- Bêta-alanine
-
Bêta-alanine 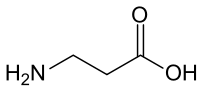
Général Nom IUPAC acide 3-aminopropanoïque No CAS No EINECS PubChem SMILES InChI Propriétés chimiques Formule brute C3H7NO2 [Isomères] Masse molaire[2] 89,0932 ± 0,0037 g·mol-1
C 40,44 %, H 7,92 %, N 15,72 %, O 35,92 %,pKa 3,63[1] Propriétés physiques T° fusion 200 °C[1] Écotoxicologie LogP 3,05[1] Composés apparentés Isomère(s) α-alanine Unités du SI & CNTP, sauf indication contraire. La β-alanine est un composé naturel de la famille des acides β-aminés, c'est-à-dire un acide aminé dans lequel le groupe amine est en position β par rapport au groupe carboxylate. Son nom IUPAC est l'acide 3-aminopropanoïque. Contrairement à son isomère, l'α-alanine (ou simplement alanine), la β-alanine n'a pas de centre chiral, et donc pas d'énantiomères.
La β-alanine n'est pas utilisée dans la biosynthèse d'une quelconque protéine ou enzyme majeure.
Sommaire
Formation et occurrence naturelle
La β-alanine est formée in vivo, par la dégradation du dihydrouracile et de la carnosine. C'est un composé de peptides comme la carnosine et l'ansérine, ainsi que de l'acide pantothénique (vitamine B5), lui-même composé du coenzyme A. Sous conditions normales, la β-alanine est métabolisée en acide acétique.
Précurseur de la carnosine
La β-alanine est un précurseur à taux limité de la carnosine, ce qui signifie que les niveaux de carnosine sont limités par la quantité de β-alanine disponible. Il a été montre qu'une quantité plus importante de β-alanine accroit la concentration de carnosine dans les muscles, fait décroître la fatigue des athlètes et permet d'augmenter le travail musculaire[3],[4].
Dérivé
Un édulcorant au pouvoir sucrant élevé (700 fois plus intense que le saccharose à poids comparé), appelé suosan, est dérivé de la β-alanine[5].
Notes et références
- (en) « » sur ChemIDplus, consulté le 5 juin 2010
- Masse molaire calculée d’après Atomic weights of the elements 2007 sur www.chem.qmul.ac.uk.
- Derave W, Ozdemir MS, Harris R, Pottier A, Reyngoudt H, Koppo K, Wise JA, Achten E., « Beta-alanine supplementation augments muscle carnosine content and attenuates fatigue during repeated isokinetic contraction bouts in trained sprinters », dans J Appl Physiol, vol. 103, August 9 2007, p. 1736 [lien PMID, lien DOI]
- Hill CA, Harris RC, Kim HJ, Harris BD, Sale C, Boobis LH, Kim CK, Wise JA., « Influence of beta-alanine supplementation on skeletal muscle carnosine concentrations and high intensity cycling capacity », dans Amino Acids, vol. 32, no 2, 2007, p. 225–33 [lien PMID, lien DOI]
- (en) C Nofre, JM Tinti & FO Chatzopoulos, « Glycine and β alanine derivatives as sweetening agents », US patent sur http://www.freepatentsonline.com, 1986. Consulté le 24/10/2008.
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
