- Tris(8-hydroxyquinoléine)aluminium(III)
-
Tris(8-hydroxyquinoléine)aluminium(III) 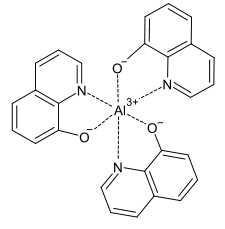
Structure du tris(8-hydroxyquinoléine)aluminium(III)Général Nom IUPAC tri(quinoléin-8-yloxy)alumane Synonymes tris(quinoléine-8-olate) d'aluminium,
tris(8-hydroxyquinolinato)aluminium,
oxinate d'aluminium, Alq3No CAS No EINECS PubChem SMILES InChI Apparence poudre jaune Propriétés chimiques Formule brute C27H18AlN3O3 [Isomères] Masse molaire[1] 459,4317 ± 0,0244 g·mol-1
C 70,59 %, H 3,95 %, Al 5,87 %, N 9,15 %, O 10,45 %,Propriétés physiques T° fusion 413-415 °C T° ébullition > 425 °C Solubilité insoluble dans l'eau Précautions Directive 67/548/EEC[2] 
XiPhrases R : 36/37/38, Phrases S : 26, 36, SGH[2] 
AttentionUnités du SI & CNTP, sauf indication contraire. Le tris(8-hydroxyquinoléine)aluminium(III), généralement abrégé en Alq3, est un complexe de formule Al(C9H6NO)3 formé d'un cation d'aluminium(III) Al3+ chélaté par trois anions de 8-hydroxyquinoléine C9H6NO-.
La dénomination de ce chélate peut varier au gré des articles publiés dans la littérature anglophone et francophone, les plus courantes étant tris(8-hydroxyquinolinato)aluminium et aluminum tris(8-hydroxyquinolinate) en anglais.
Les isomères méridionaux mer-Alq3 et faciaux fac-Alq3 ont été identifiés, ainsi que plusieurs polymorphes[3] :
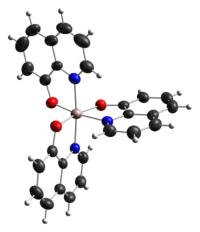
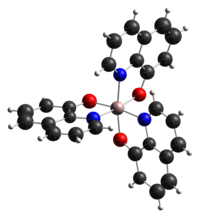
Structure du mer-Alq3[4] Structure du fac-Alq3[5] L'Alq3 est une substance couramment utilisée dans les diodes électroluminescentes organiques (OLED), les différents substituants sur le noyau quinoléine permettant de moduler la luminescence du composant[6]. On prépare l'Alq3 en faisant réagir des sources d'aluminium(III) et de 8-hydroxyquinoléine[7] :
Notes et références
- Masse molaire calculée d’après Atomic weights of the elements 2007 sur www.chem.qmul.ac.uk.
- SIGMA ALDRICH
- (en) Michael Cölle, Robert E. Dinnebier et Wolfgang Brütting, « The structure of the blue luminescent δ-phase of tris(8-hydroxyquinoline)aluminium(III) (Alq3) », dans Chemical Communications, no 23, 5 novembre 2002, p. 2908-2909 [texte intégral (page consultée le 24 juin 2011)]
DOI:10.1039/B209164J - (en) M. Brinkmann, « Correlation between Molecular Packing and Optical Properties in Different Crystalline Polymorphs and Amorphous Thin Films of mer-Tris(8-hydroxyquinoline)aluminum(III) », dans J. Am. Chem. Soc., vol. 122, no 21, 2000, p. 5147-5157 [lien DOI]
- (en) M. Rajeswaran, « Refinement of the crystal structure of the δ-modification of tris(8-hydroxyquinoline)aluminum(III), δ-Al(C9H6NO)3, the blue luminescent Alq3 », dans Z. Kristallogr. NCS, vol. 218, 2003, p. 439-440 [texte intégral]
- (en) Victor A. Montes, Dr. Radek Pohl, Prof. Joseph Shinar, Prof. Pavel Anzenbacher Jr., « Effective Manipulation of the Electronic Effects and Its Influence on the Emission of 5-Substituted Tris(8-quinolinolate) Aluminum(III) Complexes », dans Chemistry – A European Journal, vol. 12, no 17, 2 juin 2006, p. 4523-4535 [texte intégral (page consultée le 24 juin 2011)]
DOI:10.1002/chem.200501403 - (en) Ryo Katakura et Yoshihiro Koide, « Configuration-Specific Synthesis of the Facial and Meridional Isomers of Tris(8-hydroxyquinolinate)aluminum (Alq3) », dans Inorganic Chemistry, vol. 45, no 15, 30 juin 2006, p. 5730-5732 [texte intégral (page consultée le 24 juin 2011)]
DOI:10.1021/ic060594s
- Portail de la chimie
- Portail des sciences des matériaux
- Portail de l’électricité et de l’électronique
Catégories :- Composé de l'aluminium
- Produit chimique irritant
- Quinoléine
- Complexe
- Alcoolate
- Semi-conducteur organique
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
