BINAP
- BINAP
-
| BINAP |
 |
| Général |
| Nom IUPAC |
2,2'-bis(diphénylphosphino)-1,1'-binaphthyle |
| No CAS |
98327-87-8 |
| InChI |
InChIKey :
MUALRAIOVNYAIW-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
| Apparence |
solide blanc |
| Propriétés chimiques |
| Formule brute |
C44H32P2 [Isomères]
|
| Masse molaire[1] |
622,6724 ± 0,0374 g·mol-1
C 84,87 %, H 5,18 %, P 9,95 %,
|
| Propriétés physiques |
| T° fusion |
278 à 282 °C [2]
239-241 °C (R)[3]
189-193 °C (S)[4] |
| Propriétés optiques |
| Pouvoir rotatoire |
 143,7 ° (chloroforme,0,015 g·l-1) (R)[5] 143,7 ° (chloroforme,0,015 g·l-1) (R)[5]
 -139,1 ° (chloroforme,0,015 g·l-1) (S)[5] -139,1 ° (chloroforme,0,015 g·l-1) (S)[5] |
|
Unités du SI & CNTP, sauf indication contraire.
|
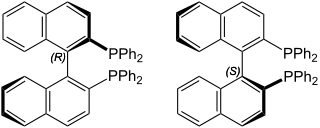
BINAP est l'abréviation nommant le composé organophosphoré 2,2'-bis(diphénylphosphino)-1,1'-binaphthyle. Il s'agit d'un ligand chiral largement utilisé en synthèse organique.
Propriétés physico-chimiques
La molécule possède un carbone asymétrique et 2 stéréoisomères sont possibles:
-
- (R)-(+)-2,2'-bis(diphénylphosphino)-1,1'-binaphthyle, numéro CAS 76189-55-4
- (S)-(–)-2,2'-bis(diphénylphosphino)-1,1'-binaphthyle, numéro CAS 76189-56-5
Notes et références
- ↑ Masse molaire calculée d’après Atomic weights of the elements 2007 sur www.chem.qmul.ac.uk.
- ↑ (en) Carl A. Busacca, « Reduction of Tertiary Phosphine Oxides with DIBAL-H », dans The Journal of Organic Chemistry, vol. 73, no 4, 2008, p. 1524-1531 [lien DOI (page consultée le 10 janvier 2011)]
- ↑ (R)-BINAP sur Sigma-Aldrich
- ↑ (S)-BINAP sur Sigma-Aldrich
- ↑ a et b (en) Christian Müller, « Self-Assembly, Chiroptical Properties, and Host−Guest Chemistry of Chiral Pt−Pt and Pt−Pd Tetranuclear Macrocycles. Circular Dichroism Studies on Neutral Guest Inclusion Phenomena », dans Journal of the American Chemical Society, vol. 120, no 38, 1998, p. 9827-9837 [lien DOI (page consultée le 10 janvier 2011)]
Wikimedia Foundation.
2010.
Contenu soumis à la licence CC-BY-SA. Source : Article BINAP de Wikipédia en français (auteurs)
Regardez d'autres dictionnaires:
BINAP — IUPAC name 2,2 bis(diphenylphosphino) 1,1 binaphthyl … Wikipedia
BINAP — Strukturformel (R) BINAP (links) und (S) BINAP (rechts) All … Deutsch Wikipedia
Ryoji Noyori — Infobox Scientist name = Ryoji Noyori image size = 180px birth date = birth date and age|1938|09|03|df=yes birth place = Kobe, Japan nationality = Japan field = Chemistry work institutions = alma mater = doctoral advisor = doctoral students =… … Wikipedia
Ryōji Noyori — Born 3 September 1938 (1938 09 03) (age 73) Kobe, Japan … Wikipedia
Asymmetric synthesis — Asymmetric synthesis, also called chiral synthesis, enantioselective synthesis or stereoselective synthesis, is organic synthesis which introduces one or more new and desired elements of chirality. [GoldBookRef|title=asymmetric synthesis| file =… … Wikipedia
Noyori asymmetric hydrogenation — The Noyori asymmetric hydrogenation is a chemical reaction described as an asymmetric reduction of β keto esters.[1][2] … Wikipedia
Achiral — In der Chemie bezeichnet die Chiralität (griechisches Kunstwort, die Händigkeit, abgeleitet vom Wortstamm χειρ , ch[e]ir hand ), in der Kristallographie auch Enantiomorphie genannt, die räumliche Anordnung von Atomen, bei denen bestimmte… … Deutsch Wikipedia
Achiralität — In der Chemie bezeichnet die Chiralität (griechisches Kunstwort, die Händigkeit, abgeleitet vom Wortstamm χειρ , ch[e]ir hand ), in der Kristallographie auch Enantiomorphie genannt, die räumliche Anordnung von Atomen, bei denen bestimmte… … Deutsch Wikipedia
Axialchiralität — In der Chemie bezeichnet die Chiralität (griechisches Kunstwort, die Händigkeit, abgeleitet vom Wortstamm χειρ , ch[e]ir hand ), in der Kristallographie auch Enantiomorphie genannt, die räumliche Anordnung von Atomen, bei denen bestimmte… … Deutsch Wikipedia
Chiral — In der Chemie bezeichnet die Chiralität (griechisches Kunstwort, die Händigkeit, abgeleitet vom Wortstamm χειρ , ch[e]ir hand ), in der Kristallographie auch Enantiomorphie genannt, die räumliche Anordnung von Atomen, bei denen bestimmte… … Deutsch Wikipedia

 143,7 ° (chloroforme,0,015 g·l-1) (R)[5]
143,7 ° (chloroforme,0,015 g·l-1) (R)[5] -139,1 ° (chloroforme,0,015 g·l-1) (S)[5]
-139,1 ° (chloroforme,0,015 g·l-1) (S)[5]