- Ceftaroline
-
Ceftaroline 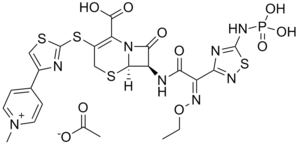
Général Nom IUPAC (6R,7R)-7-[(2Z)-2-éthoxyimino-2-[5-(phosphonoamino)-1,2,4-thiadiazol-3-yl]acétyl]amino]-3-[4-(1-méthylpyridin-1-ium-4-yl)-1,3-thiazol-2-yl]sulfanyl]-8-oxo-5-thia-1-azabicyclo[4.2.0]oct-2-ène-2-carboxylate Synonymes PPI 0903, TAK-599 No CAS PubChem SMILES Apparence solide Propriétés chimiques Formule brute C24H25N8O10PS4 Masse molaire[1] 744,737 ± 0,046 g·mol-1
C 38,71 %, H 3,38 %, N 15,05 %, O 21,48 %, P 4,16 %, S 17,22 %,Précautions Directive 67/548/EEC 
XnDonnées pharmacocinétiques Demi-vie d’élim. 2,13-2,89 heures Excrétion 46,4% rénale Considérations thérapeutiques Voie d’administration I.V., I.M. Unités du SI & CNTP, sauf indication contraire. La ceftaroline est un antibiotique de la famille des céphalosporines de cinquième génération. Elle est remarquable pour son activité contre le Staphylococcus aureus résistant à la méticilline (SARM) et les bactéries Gram positif. Elle conserve l'activité des céphalosporines des générations précédentes en ayant une activité à large spectre contre les bactéries Gram négatif. Elle est actuellement à l'étude pour les pneumonies communautaires[2] et les infections compliquées de la peau et des structures cutanées[3],[4],[5].
La Ceftaroline est sous une licence Takeda[5]. Des études in vitro montrent qu'elle a un spectre similaire à celui du ceftobiprole, la seule autre céphalosporine de cinquième génération à ce jour, bien qu'aucun essai clinique ceftaroline v. ceftobiprole n'ait été mené. Actuellement, ceftaroline et ceftobiprole sont dans une sous-classe sans nom de céphalosporines pour le Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI).
Sommaire
Mécanisme d'action
Les bêta-lactamines inhibent la synthèse du peptidoglycane des bactéries en s'intercalant dans les protéines (PBP) qui participent à la construction de la paroi cellulaire bactérienne. Ces PBP dénaturées donnent des irrégularités dans les structures de la paroi cellulaire, comme un allongement, des lésions, une perte de la perméabilité sélective et, finalement, la mort des cellules et leur lyse. En particulier, la ceftaroline peut effectivement se lier et inhiber la PBP-2a, le type de PBP produite par le SARM et qui n'est pas bien inhibée par d'autres antibiotiques actuellement utilisés en clinique[6],[7].
Utilisation clinique
Article principal : Céphalosporine.La Ceftaroline est une nouvelle céphalosporine qui a une activité contre le SARM lors d'essais cliniques de phase III pour les infections compliquées de la peau et des structures cutanées sans infériorité rapportée contre le SARM, comparativement à la vancomycine et l'aztréonam[3],[4]. Récemment, la ceftaroline a terminé ses essais cliniques de phase III pour la pneumonie communautaire comparée à la ceftriaxone avec des résultats non-inférieurs et des effets indésirables similaires[2]. Cependant seuls les résultats des essais cliniques de phase II dans le traitement des infections compliquées de la peau et des structures cutanées ont été publiés[8]. Le fabricant prévoit de déposer une demande de New Drug Application (NDA) auprès de la Food and Drug Administration d'ici la fin de cette année à la fois pour la pneumonie communautaire et les infections compliquées de la peau et des structures cutanées[9]
Chimie
La ceftaroline, aussi connue comme l'acétate de fosamil ceftaroline, est une prodrogue qui est convertie en un métabolite actif et un métabolite inactif ceftaroline-M1. Les essais préliminaires in vitro et in vivo chez l'animal donnaient à la ceftaroline les noms TAK-599 et PPI-0903[10],[11].
