- Sélénométhionine
-
Sélénométhionine 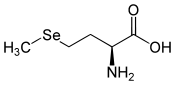
L ou S-sélénométhionine
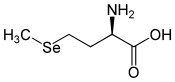
D ou R-sélénométhionineGénéral Nom IUPAC acide 2-amino-4-méthylsélanylbutanoïque Synonymes DL-sélénométhionine No CAS No EINECS No RTECS PubChem ChEBI SMILES InChI Apparence poudre blanche Propriétés chimiques Formule brute C5H11NO2Se [Isomères] Masse molaire[1] 196,11 ± 0,04 g·mol-1
C 30,62 %, H 5,65 %, N 7,14 %, O 16,32 %, Se 40,26 %,Propriétés physiques T° fusion 265 °C [2] Précautions Directive 67/548/EEC[3] 
T
NPhrases R : 23/25, 33, 50/53, Phrases S : 20/21, 28, 45, 60, 61, Transport[3] - 3283 SGH[3] 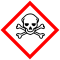
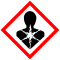
Écotoxicologie DL50 22 mg·kg-1 (souris, i.v.) [2] Unités du SI & CNTP, sauf indication contraire. La sélénométhionine est un composé chimique, analogue sélénié de la méthionine, un acide aminé soufré, à la place de laquelle elle peut être incorporée dans les protéines de façon aléatoire — elle y est alors parfois représentée par les abréviations Se-Met ou Sem. Le soufre et le sélénium sont deux éléments chalcogènes assez semblables qui rendent la substitution de méthionine par la sélénométhionine a priori sans effet biologique — jusqu'à un certain point : le sélénium, bénéfique à très faibles doses, présente en effet une toxicité certaine au-delà de 400 μg par jour, la dose quotidienne recommandée étant huit fois inférieure à cette limite[4],[5] et donc très facilement dépassée.
La sélénométhionine pourrait constituer une source de sélénium plus facilement assimilable par l'organisme que l'ion sélénite SeO32-, absorbé par exemple sous forme de sélénite de sodium Na2SeO3 dans divers compléments alimentaires, en raison précisément de sa faculté à être incorporée aux protéines, sa demie-vie dans l'organisme étant plus du double (252 jours contre 102 jours[4]) de celle de SeO32-.
La dégradation in vivo de la sélénométhionine génère du séléniure d'hydrogène H2Se[4].
Propriétés physico-chimiques
La sélénométhionine possède un carbone chiral et donc deux énantiomères:
-
- (2R)-sélénométhionine ou D-sélénométhionine, numéro CAS
- (2S)-sélénométhionine ou L-sélénométhionine, numéro CAS
Notes et références
- Masse molaire calculée d’après Atomic weights of the elements 2007 sur www.chem.qmul.ac.uk.
- (en) « DL-Selenomethionine » sur ChemIDplus, consulté le 4 janvier 2011
- Catalogue Sigma-Aldrich. Consulté le 4 janvier 2011
- (en) European Food and Safety Authority « L-selenomethionine as a source of selenium added for nutritional purposes to food supplements. »
- (en) National Institute of Health – Office of Dietary Supplements « Dietary Supplement Fact Sheet: Selenium – What is the health risk of too much selenium? »
Catégories :- Composé du sélénium
- Produit chimique toxique
- Produit chimique dangereux pour l'environnement
- Acide aminé
-
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.

