marxist Nicaraguan Revolution.
- 1979 : the Iranian Revolution overthrows the U.S.-backed Shah, resulting in an Islamist cleric-led theocracy.
- 1979 : Cambodia is liberated from the Khmer Rouge regime by the Vietnam-backed Kampuchean People's Revolutionary Party
- 1980 : Santo Rebellion in the Anglo-French condominium of New Hebrides.
- 1980-2000 : The Communist Party of Peru launched the internal conflict in Peru.
- 1980 : Printemps berbère, série de manifestations réclamant la reconnaissance de l'identité et de la langue berbère
- 1983 : Overthrow of the ruling Conseil de Salut du peuple (CSP) by Marxist forces led by Thomas Sankara in Upper Volta, renamed Burkina Faso in the following year.
- 1984-1985 : Pro-independence FLNKS forces in New Caledonia revolt following an election boycott and occupy the town of Thio from novembre 1984 to janvier 1985. Thio is retaken by the French after the assassination of Éloi Machoro, the security minister in the FLNKS provisional government and the primary leader of the occupation.[11]
- 1985 : Soviet and Afghanistan P.O.W. rose against their captors at Badaber base.
- 1986 : The People Power Revolution peacefully overthrows Ferdinand Marcos after his two decade rule in the Philippines.
- 1986 : Emeutes du quartier de Saint-Paul à Bristol, en Angleterre[12].
- 1987-1991 : First Intifada, or the Palestinian uprising, a series of violent incidents between Palestinians and Israelis
- 1988 : Émeutes d'octobre 1988 en Algérie : Soulèvement populaire contre le président Chadli Bendjedid
- 1989 : Singing Revolution, bloodless overthrow of communist rule in Estonia, Latvia and Lithuania.
- 1989 : the violent Caracazo riots in Venezuela. In the next few years, there are two attempted coups and President Carlos Andrés Pérez is impeached.
- 1989 : manifestations de la place Tian'anmen were a series of demonstrations led by students, intellectuals and labour activists in the People's Republic of China between 15 avril 1989 and 4 juin 1989.
- 1989 : the bloodless Velvet Revolution overthrows the communist regime in Czechoslovakia.
- 1989 : the Romanian Revolution violently overthrows the communist state in Romania.
- 1990-1995 : the Log Revolution in Croatia starts, triggering the Croatian War of Independence.
- 1990-1995 : the First Tuareg Rebellion in Niger and Mali.
- 1991 : Insurrection en Irak de 1991
- 1992 : Afghan Uprising against the Taliban by United Islamic Front for the Salvation of Afghanistan or Northern Alliance.
- 1994 : 1990s Uprising in Bahrain, Shiite-led rebellion for the restoration of democracy in Bahrain
- 1994 : The bloodless electoral victory of the Republican party in many simultaneous elections in the United States. (Republican Revolution)
- 1994 : Zapatista Rebellion : Uprising in the Mexican state of Chiapas demanding equal rights for indigenous peoples and in opposition to growing néolibéralisme in North America
- 1994-1996 : Première guerre de Tchétchénie contre la Russie.
- 1996 : Islamic movement in Afghanistan led by the Taliban
- 1997-1999 : Kosovo Rebellion against Yugoslavia.
- 1998 : suite à son élection à la tête du Venezuela, Hugo Chavez qualifie sa politique de révolution bolivarienne.
- 1998 : Indonesian Revolution of 1998 resulted the resignation of Suharto after three decades of the New Order period.
- 1999-present: Seconde guerre de Tchétchénie contre la Russie.
2000-aujourd'hui
- Seconde Intifada, suite de la Première Intifada.
- Les manifestations du 5 octobre 2000 en Serbie (parfois appelée révolution des bulldozers), aboutissent au départ de Slobodan Milošević en République fédérale de Yougoslavie. Ce mouvement est considéré comme la première des révolutions de couleur (ou des fleurs).
- Conflit de 2001 en Macédoine.
- Taliban insurgency following the 2001 war in Afghanistan.
- The 2001 EDSA Revolution peacefully ousts Philippine President Joseph Estrada after the collapse of his impeachment trial.
- Supporters of Philippines ancien président Joseph Estrada violently and unsuccessfully stage a rally, so-called the EDSA Tres, in an attempt of returning him to power.
- Violentes émeutes du Printemps noir en Kabylie.
- La Révolution des roses, deuxième révolution de fleurs, renverse le président de la Géorgie Edouard Chevardnadze, et débouche sur de nouvelles élections.
- Iraqi insurgency refers to the armed resistance by diverse groups within Iraq to the US occupation of Iraq and to the establishment of a liberal democracy therein.
- The Darfur rebellion led by the two major rebel groups, the Sudan Liberation Movement (SLM/A) and the Justice and Equality Movement, recruited primarily from the land-tilling Fur, Zaghawa, and Massaleit ethnic groups.
- Shi'ite Uprising against the US-led occupation of Iraq.
- Après que Viktor Yanukovych a été déclaré vainqueur de l'élection présidentielle en Ukraine, la Révolution orange installe Viktor Yushchenko comme président, dans l'idée que l'élection a été truquée. C'est la troisième des révolutions de couleur.
