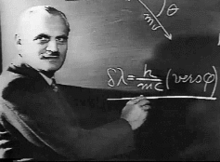Arthur Compton
- Arthur Compton
-

Pour les articles homonymes, voir
Compton.
Arthur Holly Compton (10 septembre 1892 à Wooster, Ohio, États-Unis - 15 mars 1962 à Berkeley, Californie) était un physicien américain. Il est lauréat de la moitié du prix Nobel de physique de 1927 (l'autre moitié a été remise à Charles Wilson) « pour la découverte de l'effet nommé en son nom[1] ».
Biographie
Il fut récompensé en 1927 (avec Charles Thomson Rees Wilson) par le prix Nobel de physique pour sa découverte de l'effet Compton qui a permis de valider la notion de dualité onde-corpuscule de la lumière.
Il a reçu le prix Rumford en 1926. Il fut également lauréat de la Médaille Hughes et de la Médaille Franklin en 1940.
Publications
- Compton, Arthur (1918). "American Physical Society address (Dec 1917)", Physical Review, Series II.
- Compton, Arthur (1923). "A Quantum Theory of the Scattering of X-Rays by Light Elements", Physical Review, 21(5), 483 - 502.
- Compton, Arthur (1935). The Freedom of Man, New Haven: Yale University Press.
- Compton, Arthur (1940). The Human Meaning of Science, Chapel Hill: University of North Carolina Press.
- Compton, Arthur (1956). Atomic Quest, New York: Oxford University Press.
- Compton, Arthur (1967). The Cosmos of Arthur Holly Compton, New York: Alfred A. Knopf; edited by Marjorie Johnston
- Compton, Arthur (1973). Scientific Papers of Arthur Holly Compton, Chicago: University of Chicago Press; edited by Robert S. Shankland.
Bibliographie
- Cristofv, Cristjo (1954). The real meaning of the Compton effect.
Notes et références
Voir aussi
Articles connexes
Liens externes
|
Lauréats du prix Nobel de physique |
| 1901–1925 |
|
| 1926–1950 |
|
| 1951–1975 |
Cockcroft, Walton (1951) • Bloch, Purcell (1952) • Zernike (1953) • Born, Bothe (1954) • Lamb, Kusch (1955) • Shockley, Bardeen, Brattain (1956) • Yang, T. D. Lee (1957) • Cherenkov, Frank, Tamm (1958) • Segrè, Chamberlain (1959) • Glaser (1960) • Hofstadter, Mössbauer (1961) • Landau (1962) • Wigner, Goeppert-Mayer, Jensen (1963) • Townes, Bassov, Prokhorov (1964) • Tomonaga, Schwinger, Feynman (1965) • Kastler (1966) • Bethe (1967) • Alvarez (1968) • Gell-Mann (1969) • Alfvén, Néel (1970) • Gabor (1971) • Bardeen, Cooper, Schrieffer (1972) • Esaki, Giaever, Josephson (1973) • Ryle, Hewish (1974) • A. Bohr, Mottelson, Rainwater (1975)
|
| 1976–2000 |
Richter, Ting (1976) • P. W. Anderson, Mott, Van Vleck (1977) • Kapitsa, Penzias, R. Wilson (1978) • Glashow, Salam, Weinberg (1979) • Cronin, Fitch (1980) • Bloembergen, Schawlow, K. Siegbahn (1981) • K. Wilson (1982) • Chandrasekhar, Fowler (1983) • Rubbia, van der Meer (1984) • von Klitzing (1985) • Ruska, Binnig, Rohrer (1986) • Bednorz, Müller (1987) • Lederman, Schwartz, Steinberger (1988) • Ramsey, Dehmelt, Paul (1989) • Friedman, Kendall, R. Taylor (1990) • de Gennes (1991) • Charpak (1992) • Hulse, J. Taylor (1993) • Brockhouse, Shull (1994) • Perl, Reines (1995) • D. Lee, Osheroff, R. Richardson (1996) • Chu, Cohen-Tannoudji, Phillips (1997) • Laughlin, Störmer, Tsui (1998) • 't Hooft, Veltman (1999) • Alferov, Kroemer, Kilby (2000)
|
| 2001–aujourd'hui |
Cornell, Ketterle, Wieman (2001) • Davis, Koshiba, Giacconi (2002) • Abrikosov, Ginzburg, Leggett (2003) • Gross, Politzer, Wilczek (2004) • Glauber, Hall, Hänsch (2005) • Mather, Smoot (2006) • Fert, Grünberg (2007) • Nambu, Kobayashi, Maskawa (2008) • Kao, Boyle, Smith (2009) • Geim, Novoselov (2010)
|
| Prix Nobel • Chimie • Littérature • Paix • Économie • Physique • Physiologie ou médecine |
Catégories :
- Physicien américain
- Physicien du XXe siècle
- Lauréat du prix Nobel de physique
- Lauréat américain du prix Nobel
- Naissance en 1892
- Décès en 1962
- Rayons X
- Étudiant de l'université de Princeton
Wikimedia Foundation.
2010.
Contenu soumis à la licence CC-BY-SA. Source : Article Arthur Compton de Wikipédia en français (auteurs)
Regardez d'autres dictionnaires:
Arthur Compton — Saltar a navegación, búsqueda Imagen de Compton en 1936 … Wikipedia Español
Arthur Compton — Infobox Scientist name = Arthur Holly Compton image size = caption = Arthur Holly Compton on the cover of Time magazine, January 13, 1936. birth date = birth date|mf=yes|1892|9|10 birth place = Wooster, Ohio, USA death date = death date and… … Wikipedia
Arthur Compton — Arthur Holly Compton. Arthur Holly Compton (* 10. September 1892 in Wooster; † 15. März 1962 in Berkeley) war ein US amerikanischer Physiker und Nobelpreisträger. Leben Nach Abschluss der Schule besucht … Deutsch Wikipedia
Arthur Compton — Arthur Holly Compton (n. Wooster, Ohio, 10 de septiembre de 1892 † Berkeley, California, 15 de marzo de 1962). Físico y Premio Nobel estadounidense. Sus estudios de los rayos X le llevaron a descubrir en 1922 el denominado efecto Compton. El … Enciclopedia Universal
Arthur Compton — noun United States physicist noted for research on x rays and gamma rays and nuclear energy; his observation that X rays behave like miniature bowling balls in their interactions with electrons provided evidence for the quantal nature of light… … Useful english dictionary
Arthur Compton — n. Arthur Holly Compton (1892 1962), American physicist, winner of the 1927 Nobel Prize in Physics … English contemporary dictionary
Arthur Holly Compton — Arthur Holly Compton. Arthur Holly Compton (* 10. September 1892 in Wooster, Ohio; † 15. März 1962 in Berkeley, Kalifornien) war ein US amerikanischer Physiker und Nobelpreisträger … Deutsch Wikipedia
Arthur H. Compton House — Compton, Arthur H., House U.S. National Register of Historic Places U.S. National Historic Landmark … Wikipedia
Compton (surname) — Compton is a surname of English origin, and may refer to: Ann Compton, journalist Arthur Compton, physicist and Nobel Prize winner, of the Compton effect, brother of Karl Taylor Compton and Wilson Martindale Compton, below Barnes Compton,… … Wikipedia
Arthur H. Compton — Arthur Compton Pour les articles homonymes, voir Compton. Arthur Holly Compton. Arthur Holly Compton (né le 10 septembre 1892 à Wooster (Ohio) … Wikipédia en Français
 Pour les articles homonymes, voir Compton.
Pour les articles homonymes, voir Compton.
 États-Unis
États-Unis