Fluoranthène
- Fluoranthène
-
| Fluoranthène |
|
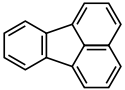 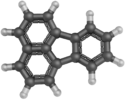
Structure du fluoranthène. |
| Général |
| Nom IUPAC |
Fluoranthène |
| Synonymes |
Benzo[j,k]fluorène |
| No CAS |
206-44-0 |
| No EINECS |
205-912-4 |
| PubChem |
9154 |
| SMILES |
|
| InChI |
InChI : Vue 3D
InChI= 1S/ C16H10/ c1- 2- 8- 13- 12( 7- 1) 14- 9- 3- 5- 11- 6- 4- 10- 15( 13) 16( 11) 14/ h1- 10H
InChIKey :
GVEPBJHOBDJJJI- UHFFFAOYSA- N
|
| Propriétés chimiques |
| Formule brute |
C16H10 [Isomères]
|
| Masse molaire[2] |
202,2506 ± 0,0135 g·mol-1
C 95,02 %, H 4,98 %,
|
| Susceptibilité magnétique |
χM 138×10-6 cm3·mol-1[1] |
| Propriétés physiques |
| T° fusion |
110,8 °C |
| T° ébullition |
383,5 °C[3]. |
| Masse volumique |
1 252 kg·m-3 |
| Thermochimie |
| Cp |
équation[4] : 
Capacité thermique du gaz en J·mol-1·K-1 et température en kelvins, de 298 à 1 500 K.
Valeurs calculées :
214,409 J·mol-1·K-1 à 25 °C.
T
(K) |
T
(°C) |
Cp
 |
Cp
 |
| 298 |
24,85 |
214 290 |
1 060 |
| 378 |
104,85 |
272 859 |
1 349 |
| 418 |
144,85 |
298 520 |
1 476 |
| 458 |
184,85 |
321 996 |
1 592 |
| 498 |
224,85 |
343 452 |
1 698 |
| 538 |
264,85 |
363 046 |
1 795 |
| 578 |
304,85 |
380 927 |
1 883 |
| 618 |
344,85 |
397 238 |
1 964 |
| 658 |
384,85 |
412 113 |
2 038 |
| 698 |
424,85 |
425 678 |
2 105 |
| 738 |
464,85 |
438 055 |
2 166 |
| 778 |
504,85 |
449 355 |
2 222 |
| 818 |
544,85 |
459 684 |
2 273 |
| 858 |
584,85 |
469 137 |
2 320 |
| 899 |
625,85 |
478 012 |
2 363 |
|
T
(K) |
T
(°C) |
Cp
 |
Cp
 |
| 939 |
665,85 |
485 961 |
2 403 |
| 979 |
705,85 |
493 284 |
2 439 |
| 1 019 |
745,85 |
500 047 |
2 472 |
| 1 059 |
785,85 |
506 310 |
2 503 |
| 1 099 |
825,85 |
512 127 |
2 532 |
| 1 139 |
865,85 |
517 540 |
2 559 |
| 1 179 |
905,85 |
522 587 |
2 584 |
| 1 219 |
945,85 |
527 298 |
2 607 |
| 1 259 |
985,85 |
531 695 |
2 629 |
| 1 299 |
1 025,85 |
535 793 |
2 649 |
| 1 339 |
1 065,85 |
539 599 |
2 668 |
| 1 379 |
1 105,85 |
543 111 |
2 685 |
| 1 419 |
1 145,85 |
546 324 |
2 701 |
| 1 459 |
1 185,85 |
549 220 |
2 716 |
| 1 500 |
1 226,85 |
551 838 |
2 728 |
|
|
| Précautions |
|
Directive 67/548/EEC[6]
|

Xn
|
|
Symboles :
Xn : Nocif
Phrases R :
R22 : Nocif en cas d’ ingestion.
|
| Phrases R : 22, |
|
SGH[6]
|
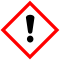 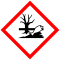
Attention
H302, H410, P273, P501,
H302 : Nocif en cas d'ingestion
H410 : Très toxique pour les organismes aquatiques, entraîne des effets à long terme
P273 : Éviter le rejet dans l’environnement.
