Pantéthéine
- Pantéthéine
-
| Pantéthéine |
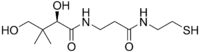 |
| Général |
| Nom IUPAC |
(2R)-2,4-dihydroxy-3,3-diméthyl-N-[2-(2-sulfanyléthylcarbamoyl)éthyl]butanamide |
| Synonymes |
(R)-Pantéthéine |
| No CAS |
496-65-1 |
| No EINECS |
207-824-1 |
| SMILES |
|
| InChI |
InChI : Vue 3D
InChI=1/C11H22N2O4S/c1-11(2,7-14)9(16)10(17)13-4-3-8(15)12-5-6-18/h9,14,16,18H,3-7H2,1-2H3,(H,12,15)(H,13,17)
|
| Propriétés chimiques |
| Formule brute |
C11H22N2O4S [Isomères]
|
| Masse molaire[1] |
278,368 ± 0,017 g·mol-1
C 47,46 %, H 7,97 %, N 10,06 %, O 22,99 %, S 11,52 %,
|
| Écotoxicologie |
| DL50 |
440 mg·kg-1 (souris, i.p.)[2] |
|
Unités du SI & CNTP, sauf indication contraire.
|
La pantéthéine est l'analogue cystéamine amidé de l'acide pantothénique (vitamine B5). Son dimère, la pantéthine, est plus connu, et considéré comme une plus grande source en vitamine B5 que l'acide pantothénique. La pantéthéine (plus précisément la 4'-phosphopantéthéine) est un intermédiaire dans la production du coenzyme A dans le corps.
Notes et références
Wikimedia Foundation.
2010.
Contenu soumis à la licence CC-BY-SA. Source : Article Pantéthéine de Wikipédia en français (auteurs)
Regardez d'autres dictionnaires:
Pantetheine — Chembox new ImageFile = Pantetheine structure.png ImageSize = IUPACName = ( 2R ) 2,4 Dihydroxy 3,3 dimethyl N [2 (2 sulfanylethylcarbamoyl)ethyl] butanamide OtherNames = (R) Pantetheine Section1 = Chembox Identifiers CASNo = 496 65 1 PubChem =… … Wikipedia
Pantetheine kinase — In enzymology, a pantetheine kinase (EC number|2.7.1.34) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction:ATP + pantetheine ightleftharpoons ADP + pantetheine 4 phosphateThus, the two substrates of this enzyme are ATP and pantetheine, whereas… … Wikipedia
Pantetheine-phosphate adenylyltransferase — In enzymology, a pantetheine phosphate adenylyltransferase (EC number|2.7.7.3) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction:ATP + pantetheine 4 phosphate ightleftharpoons diphosphate + 3 dephospho CoAThus, the two substrates of this enzyme… … Wikipedia
Pantetheine hydrolase — In enzymology, a pantetheine hydrolase (EC number|3.5.1.92) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction:(R) pantetheine + H2O ightleftharpoons (R) pantothenate + 2 aminoethanethiolThus, the two substrates of this enzyme are (R) pantetheine… … Wikipedia
pantetheine — noun The cysteamine amide analogue of pantothenic acid, an intermediate in the production of coenzyme A by the body … Wiktionary
pantetheine — The condensation product of pantothenic acid and aminoethanethiol; N pantothenyl 2 aminoethanethiol; an intermediate in biosynthesis of coenzyme A via 4′ phosphopantetheine (a phosphoryl on the terminal –CH2O group) and ATP. SYN: Lactobacillus… … Medical dictionary
pantetheine — pan·te·the·ine … English syllables
pantetheine — ˌpantəˈthēˌēn, thēə̇n, pan.ˈteth noun ( s) Etymology: pantethe (by shortening & alteration from pantothenic in pantothenic acid) + ine : a growth factor C11H22N2O4S that is essential for various microorganisms (as Lactobacillus bulgaricus) and… … Useful english dictionary
pantothenic acid — /pan teuh then ik, pan /, Biochem. a hydroxy acid, C9H17O5N, found in plant and animal tissues, rice, bran, etc., that is part of the B complex of vitamins and is essential for cell growth. [1930 35; < Gk pántothen from all quarters (panto PANTO… … Universalium
GRAS (MÉTABOLISME DES ACIDES) — Les acides gras représentent l’unité de base des diverses classes de lipides: phospholipides, lipides neutres, esters de stéroïdes, etc. Rarement présents dans la matière vivante sous forme libre, ils existent surtout sous forme combinée et leur… … Encyclopédie Universelle

