Allyl méthyl thioéther
- Allyl méthyl thioéther
-
| Allyl méthyl thioéther |
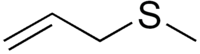 |
| Général |
| Nom IUPAC |
3-(méthylsulfanyl)prop-1-ène[1] |
| No CAS |
10152-76-8 |
| No EINECS |
233-422-0 |
| PubChem |
66282 |
| SMILES |
|
| InChI |
InChI : Vue 3D
InChI=1/C4H8S/c1-3-4-5-2/h3H,1,4H2,2H3
|
| Propriétés chimiques |
| Formule brute |
C4H8S [Isomères]
|
| Masse molaire[2] |
88,171 ± 0,009 g·mol-1
C 54,49 %, H 9,15 %, S 36,37 %,
|
| Propriétés physiques |
| T° ébullition |
91-93 °C[1] |
| Masse volumique |
0,803 g·cm-3[1] |
| Point d’éclair |
18 °C[1] |
| Précautions |
|
Directive 67/548/EEC
|

F
|
|
Symboles :
F : Facilement inflammable
Phrases R :
R11 : Facilement inflammable.
Phrases S :
S16 : Conserver à l’écart de toute flamme ou source d’étincelles - Ne pas fumer.
S29 : Ne pas jeter les résidus à l’égout.
S33 : Éviter l’accumulation de charges électrostatiques.
|
| Phrases R : 11, |
| Phrases S : 16, 29, 33, |
|
Unités du SI & CNTP, sauf indication contraire.
|
L'allyl méthyl thioéther est un thioéther de formule brute C4H8S. il est le plus souvent rencontré comme sous-produit de la digestion de l'ail et cause une mauvaise haleine (halitose). Manger de l'ail provoque la production de nombreux dérivés soufrés gazeux dans le système digestif, la plupart étant métabolisés par l'intestin et le foie. Cependant l'allyl méthyl thioéther ne l'est pas, il passe dans le système sanguin de l'intestin, puis il peut arriver aux poumons et retourner à la bouche provoquant des heures de mauvaise haleine après l'ingestion et dans l'urine et la peau où il peut être aussi libéré, provoquer des sueurs malodorantes[3].
Notes
Wikimedia Foundation.
2010.
Contenu soumis à la licence CC-BY-SA. Source : Article Allyl méthyl thioéther de Wikipédia en français (auteurs)
Regardez d'autres dictionnaires:
10152-76-8 — Allyl méthyl thioéther Allyl méthyl thioéther Général Nom IUPAC 3 (méthylsulfanyl)prop 1 ène … Wikipédia en Français
C4H8S — Cette page répertorie différents isomères, c’est à dire les molécules qui partagent la même formule brute. C4H8 … Wikipédia en Français
Groupe fonctionnel — En chimie organique, un groupe fonctionnel est une structure sub moléculaire constituée d un assemblage d atomes donnés qui confère une réactivité propre à la molécule qui le contient. Cette manière de considérer les molécules comme étant un… … Wikipédia en Français
Functional group — For other uses, see Functional group (disambiguation) and Moiety (disambiguation). Benzyl acetate has an ester functional group (in red), an acetyl moiety (circled with green) and a benzyloxy moiety (circled with orange). Other divisions can be… … Wikipedia
Mukaiyama Taxol total synthesis — overview from raw material perspective The Mukaiyama taxol total synthesis published by the group of Teruaki Mukaiyama of the Tokyo University of Science between 1997 and 1999 was the 6th successful taxol total synthesis. The total synthesis of… … Wikipedia
Ester — For other uses, see Ester (disambiguation). A carboxylic acid ester. R and R denote any alkyl or aryl group, respectively Esters are chemical compounds derived by reacting an oxoacid with a hydroxyl compound such as an alcohol or phenol … Wikipedia
Alcohol — This article is about the generic chemistry term. For the kind of alcohol found in alcoholic beverages, see Ethanol. For beverages containing alcohol, see Alcoholic beverage. For other uses, see Alcohol (disambiguation) … Wikipedia
Alkene — This article is about the chemical compound. For the material, see Olefin fiber. Not to be confused with Alkane or Alkyne. A 3D model of ethylene, the simplest alkene. In organic chemistry, an alkene, olefin, or olefine is an unsaturated ch … Wikipedia