P501 : Éliminer le contenu/récipient dans ...
|
|
Classification du CIRC
|
| Groupe 3 : Inclassable quant à sa cancérogénicité pour l'Homme[5] |
| Composés apparentés |
| Isomère(s) |
Pyrène |
|
Unités du SI & CNTP, sauf indication contraire.
|
Le fluoranthène est un hydrocarbure aromatique polycyclique dérivant structurellement d'un naphtalène lié à un benzène par deux liaisons simples formant avec celui-ci un cycle pentagonal. Il s'agit donc d'un HAP dit non alternant, isomère structurel du pyrène, qui est, lui, un HAP alternant ; les électrons π ne sont pas délocalisés dans l'ensemble de la molécule, contrairement au pyrène, qui est, pour cette raison, plus stable que le fluoranthène.
Comme son nom l'indique, il présente une fluorescence induite par les ultraviolets.
Le fluoranthène est un polluant cancérogène inscrit sur la liste des cancérogènes du groupe 3 du CIRC considéré comme l'un des plus nocifs.
Production et synthèse
Le fluoranthène est extrait du goudron par distillation[3].
Notes et références
- ↑ (en) Hyp J. Dauben, Jr., James D. Wilson et John L. Laity, « Diamagnetic Susceptibility Exaltation in Hydrocarbons », dans Journal of the American Chemical Society, vol. 91, no 8, 9 avril 1968, p. 1991-1998
- ↑ Masse molaire calculée d’après Atomic weights of the elements 2007 sur www.chem.qmul.ac.uk.
- ↑ a et b (en) Gerd Collin and Hartmut Höke, Tar and Pitch, Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co, coll. « Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry », 15 juin 2000 [présentation en ligne]
- ↑ (en) Carl L. Yaws, Handbook of Thermodynamic Diagrams, vol. 3, Huston, Texas, Gulf Pub. Co. (ISBN 0-88415-859-4)
- ↑ IARC Working Group on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans, « Evaluations Globales de la Cancérogénicité pour l'Homme, Groupe 3 : Inclassables quant à leur cancérogénicité pour l'Homme » sur http://monographs.iarc.fr, CIRC, 16 janvier 2009. Consulté le 22 août 2009
- ↑ a et b SIGMA-ALDRICH
Articles connexes
Wikimedia Foundation.
2010.
Contenu soumis à la licence CC-BY-SA. Source : Article Fluoranthène de Wikipédia en français (auteurs)
Regardez d'autres dictionnaires:
Fluoranthene — Flu or*an thene, n. [Fluorene + anthracene.] (Chem.) A white crystalline hydrocarbon {C15H10}, of a complex structure, found as one ingredient of the higher boiling portion of coal tar. [1913 Webster] … The Collaborative International Dictionary of English
Fluoranthene — Chembox new Name = Fluoranthene ImageFile = Fluoranthene.svg ImageSize = 154px ImageName = Chemical structure of fluoranthene IUPACName = Fluoranthene OtherNames = Benzo(j, k)fluorene Section1 = Chembox Identifiers SMILES =… … Wikipedia
fluoranthene — fluorantenas statusas T sritis chemija formulė C₁₆H₁₀ atitikmenys: angl. fluoranthene rus. флуорантен … Chemijos terminų aiškinamasis žodynas
fluoranthene — noun A polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon consisting of a benzene ring attached to each of the rings of a naphthalene molecule; it is carcinogenic, and is a product of incomplete combustion … Wiktionary
fluoranthene — flu·o·ran·thene … English syllables
fluoranthene — flu̇(ə)ˈranˌthēn, flōˈ , flȯˈ noun ( s) Etymology: International Scientific Vocabulary fluor + anthracene; originally formed as German fluoranthen : a white crystalline hydrocarbon C15H10 obtained especially from the coal tar distillates having… … Useful english dictionary
Benzo(b)fluoranthène — Benzo[b]fluoranthène Structure du benzo[b]fluoranthène Général Nom IUPAC benzo[ … Wikipédia en Français
Benzo(j)fluoranthène — Benzo[j]fluoranthène Structure du benzo[j]fluoranthène Général Nom IUPAC benzo[ … Wikipédia en Français
Benzo(k)fluoranthène — Benzo[k]fluoranthène Structure du benzo[k]fluoranthène Général Nom IUPAC benzo[k … Wikipédia en Français
206-44-0 — Fluoranthène Fluoranthène Structure du fluoranthène Général Nom IUPAC Fluoranthène … Wikipédia en Français








