- SYBR Green I
-
SYBR green 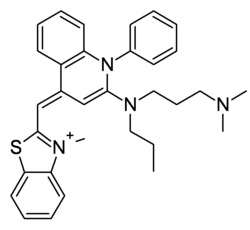
Général Synonymes [2-[N-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)-
N-propylamino]-4-[2,3-
dihydro-3-methyl-
(benzo-1,3-thiazol-2-yl)-
methylidene]-1-
phenyl-quinolinium]+°No CAS Propriétés chimiques Formule brute C32H37N4S [Isomères] Masse molaire[1] 509,728 ± 0,034 g·mol-1
C 75,4 %, H 7,32 %, N 10,99 %, S 6,29 %,Propriétés physiques T° fusion 262 °C T° d'auto-inflammation non inflamable (>-6 °C) Précautions Inhalation Officiellement aucune (voir Toxicité...) Peau Officiellement aucune (voir Toxicité...) Yeux Officiellement aucune (voir Toxicité...) Risque biologique officiel non dangereux (norme américaine OSHA) Statut officiel des déchets ni dangereux ni toxique (norme américaine) Unités du SI & CNTP, sauf indication contraire. Le SYBR Green I est un composé organique aromatique de formule chimique C32H37N4S faisant partie des cyanines asymétriques (fluorophores)
Sommaire
Historique
Par souci de clarté, les dates correspondent à la première publication sur le domaine et seul les premiers auteurs sont cités, les références complètes étant dans le chapitre "bibliographie".
- 1975 : Invention d’un test de détection des agents mutagènes et carcinogènes par Ames BN (révisé dans une étude de 1983)
- 1992 : Première publication sur les marqueurs fluorescents de l’ADN de la famille des cyanines asymétriques par Rye HS.
- 1993 : Première mention du SYBR green I par Molecular Probes dans le Bioprobes no 18 (numéro en ligne jusqu’au 23, à vérifier)
- 1994 : Premières études de caractérisation du SYBR green I par Jin X.
- 1994 : Premier marquage d’ADN et d’ARN par du SYBR green I sur gel d’électrophorèse de poly-acrylamide par Singer VL.
- 1995 : Premier marquage de produit de RT-PCR sur gel d’électrophorèse d’agarose par Schneeberger CS.
- 1995 : Première révélation de courtes répétitions en tandem sur gel de polyacrylamide avec une méthode non radioactive par Morin PA.
- 1995 : Première détection des nucléase en gel sensible avec du SYBR green I par Jin X.
- 1995 : Première utilisation en électrophorèse capillaire par Skeidsvoll J.
- 1997 : Dépôt du brevet américain no 5658751 sur les cyanines asymétriques par Molecular Probes. Le SYBR green I semble être le composant no 937.
- 1997 : Première détection des ADN endommagés sur gels d'agarose en champs pulsés par Kiltie AE.
- 1998 : Première quantification de l'activité des nucléases en diffusion radiale par Yasuda T.
- 2000 : Détection de virus en cytométrie de flux avec du SYBR green I par Brussaard CP.
- 2001 : quantification de l’ADN double brin en extraits bruts sur échantillons environnementaux par Bachoon DS.
- 2004 : Publication de la structure et de variabilité du spectre d’émission du SYBR green I par Zipper H.
Utilisation
Le SYBR green I est une molécule pouvant se fixer sur tous les types d’acides nucléique double brins et devenant alors un très bon fluorophore. Il a donc très rapidement servi de méthode alternative au Bromure d'éthidium (BET) ou au marquage radioactif pour un grand nombre de méthodes, dont la détection d’ADN et d’ARN sur gels de polyacrylamide ou d’agarose, classique, en champs pulsé ou « sensible », pré ou post marqués. Il permet également de quantifier les acides nucléiques en solution et, n’interférant que peu avec la réaction en chaîne par polymérase, il est le principal marqueur séquence aspécifique utilisé en PCR en temps réel. Sa très grande sensibilité le rend exploitable en électrophorèse capillaire (détection jusqu’à 80 femtogrammes d’ADN double brin), en cytométrie de flux, pour des puces à ADN, pour de l’imagerie en fluorescence. Il sert également à la quantification d’activités enzymatiques (DNases, télomérases) ou pour celle de l’ADN double brin en milieu défavorable (par la présence d’inhibiteur de fluorescence).
