Phénalène
- Phénalène
-
| Phénalène |
|
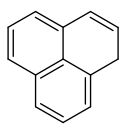 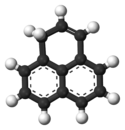
Structure du phénalène. |
| Général |
| Nom IUPAC |
1H-phénalène |
| No CAS |
203-80-5 |
| No EINECS |
205-907-7 |
| PubChem |
9149 |
| SMILES |
|
| InChI |
InChI : Vue 3D
InChI= 1/ C13H10/ c1- 4- 10- 6- 2- 8- 12- 9- 3- 7- 11( 5- 1) 13( 10) 12/ h1- 8H, 9H2
InChIKey :
XDJOIMJURHQYDW- UHFFFAOYAK
|
| Propriétés chimiques |
| Formule brute |
C13H10 [Isomères]
|
| Masse molaire[1] |
166,2185 ± 0,0111 g·mol-1
C 93,94 %, H 6,06 %,
|
| Propriétés physiques |
| T° fusion |
84 à 85 °C [2] |
| T° ébullition |
292 à 316,4 °C |
| Solubilité |
~ 0,8235 à 1,7174 mg/l |
| Masse volumique |
1 139 kg·m3 |
| Point d’éclair |
150,7 °C |
| Composés apparentés |
| Isomère(s) |
Fluorène |
|
Unités du SI & CNTP, sauf indication contraire.
|
Le phénalène est un hydrocarbure aromatique polycyclique de formule C13H10.
Références
- ↑ Masse molaire calculée d’après Atomic weights of the elements 2007 sur www.chem.qmul.ac.uk.
- ↑ (en) Edward M. Arnett, Kalyani Amarnath, Noel G. Harvey et Jinpei Cheng, « Determination and interrelation of bond heterolysis and homolysis energies in solution », dans Journal of the American Chemical Society, vol. 112, no 1, 1990-01, p. 344-355 [lien DOI (page consultée le 9 novembre)]
Wikimedia Foundation.
2010.
Contenu soumis à la licence CC-BY-SA. Source : Article Phénalène de Wikipédia en français (auteurs)
Regardez d'autres dictionnaires:
Phenalene — chembox new ImageFile=Phenalene.png ImageSize=150px IUPACName=1 H Phenalene OtherNames=Perinaphthene Section1=Chembox Identifiers CASNo=203 80 5 PubChem=9149 SMILES=C1C=CC2=CC=CC3=C2C1=CC=C3 Section2=Chembox Properties Formula=C13H10… … Wikipedia
phenalene — noun A tricyclic hydrocarbon consisting of a cyclohexene ring ortho and peri fused to naphthalene … Wiktionary
Brønsted catalysis equation — The Brønsted catalysis equation or law or correlation, after Johannes Nicolaus Brønsted, gives the relationship between acid strength and catalytic activity. log(k) = alpha*log(K a) + CA plot of the common logarithm of the reaction rate constant… … Wikipedia
Zethrene — IUPAC name … Wikipedia
Fluorène — Structure du fluorène. Gén … Wikipédia en Français
Zéthrène — Structure du zéthrène. Général … Wikipédia en Français
Aromatic hydrocarbon — Arene redirects here. For other uses, see Arene (disambiguation). An aromatic hydrocarbon or arene[1] (or sometimes aryl hydrocarbon)[2] is a hydrocarbon with alternating double and single bonds between carbon atoms. The term aromatic was… … Wikipedia
Naphthalene — Not to be confused with Naphtha, a broad term describing liquid hydrocarbon mixtures. Naphthalene … Wikipedia
Coronene — Other names … Wikipedia
Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon — An illustration of typical polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Clockwise from top left: benz(e)acephenanthrylene, pyrene and dibenz(ah)anthracene … Wikipedia


