Allysine
- Allysine
-
| Allysine |
|
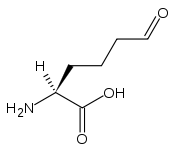
Structure de l'allysine |
| Général |
| Nom IUPAC |
acide 2-amino-6-oxohexanoïque |
| Synonymes |
acide 2-aminoadipique-6-semialdéhyde,
5-formylnorvaline,
6-oxonorleucine |
| No CAS |
1962-83-0 |
| PubChem |
207 |
| ChEBI |
17027 |
| SMILES |
|
| InChI |
Std. InChI : Vue 3D
InChI= 1S/ C6H11NO3/ c7- 5( 6( 9) 10) 3- 1- 2- 4- 8/ h4- 5H, 1- 3, 7H2,( H, 9, 10)
Std. InChIKey :
GFXYTQPNNXGICT- UHFFFAOYSA- N
|
| Propriétés chimiques |
| Formule brute |
C6H11NO3 [Isomères]
|
| Masse molaire[1] |
145,1564 ± 0,0067 g·mol-1
C 49,65 %, H 7,64 %, N 9,65 %, O 33,07 %,
|
|
Unités du SI & CNTP, sauf indication contraire.
|
L’allysine, ou acide 2-aminoadipique-6-semialdéhyde, est un composé chimique de formule HOOC–HC(NH2)–CH2–CH2–CH2–CHO. C'est un acide aminé dérivé de la lysine sous l'action d'une protéine-lysine 6-oxydase (EC 1.4.3.13), ou lysyl oxydase, enzyme qui oxyde l'amine –CH2–NH2 terminale des résidus lysine en groupe aldéhyde –CHO avec libération d'ammoniac NH3 et de peroxyde d'hydrogène H2O2 moyennant consommation d'une molécule d'oxygène O2 et d'une molécule d'eau H2O. Cette réaction a lieu dans la matrice extracellulaire afin de produire des résidus à chaîne latérale réactives permettant des pontages aldoliques entre molécules d'élastine ou de collagène pour renforcer leur cohésion globale, en formant par exemple de la desmosine dans le cas de l'élastine.
L'allysine est formée également au cours de la dégradation de la lysine par l'action de la saccharopine déshydrogénase (EC 1.5.1.10) sur la saccharopine avec libération de glutamate.
Notes et références
Wikimedia Foundation.
2010.
Contenu soumis à la licence CC-BY-SA. Source : Article Allysine de Wikipédia en français (auteurs)
Regardez d'autres dictionnaires:
Allysine — Chembox new ImageFile=Allysine.svg ImageSize= IUPACName=2 amino 6 oxo hexanoic acid OtherNames=2 aminoadipate semialdehyde Section1= Chembox Identifiers CASNo=1962 83 0 PubChem=207 ChemSpiderID = 202 SMILES=C(CC=O)CC(C(=O)O)N MeSHName=allysine… … Wikipedia
allysine — al·ly·sine (ă liґsēn) a product of the oxidative deamination of lysine, formed by the action of lysyl oxidase. It is an intermediate in the formation of cross linkages in collagens … Medical dictionary
Amino acid — This article is about the class of chemicals. For the structures and properties of the standard proteinogenic amino acids, see Proteinogenic amino acid. The generic structure of an alpha amino acid in its unionized form … Wikipedia
Disulfide bond — In chemistry, a disulfide bond (Br.E. disulphide bond) is a covalent bond, usually derived by the coupling of two thiol groups. The linkage is also called an SS bond or disulfide bridge. The overall connectivity is therefore R S S R. The… … Wikipedia
Methylation — In the chemical sciences, methylation denotes the addition of a methyl group to a substrate or the substitution of an atom or group by a methyl group. Methylation is a form of alkylation with, to be specific, a methyl group, rather than a larger… … Wikipedia
Hydroxylation — is a chemical process that introduces a hydroxyl group ( OH) into an organic compound. In biochemistry, hydroxylation reactions are often facilitated by enzymes called hydroxylases. Hydroxylation is the first step in the oxidative degradation of… … Wikipedia
Glycosylation — (see also chemical glycosylation) is the reaction in which a carbohydrate, i.e. a glycosyl donor, is attached to a hydroxyl or other functional group of another molecule (a glycosyl acceptor). In biology glycosylation refers to the enzymatic… … Wikipedia
Acetylation — Salicylic acid is acetylated to form aspirin Acetylation (or in IUPAC nomenclature ethanoylation) describes a reaction that introduces an acetyl functional group into a chemical compound. (Deacetylation is the removal of the acetyl group.)… … Wikipedia
Myristoylation — In myristoylation, a myristoyl group (derived from myristic acid, pictured above) is added. Myristoylation is an irreversible, co translational (during translation) protein modification found in animals, plants, fungi, protozoans[1] and viruses.… … Wikipedia
Phosphocholine — Other names Choline phosphate Identifiers … Wikipedia

