- Sitocalciférol
-
Sitocalciférol 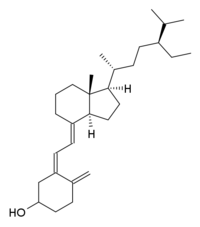
Général Nom IUPAC (1S,3Z)-3-[(2E)-2-[(1R,3aS,7aR)-1-[(1R,4S)-4-éthyl-1,5-diméthylhexyl]-7a-méthyl-2,3,3a,5,6,7-hexahydro-1H-inden-4-ylidène]éthylidène]-4-méthylène-1-cyclohexanol Synonymes Vitamine D5
24-éthylcholécalciférolNo CAS PubChem ChEBI SMILES InChI Propriétés chimiques Formule brute C29H48O [Isomères] Masse molaire[1] 412,6908 ± 0,0269 g·mol-1
C 84,4 %, H 11,72 %, O 3,88 %,
412.69082Propriétés physiques T° fusion 517 °C Point d’éclair 225,1 °C Unités du SI & CNTP, sauf indication contraire. Le sitocalciférol, également appelé vitamine D5, est une forme de vitamine D découverte en 1936 par W. Wunderlich[2]. Il est biosynthétisé à partir du 7-déshydrositostérol, et peut être obtenu à partir du β-sitostérol par synthèse organique.
Des analogues synthétiques du sitocalciférol ont été proposés comme étant de potentiels agents antitumoraux[3],[4],[5].
Voir aussi
- 7-déshydrositostérol
- Vitamines
- Vitamine D2 (Ergocalciférol)
- Vitamine D3 (Cholécalciférol)
Références
- Masse molaire calculée d’après Atomic weights of the elements 2007 sur www.chem.qmul.ac.uk.
- (en) W. Wunderlich, « Hoppe-Seyler's Z. Physiol. Chem. », 1936, vol. 241, p. 116-124.
- (en) R. G. Mehta, R. M. Moriarty, R. R. Mehta et al., « Prevention of preneoplastic mammary lesion development by a novel vitamin D analogue, 1alpha-hydroxyvitamin D5 », dans J. Natl. Cancer Inst., vol. 89, no 3, février 1997, p. 212-218 [texte intégral, lien PMID]
- (en) G. Murillo, R. G. Mehta, « Chemoprevention of chemically-induced mammary and colon carcinogenesis by 1alpha-hydroxyvitamin D5 », dans J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol., vol. 97, no 1-2, octobre 2005, p. 129–36 [texte intégral, lien PMID, lien DOI]
- (en) R.G. Mehta, « Stage-specific inhibition of mammary carcinogenesis by 1alpha-hydroxyvitamin D5 », dans Eur. J. Cancer, vol. 40, no 15, octobre 2004, p. 2331-2337 [texte intégral, lien PMID, lien DOI]
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
