Terrestrial Planet Finder
- Terrestrial Planet Finder
-
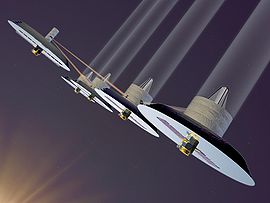
Terrestrial Planet Finder -
Infrared interferometer concept
Le Terrestrial Planet Finder (TPF, « Chercheur de planète terrestre ») était un projet de système de télescope de la NASA pour l'horizon 2015-2020, annulé en 2007.
Il s'agissait d'une suite de deux observatoires complémentaires qui seraient capable de détecter et d'étudier des planètes extrasolaires sous tous leurs aspects. Le TPF aurait permis ainsi d'étudier la formation des planètes – depuis le développement de disques de poussières et de gaz autour des étoiles nouvellement formées – mais également de mesurer la taille, la température, la composition atmosphérique et d'autres caractéristiques de planètes telluriques lointaines.
Le TPF comprend un coronographe de recherche planétaire (TPF-C) et un interféromètre de recherche planétaire (TPF-I).
La publication du budget et du calendrier de la NASA pour l'année 2007 montre que le projet a été retardé ou annulé [1].
L'Agence spatiale européenne (ESA) envisage un projet similaire, appelé Projet spatial Darwin.
Dix premières étoiles cibles
Références
Voir aussi
Articles connexes
Liens externes
v · Programme spatial américain |
| Lanceurs |
Ares (I, V) · Athena · Atlas (I, II, III,V) · Delta (II,III,IV) · Falcon 1,5,9 · Juno I,II · Minotaur · Pegasus · Saturn (Saturn I, IB, V, INT-21) · SLS · Taurus, II · Thor (Agena, Burner) · Scout · Titan (II, III, IIIB, 34D, IV) · Vanguard |
| Missions habitées |
Mercury (1961-1963) · Gemini (1965-1966) · Apollo (1967-1975) · Skylab (1973-1974) · Navette spatiale (1981-2011) · Station spatiale internationale (1998-) · Constellation |
| Exploration du système solaire |
Pioneer¹ (1958-1978) · Ranger¹ (1961-1965) · Mariner¹ ( 1962-1973) · Surveyor¹ (1966-1968) · Viking¹ (1975) · Voyager¹ (1977) · ICE (1978) · Galileo (1989) · Magellan (1989) · Mars Observer (1992) · Near (1996) · Mars Global Surveyor (1996) · Mars Pathfinder (1996) · Cassini-Huygens ²(1997) · Mars Climate Orbiter (1998) · Deep Space (1998) · Stardust (1999) · Mars Polar Lander (2000) · 2001 Mars Odyssey (2001) · CONTOUR (2002) · Mars Exploration Rover¹ (Spirit) (2003) · Deep Impact (2004) · MESSENGER (2004) · Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (2005) · New Horizons (2006) · Phoenix (2007) · Dawn (2007) · Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter (2009) · LCROSS (2009) · Mars Science Laboratory (2011) · Juno (2011) · GRAIL (2011) · MAVEN (2013) · LADEE (2013) · Venus In-Situ Explorer (2013) · Solar sentinels¹ (2015) - OSIRIS-REx (2016) - Jupiter Europa Orbiter² (2020) |
| Satellites |
|
| Centres de lancement |
Centre spatial Kennedy · Cap Canaveral · Vandenberg · Wallops Island · Kodiak Launch Complex · Mars · Spaceport America · Ronald Reagan Test Site |
| Établissements de la NASA |
NASA · Lyndon B. Johnson · Langley · Marshall · Dryden Flight Research Center · JPL · Ames · Glenn · Goddard · John C. Stennis · Michoud · White Sands · Deep Space Network |
| Histoire - programmes |
Programme Explorer (1959-) · Programme Lunar Precursor Robotic (en cours) · Programme Flagship (en cours) · Programme Discovery (en cours) · Programme Mars Scout (en cours) · Programme New Frontiers (en cours) · Projet Constellation (en cours) · Programme Earth Observing System (1997-) · Vision for Space Exploration (2004) · NMP (1998-2006) · ESE · Grands observatoires · Innovative Interstellar Explorer · Planetary Grand Tour · Planetary Observer program · SERT · Hitchhiker Program (1984) · NACA (1915-1958) |
| Voir aussi |
X-15 X-33
Les articles rangés dans les catégories NASA , Astronaute américain, Programme spatial américain,
Les autres agences spatiales américaines : DoD, NRO, NGA, NOAA |
| Les dates sont celles du lancement ¹ Programme ou plusieurs satellites ou sondes ²Satellite ou programme international |
Wikimedia Foundation.
2010.
Contenu soumis à la licence CC-BY-SA. Source : Article Terrestrial Planet Finder de Wikipédia en français (auteurs)
Regardez d'autres dictionnaires:
Terrestrial Planet Finder — Infrared interferometer concept … Wikipedia
Terrestrial Planet Finder — Concepción artística del interferómetro infrarrojo. Terrestrial Planet Finder (TPF, en inglés «Buscador de planetas terrestres») es un proyecto de la NASA para la creación de un sistema de telescopios capaz de detectar planetas extrasolares… … Wikipedia Español
Terrestrial Planet Finder — Инфракрасный интерферометр TPF I в представлении художника. «Детектор планет земного типа» (англ … Википедия
Terrestrial Planet Finder — Ein Konzeptbild des TPF Infrarot Interferometers Der Terrestrial Planet Finder (TPF) war ein geplantes NASA Projekt, das mit Hilfe mehrerer Weltraumteleskope ab 2020 nach erdähnlichen Planeten (Exoplaneten) in anderen Sonnensystemen der… … Deutsch Wikipedia
Terrestrial planet — The terrestrial planets Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars, and dwarf planet Ceres. Sizes to scale A terrestrial planet, telluric planet or rocky planet is a planet that is composed primarily of silicate rocks and/or … Wikipedia
Planet — This article is about the astronomical object. For other uses, see Planet (disambiguation) … Wikipedia
Extrasolar planet — Planet Fomalhaut b (inset against Fomalhaut s interplanetary dust cloud) imaged by the Hubble Space Telescope s coronagraph (NASA photo) … Wikipedia
Planetshine — Saturn s moon Iapetus lit by Saturnshine. This is an enhanced picture; the Saturn light is too faint by contrast to be visible to the unaided human eye … Wikipedia
Methods of detecting extrasolar planets — Any planet is an extremely faint light source compared to its parent star. In addition to the intrinsic difficulty of detecting such a faint light source, the light from the parent star causes a glare that washes it out. For those reasons, only a … Wikipedia
Space Interferometry Mission — Infobox Space telescope name = Space Interferometry Mission (SIM) caption = Artist s concept of the SIM telescope in space organization = NASA / JPL major contractors = Northrop Grumman alt names = SIM PlanetQuest nssdc id = location = orbit type … Wikipedia

