- 552-58-9
-
Eriodictyol
Eriodictyol 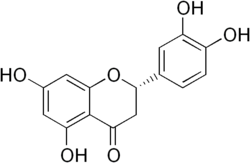
Structure de l'eriodictyol. Général Nom IUPAC (2S)-2-(3,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)-5,7-dihydroxy-4-chromanone Synonymes Eriodictiol
3',4',5,7-TetrahydroxyflavanoneNo CAS No EINECS PubChem SMILES Apparence Solide blanc Propriétés chimiques Formule brute C15H12O6 [Isomères] Masse molaire 288,2522 g∙mol-1
C 62,5 %, H 4,2 %, O 33,3 %,Propriétés physiques T° fusion 257 °C[1] Solubilité Eau froide 0,07 g⋅L-1,
eau chaude 0,2 g⋅L-1[1]Composés apparentés Autres composés Stérubine, Homoeriodictyol Unités du SI & CNTP, sauf indication contraire. L'Eriodictyol est une flavanone (flavonoïde) extraite des feuilles de l'Herba Santa (Eriodictyon californicum)[2], une plante poussant dans le nord du Mexique et dans l'état de Californie[3].
Sommaire
Masqueur
La capacité de l'eriodictyol de réduire l'amertume de composé amer été mis en évidence par Symrise une entreprise de l'aromatique alimentaire. Dans cette même plante, 3 autres flavonoïdes ont été identifié avec la même capacité à modifier le goût : la stérubine, l'homoeriodictyol et l'homoeriodictyol sodique[2].
Autre source
L'eriodictyol a aussi été indentifié dans d'autre végétaux comme le Millettia duchesnei[4] et l'Eupatorium arnottianum[5].
Un de ses hétéroside a été identifié dans l'églantier (Rosa canina)[6].
Notes et références de l'article
- ↑ a et b (en) SH Yalkowsky, Y He (2003) Handbook of Aqueous Solubility Data, Eriodytol. CRC Press, p993 (ISBN 0849315328)
- ↑ a et b (en) Ley JP, Krammer G, Reinders G, Gatfield IL, Bertram HJ (2005) Evaluation of bitter masking flavanones from Herba Santa (Eriodictyon californicum (H. and A.) Torr., Hydrophyllaceae). J Agric Food Chem. 27;53(15):6061-6. PMID 16028996
- ↑ (en) Patricia Kaminski and Richard Katz. Yerba Santa Eriodictyon californicum. Flower Essence Society.
- ↑ (en) F Ngandeu, M Bezabih, D Ngamga, AT Tchinda, BT Ngadjui, BM Abegaz, H Dufat, F Tillequin (2007) Rotenoid derivatives and other constituents of the twigs of Millettia duchesnei. Phytochemistry. 2007 Jul 17. PMID 17640692
- ↑ (en) M Clavin, S Gorzalczany, A Macho, E Muñoz, G Ferraro, C Acevedo, V Martino (2007). Anti-inflammatory activity of flavonoids from Eupatorium arnottianum. J Ethnopharmacol. 2007 Jul 25;112(3):585-9. PMID 17570627
- ↑ (en) E Hvattum (2002). Determination of phenolic compounds in rose hip (Rosa canina) using liquid chromatography coupled to electrospray ionisation tandem mass spectrometry and diode-array detection. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom. 2002;16(7):655-62. PMID 11921243
Voir aussi
Articles connexes
Liens et documents externes
- Portail de la chimie
- Portail de l’alimentation et de la gastronomie
- Portail de la biochimie
Catégories : Flavonoïde | Polyphénol | Modificateur de goût
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