Propriétés
Toxicité et consigne de sécurité
Le SYBR Green présente une mutagenicité non nulle mais cependant très inférieure au Bromure d'éthidium. Les précautions d'usage doivent être néanmoins conservées.
Notes et références
- Masse molaire calculée d’après Atomic weights of the elements 2007 sur www.chem.qmul.ac.uk.
Bibliographie
Bibliographie francophone
Bibliographie anglophone
- Ames BN, McCann J, Yamasaki E, Methods for detecting carcinogens and mutagens with the Salmonella/mammalian-microsome mutagenicity test. 1975. Mutat. Res. 31:347–364.
- Bachoon DS, Otero E, Hodson RE. Effects of humic substances on fluorometric DNA quantification and DNA hybridization. 2001. J. Microbiol. Methods, 47:73–82.
- Brussaard CP, Marie D, Bratbak G. Flow cytometric detection of viruses. 2000. J. Virol. Methods, 85:175–182
- Jin X, Yue S, Wells KS, Singer VL, SYBRTM Green I: a new fluorescent dye optimized for detection of picogram amounts of DNA in gels. 1994. Biophys. J. 66:A159.
- Jin X, Yue S, Singer VL, Highly sensitive gel assays for detecting nucleases. 1995. FASEB J. 9:A1400.
- Kiltie AE, Ryan AJ. SYBR Green I staining of pulsed field agarose gels is a sensitive and inexpensive way of quantitating DNA double-strand breaks in mammalian cells. 1997. Nucleic Acids Res. 25:2945–2946.
- Maron DM, Ames B. Revised methods for the Salmonella mutagenicity test. 1983; Mutat. Res. 113:173–215.
- Morin PA, Smith DG, Nonradioactive detection of hypervariable simple sequence repeats in short polyacrylamide gels. 1995. BioTechniques 19:223–227.
- Ohta T, Tokishita S, Yamagata H. Ethidium bromide and SYBR Green I enhance the genotoxicity of UV-irradiation and chemical mutagens in E. coli. 2001. Mutat Res. May 31;492(1-2):91-7.
- Rye HS, Yue S, Wemmer DE, Quesada MA, Haugland RP, Mathies RA, Glazer AN. Stable fluorescent complexes of double-stranded DNA with bis-intercalating asymmetric cyanine dyes: properties and applications. 1992. Nucleic Acids Res. 20:2803–2812.
- Schneeberger CS, Speiser P, Kury F, Zeillinger R. Quantitative detection of reverse transcriptase–PCR products by means of a novel and sensitive DNA stain, PCR Methods. 1995. Appl. 4 :234–238.
- Singer VL, Jin X, Ryan D, Yue S. SYBRTM Green dyes: ultrasensitive stains for detection of DNA and RNA in electrophoretic gels. 1994. Biomed. Products 19:68–72.
- Singer VL, Lawlor TE, Yue S. Comparison of SYBR Green I nucleic acid gel stain mutagenicity and ethidium bromide mutagenicity in the Salmonella/mammalian microsome reverse mutation assay (Ames test). 1999. Mutat Res 439:37–47.
- Skeidsvoll J, Ueland PM, Analysis of double-stranded DNA by capillary electrophoresis with laser-induced fluorescence detection using the monomeric dye SYBR Green I. 1995. Anal. Biochem. 231:359–365.
- Yasuda T, Takeshita H, Nakazato E, Nakajima O, Hosomi O, Nakashima Y, Kishi K, Activity measurement for deoxyribonucleases I and II with picogram sensitivity based on DNA SYBR Green I fluorescence. 1998. Anal. Biochem. 255:274–276.
- Zipper H, Brunner H, Bernhagen J, Vitzthum F. Investigations on DNA intercalation and surface binding by SYBR Green I, its structure determination and methodological implications. 2004. Nucl Acids Res; 32:e103.
Catégories :- Marqueur fluorescent
- Mutagène
- Réaction en chaîne par polymérase
- Ammonium quaternaire
- Benzothiazole
- Quinoléine
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.