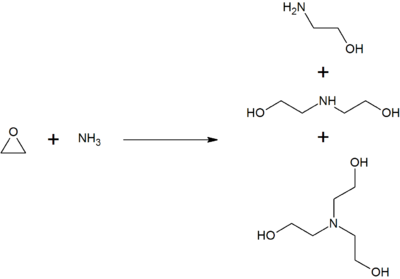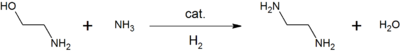- Éthanolamine
-
Éthanolamine 
Général Nom IUPAC 2-aminoéthanol Synonymes 2-amino-l-éthanol, éthanolamine, monoéthanolamine, β-aminoéthanol, β-hydroxyéthylamine, alcool β-aminoéthyliquel, glycinol, olamine, MEA No CAS No EINECS No RTECS PubChem ChEBI SMILES InChI Apparence liquide visqueux incolore avec une odeur d'ammoniac Propriétés chimiques Formule brute C2H7NO [Isomères] Masse molaire[1] 61,0831 ± 0,0026 g·mol-1
C 39,33 %, H 11,55 %, N 22,93 %, O 26,19 %,Propriétés physiques T° fusion 10,3 °C T° ébullition 170 °C Masse volumique 1,012 g·cm-3 T° d'auto-inflammation 410 °C Point d’éclair 85 °C Limites d’explosivité dans l’air 5,5 - 17% Pression de vapeur saturante 25 Pa à 20 °C Thermochimie Cp Propriétés optiques Indice de réfraction  = 1,4539 à 20 °C[3]
= 1,4539 à 20 °C[3]Précautions Directive 67/548/EEC 
CPhrases R : 20, 34, 36/37/38, Phrases S : 26, 27, 36/37, 39, 45, Unités du SI & CNTP, sauf indication contraire. L'éthanolamine, également appelée 2-aminoéthanol ou monoéthanolamine, est un composé chimique organique qui est à la fois une amine primaire (par son groupe amine) et un alcool primaire (par son groupe hydroxyle). À l'instar des autres amines, la monoéthanolamine se comporte en base faible. L'éthanolamine est un liquide toxique, inflammable, corrosif, incolore et visqueux ; son odeur est similaire à celle de l'ammoniac.
L'éthanolamine est communément appelée monoéthanolamine afin de la distinguer de la diéthanolamine et de la triéthanolamine. Le groupe éthanolamine est le deuxième plus fréquent groupe de tête des phospholipides, des substances que l'on retrouve dans les membranes biologiques.
Sommaire
Production
On produit la monoéthanolamine en faisant réagir l'oxyde d'éthylène avec l'ammoniaque aqueux ; cette réaction produit également de la diéthanolamine et de la triéthanolamine. Il est possible d'exercer un contrôle sur les proportions de ces produits en changeant la stœchiométrie des réactifs[4].
Applications
La monoéthanolamine est utilisée en solution aqueuse pour neutraliser certains gaz. Elle sert d'ingrédient de base dans la production de détergents, émulsifiants,, produits pharmaceutiques, inhibiteurs de corrosion, etc.[4] Par exemple, la réaction entre l'éthanolamine et l'ammoniac donne de l'éthylènediamine, un agent chélateur courant[4] :
Amine contrôlant le pH
Notes et références
- (en) Cet article est partiellement ou en totalité issu de l’article de Wikipédia en anglais intitulé « Ethanolamine » (voir la liste des auteurs)
- Masse molaire calculée d’après Atomic weights of the elements 2007 sur www.chem.qmul.ac.uk.
- (en) Carl L. Yaws, Handbook of Thermodynamic Diagrams, vol. 1, Huston, Texas, Gulf Pub. Co., 1996 (ISBN 0-88415-857-8)
- R. E. Reitmeier, « Some Properties of Monoethanolamine and its Aqueous Solutions », dans Journal of the American Chemical Society, vol. 62, no 8, 1940, p. 1943–1944 [lien DOI (page consultée le 2010-02-24)]
- (en) Klaus Weissermel, Hans-Jürgen Arpe, Charlet R. Lindley, Stephen Hawkins, Industrial Organic Chemistry, Weinheim, Wiley-VCH, 2003, 4e éd. (ISBN 978-3-527-30578-0) (LCCN 2003284086), « Chap. 7. Oxidation Products of Ethylene », p. 159–161
Catégories :- Produit chimique corrosif
- Aminoalcool
- Éthylamine
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.