Xanthine
- Xanthine
-
| Xanthine |
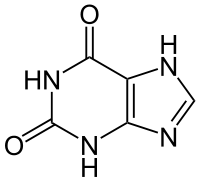
 |
| Xanthine |
| Général |
| No CAS |
69-89-6 |
| No EINECS |
200-718-6 |
| SMILES |
|
| InChI |
InChI : Vue 3D
InChI= 1/ C5H4N4O2/ c10- 4- 2- 3( 7- 1- 6- 2) 8- 5( 11) 9- 4/ h1H,( H3, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11)
|
| Propriétés chimiques |
| Formule brute |
C5H4N4O2 [Isomères]
|
| Masse molaire[2] |
152,1109 ± 0,0057 g·mol-1
C 39,48 %, H 2,65 %, N 36,83 %, O 21,04 %,
|
| pKa |
7.53 [1] |
| Propriétés physiques |
| Solubilité |
69 mg·l-1 (eau, 16 °C) [1] |
| Écotoxicologie |
| DL50 |
500 mg·kg-1 (souris, i.p.) [1] |
|
Unités du SI & CNTP, sauf indication contraire.
|
La xanthine est une substance issue de la dégradation des bases puriques (adénine et guanine). Elle a été découverte et décrite par Frédéric Kuhlmann[3].
Elle est convertie en acide urique par l'action de la xanthine oxydase.
Les méthylxanthines sont communément utilisés comme stimulants légers et pour leurs effets bronchodilatateurs, notamment dans le traitement de l'asthme. Ils ne sont pas considerés comme alcaloïdes car ils ne possèdent pas d'azote basique dans leur structure. La caféine, la théophylline, la théobromine font partie de ce groupe.
Voir aussi
Notes et références
|
Acides nucléiques |
| Bases azotées |
Puriques : adénine, guanine, hypoxanthine, xanthine · Pyrimidiques : thymine, uracile, cytosine. |
| Nucléosides |
|
| Nucléotides |
| Ribonucléotides |
Monophosphate : AMP, TMP, UMP, GMP, CMP, IMP, XMP · Diphosphate : ADP, TDP, UDP, GDP, CDP, IDP, XDP · Triphosphate : ATP, TTP, UTP, GTP, CTP, ITP, XTP · Cycliques : AMPc, GMPc, di-GMPc, ADPRc. |
| Désoxyribonucléotides |
Monophosphate : dAMP, dTMP, dUMP, dGMP, dCMP · Diphosphate : dADP, dTDP, dUDP, dGDP, dCDP · Triphosphate : dATP, dTTP, dUTP, dGTP, dCTP. |
| Acides nucléiques |
ADN • ADNn • ADNmt • ADN chloroplastique • ADNc • ARN • ARNm • ARN non codant • miARN • ARNr • ARNt • shARN • pARNi • pARNn • ARNpi • snoARN • ARNtm • Oligonucléotide • Liste de différents types d'ADN • Liste de différents types d'ARN |
|
| Analogues non ribosidiques |
GNA • LNA • PNA • TNA • Morpholino |
| Didésoxyribonucléotide |
Wikimedia Foundation.
2010.
Contenu soumis à la licence CC-BY-SA. Source : Article Xanthine de Wikipédia en français (auteurs)
Regardez d'autres dictionnaires:
xanthine — [ gzɑ̃tin ] n. f. • 1890; du gr. xanthos « jaune » et ine ♦ Biochim. Base organique dérivée de la purine et qui donne sa couleur jaune à l urine. ● xanthine nom féminin Base purique entrant dans la composition des nucléotides et des acides… … Encyclopédie Universelle
Xanthine — Xan thine, n. Also Xanthin Xan thin . [Gr. xanqo s yellow.] (Physiol. Chem.) A type of purine obtainable as a white microcrystalline powder, {C5H4O2N4}, present in muscle tissue, in the liver, spleen, pancreas, and other organs, and also in urine … The Collaborative International Dictionary of English
xanthine — xanthine. См. ксантин. (Источник: «Англо русский толковый словарь генетических терминов». Арефьев В.А., Лисовенко Л.А., Москва: Изд во ВНИРО, 1995 г.) … Молекулярная биология и генетика. Толковый словарь.
xanthine — [zan′thēn΄, zan′thin] n. [Fr: see XANTHO & IN1] 1. a white, crystalline, nitrogenous compound, C5H4N4O2, resembling uric acid: it is present in blood, urine, and certain plants 2. any of various derivatives of this compound … English World dictionary
Xanthine — Not to be confused with xanthene. Xanthine … Wikipedia
Xanthine — A substance found in caffeine, theobromine, and theophylline and encountered in tea, coffee, and the colas. Chemically, xanthine is a purine. There is a genetic disease of xanthine metabolism, xanthinuria, due to deficiency of an enzyme, xanthine … Medical dictionary
Xanthine — Strukturformel Allgemeines Name Xanthin Andere Namen 2,6 Dihydroxypurin 2,6(1H,3H) Purindion … Deutsch Wikipedia
xanthine — noun Etymology: International Scientific Vocabulary Date: 1857 a feebly basic compound C5H4N4O2 that occurs especially in animal or plant tissue, is derived from guanine and hypoxanthine, and yields uric acid on oxidation; also any of various… … New Collegiate Dictionary
xanthine — (gzan ti n ) s. f. Terme de chimie. Matière colorante de la garance. Xanthine azotée, oxyde xanthique, principe découvert dans quelques calculs urinaires de l homme, et qui paraît exister aussi en grande quantité dans le guano. ÉTYMOLOGIE… … Dictionnaire de la Langue Française d'Émile Littré
xanthine — n. a nitrogenous breakdown product of the purines adenosine and guanine. Xanthine is an intermediate product of the breakdown of nucleic acids to uric acid … The new mediacal dictionary