- Échec d'une révolution de couleur menée par les groupes Yox! et Azadlig en Azerbaïdjan.
- Naxalite insurgency in India, led by the Communist Party of India (Maoist)
- La révolution du cèdre, provoquée par l'assassinat de Rafik Hariri, demande le retrait des troupes syriennes du Liban.
- La révolution des tulipes (a.k.a. Pink/Yellow Revolution) overthrows the President of Kyrgyzstan, Askar Akayev, and set new elections. This is the fourth color revolution.
- Grève générale d'avril 2006 au Népal
- Révolte d'Oaxaca, au Mexique
- The popular uprising against al-Qa'eda by residents of Anbar Province, Iraq.[13]
- Émeutes de la faim au Bengale.
- Second Tuareg Rebellion in Niger.
- Révolution de safran (soulèvement anti-gouvernemental en Birmanie).
- Troubles au Tibet en mars 2008.
- Shiite uprising in Basra.
- émeute insurrectionnelle en Grèce à partir de décembre 2008.
Révolutions culturelles, intellectuelles, philosophiques et technologiques
 Une machine de Watt à Madrid. The development of the steam engine propelled the Industrial Revolution in Britain and the world. The steam engine was created to pump water from coal mines, enabling them to be deepened beyond groundwater levels.
Une machine de Watt à Madrid. The development of the steam engine propelled the Industrial Revolution in Britain and the world. The steam engine was created to pump water from coal mines, enabling them to be deepened beyond groundwater levels.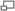
Le terme révolution a aussi été utilisé pour qualifier de grands changements en dehors de la sphère politique, quand ceux-ci ont modifié profondément la société, la culture, la philosophie ou la technologie dans des portions plus ou moins grandes de l'humanité. On parle notamment de (ordre alphabétique):
- Révolution agraire, dans les cas suivants:
- Neolithic Revolution (perhaps 13000 years ago), which formed the basis for human civilization to develop. It is commonly referred to as the 'First Agricultural Revolution'.
- Révolution verte (1945- ), the use of industrial fertilizers and new crops greatly increased the world's agricultural output. It is commonly referred to as the 'Second Agricultural Revolution'.
- British Agricultural Revolution (18th century), which spurred urbanisation and consequently helped launch the Industrial Revolution.
- Scottish Agricultural Revolution (18th st century), which led to the Lowland Clearances.
- Révolution culturelle - a struggle for power within the Communist Party of China, which grew to include large sections of Chinese society and eventually brought the People's Republic of China to the brink of civil war, and which lasted from 1966 to 1976
- Révolution digitale - the sweeping changes brought about by computing and communication technology from the later half of the 20th Century till today
- Révolution industrielle - the major shift of technological, socioeconomic and cultural conditions in the late 18th and early 19th centuries that began in Britain and spread throughout the world
- Deuxième révolution industrielle (1871–1914)
- Price revolution - a series of economic events from the second half of the 15th century to the first half of the 17th, the price revolution refers most specifically to the high rate of inflation that characterized the period across Western Europe
- Révolution tranquille - a period of rapid change in Québec, Canada, in the 1960s
- Révolution scientifique - a fundamental transformation in scientific ideas around the 16th century
- The Counterculture Revolution (or The Hippie Revolution). A Social and Cultural Revolution that swept through the United States and much of the western world in the 1960's and 1970's. In America, it was a revolt against the conservative social norms of the 1950s, the political conservatism and social repression of the Cold War period, and the US government's extensive military intervention in Vietnam. The growing use of psychedelic drugs are also included.
- Révolution sexuelle - a change in sexual morality and sexual behavior throughout the Western world, mainly during the 1960s and 1970s.
- Upper Paleolithic Revolution - The emergence of "high culture", new technologies and regionally distinct cultures.
Notes et références
- ↑ Jason Burke, "Dig uncovers Boudicca's brutal streak", The Observer , 3 décembre 2000
- ↑ History and chronology of Rebellion in Roman Empire
- ↑ Zanj rebellion
- ↑ Shimabara Rebellion (Japanese history)
- ↑ The Slave Revolts
- ↑ White, Richard Alan. Paraguay's Autonomous Revolution, 1810-1840. Albuquerque: University of New Mexico Press, 1978.
- ↑ Summary: the First Anglo-Afghan War, 1838-42
- ↑ Marianne Kunnen-Jones, « Anniversary Volume Gives New Voice To Pioneer Accounts of Sioux Uprising », 2002-08-21, University of Cincinnati. Consulté le 2007-06-06
- ↑ Renowned author to speak about 1863 New York draft riots at Fairfield University's DiMenna-Nyselius Library press release Fairfield University
- ↑ I. Baltic Prisoners of the Gulag Revolts of 1953 - L. Latkovskis
- ↑ Ibid., pp. 116-126.
- ↑ A propos des émeutes de Bristol de 1986 en Angleterre
- ↑ Iraq insurgency: People rise against al-Qa'eda
- ↑ Riots and hunger feared as demand for grain sends food costs soaring
- ↑ Feed the world? We are fighting a losing battle, UN admits
- ↑ The World's Growing Food-Price Crisis
- Portail de l’histoire
Catégories : Révolte | Révolution | Liste en rapport avec la politique
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.





