- Imidazolinone
-
L'imidazolinone ou imidazolone est un composé hétérocyclique nitré de formule brute C3H4N2O. C'est une cétone de l'imidazoline, elle-même forme réduite de l'imidazole. Il existe ainsi 3 isomères imidazolinone[1] :
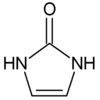
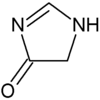
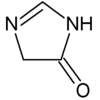
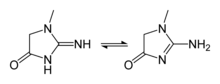
données isomère 1 isomère 2 isomère 3 structure nom 4-imidazolin-2-one imidazolin-5-one imidazolin-4-one nom IUPAC 1,3-dihydro-2H-imidazol-2-one 1,5-dihydro-4H-imidazol-4-one 3,5-dihydro-4H-imidazol-4-one numéro CAS ? ? ChEBI 51022 51023 28470 SMILES O=c1[nH]cc[nH]1 O=C1CNC=N1 O=C1CN=CN1 InChI 1S/C3H4N2O/c6-3-4-1-2-5-3/h1-2H,(H2,4,5,6) 1S/C3H4N2O/c6-3-1-4-2-5-3/h2H,1H2,(H,4,5,6) 1S/C3H4N2O/c6-3-1-4-2-5-3/h2H,1H2,(H,4,5,6) InChIKey AICIYIDUYNFPRY-UHFFFAOYSA-N CAAMSDWKXXPUJR-UHFFFAOYSA-N CAAMSDWKXXPUJR-UHFFFAOYSA-N De fait, les composés 4- et 5-imidazolinone sont tautomères et ne sont discernables que dans leur dérivés substitués. Les dérivés de l'imidazolin-4-one sont plus courants que ceux de la 5-one dont un exemple fameux est une des formes limites de la créatinine :
Plus généralement, les imidazolinones sont donc la famille de substances chimiques dérivées des imidazolinones et dont une bonne partie est utilisée comme herbicides. Leurs propriétés herbicides sont liées à leur pouvoir d'inhibition de l'action de l'acétolactate synthase (ALS)[2], enzyme nécessaire à la synthèse chez les plantes de trois acides aminés ramifiés (leucine, isoleucine, et valine). Ces substances ont été découvertes dans les années 1970 par la société américaine American Cyanamid[3].
Liste des herbicides de la famille des imidazolinones
La famille des imidazolinones utilisées comme herbicides comprend six composés commerciaux principaux[4] :
- imazaméthabenz ;
- imazamox ;
- imazapic ;
- imazapyr ;
- imazaquine ;
- imazéthapyr.
Notes et références
- http://www.ebi.ac.uk/chebi/searchId.do?chebiId=CHEBI%3A24781
- appelée aussi « acétohydroxy acide synthase » (AHAS).
- (en) Imidazolinone Herbicides, Agricultural Research Service. Consulté le 5 mars 2011.
- (en) Compendium of Pesticide Common Names - Herbicides, Alan Wood.net. Consulté le 5 mars 2011.
- Portail de l’agriculture et l’agronomie
- Portail de la chimie
Catégories :- Substance active de produit phytosanitaire
- Herbicide
- Imidazolinone
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.