Cystine
- Cystine
-
| Cystine |
 |
| Général |
| No CAS |
56-89-3 (L)(–) |
| No EINECS |
200-296-3 |
| DrugBank |
DB00138 |
| PubChem |
47205875 |
| No E |
E921 |
| SMILES |
|
| InChI |
InChI : Vue 3D
InChI=1/C6H12N2O4S2/c7-3(5(9)10)1-13-14-2-4(8)6(11)12/h3-4H,1-2,7-8H2,(H,9,10)(H,11,12)/t3-,4-/m0/s1
|
| Propriétés chimiques |
| Formule brute |
C6H12N2O4S2
|
| Masse molaire[1] |
240,3 ± 0,017 g·mol-1
C 29,99 %, H 5,03 %, N 11,66 %, O 26,63 %, S 26,69 %,
|
| Propriétés physiques |
| T° fusion |
260,5 °C (décomposition)[2] |
| Solubilité |
190 mg·l-1 (eau,20 °C)[2] |
|
Unités du SI & CNTP, sauf indication contraire.
|
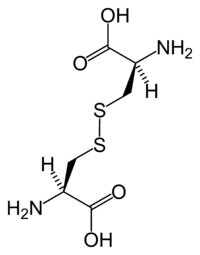
La cystine est un acide aminé dipeptide composé de deux acides aminés cystéines joints par un pont disulfure.
La cystine peut être responsable de la formation de calculs rénaux, notamment chez les personnes atteintes de cystinurie. Dans la bouche, la cystine provoque l'halitose (mauvaise haleine), comme les autres acides aminés soufrés (cystéine et méthionine).
Rôle thérapeutique
Associée à la vitamine B6 dans un médicament, la cystine est utilisée pour favoriser un développement normal des cheveux et des ongles. Elle est aussi employée pour favoriser la cicatrisation de la cornée.
Notes et références
Wikimedia Foundation.
2010.
Contenu soumis à la licence CC-BY-SA. Source : Article Cystine de Wikipédia en français (auteurs)
Regardez d'autres dictionnaires:
cystine — [ sistin ] n. f. • 1834; du gr. kustis « vessie » ♦ Biochim. Forme oxydée de la cystéine faite de deux molécules de cet acide aminé, reliées par leurs atomes de soufre. ● cystine nom féminin Aminoacide soufré, constituant essentiel des protéines … Encyclopédie Universelle
Cystine — Cyst ine (s?s t?n; 104), n. [See {Cyst}.] (Physiol. Chem.) A white crystalline substance, {C3H7NSO2}, containing sulphur, occuring as a constituent of certain rare urinary calculi, and occasionally found as a sediment in urine. [1913 Webster] … The Collaborative International Dictionary of English
cystine — cystine. См. цистин. (Источник: «Англо русский толковый словарь генетических терминов». Арефьев В.А., Лисовенко Л.А., Москва: Изд во ВНИРО, 1995 г.) … Молекулярная биология и генетика. Толковый словарь.
cystine — [sis′tēn, sis′tin] n. [ CYST(O) + INE3: so named from having been found first in urinary calculi] a nonessential amino acid, C4H6 (NH2) 2S2 (COOH) 2: see AMINO ACID … English World dictionary
Cystine — Not to be confused with cysteine. Cystine Identifiers CAS number … Wikipedia
Cystine — An amino acid, one of the 20 amino acids which serve as the building blocks of protein. Cystine is not an essential amino acid, that is, it is not essential to the diet since the body can synthesize (make) it. Cystine is particularly notable… … Medical dictionary
cystine — /sis teen, tin/, n. Biochem. a crystalline amino acid, C6H12O4N2S2, occurring in most proteins, esp. the keratins in hair, wool, and horn, and yielding cysteine on reduction. [1835 45; CYST + INE2; so called because found in the bladder] * * * ▪… … Universalium
cystine — cistinas statusas T sritis chemija formulė [SCH₂CH(NH₂)COOH]₂ atitikmenys: angl. cystine rus. цистин ryšiai: sinonimas – 3,3ˊ ditio bis(2 aminopropano rūgštis) … Chemijos terminų aiškinamasis žodynas
Cystine reductase — Identifiers EC number 1.8.1.6 CAS number 9029 18 9 … Wikipedia
Cystine kidney stones — are due to cystinuria, an inherited (genetic) disorder of the transport of an amino acid (a building block of protein) called cystine that results in an excess of cystine in the urine (cystinuria) and the formation of cystine stones. Cystinuria… … Medical dictionary