Caractéristique des céphalosporines, la ceftaroline a un double cycle avec un cycle β-lactame à quatre atomes fusionné à un cycle céphem à six atomes. La ceftaroline est supposée avoir une activité contre le SARM avec son cycle 1,3thiazole[12].
Références
- Masse molaire calculée d’après Atomic weights of the elements 2007 sur www.chem.qmul.ac.uk.
- P, Eckberg; Friedland HD, et al.. "FOCUS 1 and 2: Randomized, Double-blinded, Multicenter Phase 3 Trials of the Efficacy and Safety of Ceftaroline (CPT) vs. Ceftriaxone (CRO) in Community-acquired pneumonia (CAP)." in 2009 Interscience Conference on Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy / Infectious Disease Society of America Conference. .
- R, Corey; Wilcox M, Talbot GH, et al.. "CANVAS-1: Randomized, Double-blinded, Phase 3 Study (P903-06) of the Efficacy and Safety of Ceftaroline vs. Vancomycin plus Aztreonam in Complicated Skin and Skin Structure Infections (cSSSI)." in 2008 Interscience Conference on Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy / Infectious Disease Society of America Conference. .
- Kanafani ZA, Corey GR, « Ceftaroline: a cephalosporin with expanded Gram-positive activity », dans Future Microbiology, vol. 4, février 2009, p. 25–33 [texte intégral, lien PMID, lien DOI]
- Parish D, Scheinfeld N, « Ceftaroline fosamil, a cephalosporin derivative for the potential treatment of MRSA infection », dans Current Opinion in Investigational Drugs (London, England : 2000), vol. 9, no 2, février 2008, p. 201–9 [lien PMID]
- Villegas-Estrada A, Lee M, Hesek D, Vakulenko SB, Mobashery S, « Co-opting the cell wall in fighting methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: potent inhibition of PBP 2a by two anti-MRSA beta-lactam antibiotics », dans Journal of the American Chemical Society, vol. 130, no 29, juillet 2008, p. 9212–3 [texte intégral, lien PMID, lien DOI]
- Zhanel GG, Sniezek G, Schweizer F, Zelenitsky S, Lagacé-Wiens PR, Rubinstein E, Gin AS, Hoban DJ, Karlowsky JA, « Ceftaroline: a novel broad-spectrum cephalosporin with activity against meticillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus », dans Drugs, vol. 69, no 7, 2009, p. 809–31 [lien PMID, lien DOI]
- Talbot GH, Thye D, Das A, Ge Y, « Phase 2 study of ceftaroline versus standard therapy in treatment of complicated skin and skin structure infections », dans Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy, vol. 51, no 10, octobre 2007, p. 3612–6 [texte intégral, lien PMID, lien DOI]
- BUSINESS WIRE (2009-09-12). Forest Laboratories Presents Analysis of Two Positive Pivotal Phase III Studies of Ceftaroline for the Treatment of Community-Acquired Pneumonia (CAP) at ICAAC. Communiqué de presse. Consulté le 2009-10-19.
- Y, Ge; Floren L, Redman R, et. al.. "The pharmacokinetics and safety of ceftaroline (PPI-0903) in healthy subjects receiving multiple-dose intravenous infusions." in 2006 Interscience Conference on Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy / Infectious Disease Society of America Conference. .
- Yukihiro I, Junko B, « Stability and Stabilization Studies of TAK-599 (Ceftaroline Fosamil) a Novel N-Phosphono Type Prodrug of Anti-methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Cephalosporin T-91825 », dans Chem Pharm Bull, vol. 56, no 10, 2008, p. 1406-11 [texte intégral, lien PMID, lien DOI]
- Ishikawa t, Nobuyuki M, et al., « TAK-599, a novel N-phosphono type prodrug of anti-MRSA cephalosporin T-91825: Synthesis, physicochemical and pharmacological properties », dans Bioorg Med Chem, vol. 11, no 11, 2003, p. 2427-2437 [lien PMID]
- Wikipedia anglophone
Catégories :- Composé du phosphore
- Produit chimique nocif
- Antibiotique
- Thiadiazole
- Céphalosporine
- Thiazole
- Azine
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
