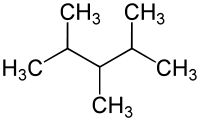
2,3,4-triméthylpentane
- 2,3,4-triméthylpentane
-
| 2,3,4-triméthylpentane |
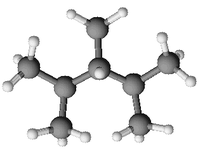 |
| Représentations du 2,3,4-triméthylpentane |
| Général |
| Nom IUPAC |
2,3,4-triméthylpentane |
| No CAS |
565-75-3 |
| No EINECS |
209-292-6 |
| Apparence |
Liquide |
| Propriétés chimiques |
| Formule brute |
C8H18 [Isomères]
|
| Masse molaire[1] |
114,2285 ± 0,0077 g·mol-1
C 84,12 %, H 15,88 %,
|
| Propriétés physiques |
| T° fusion |
-109,35 °C |
| T° ébullition |
113,47 °C [2] |
| Point critique |
2 730 kPa [3], 293,26 °C [2] |
| Point triple |
-109,52 °C |
| Thermochimie |
| S0gaz, 1 bar |
427,2 J·K-1·mol-1 |
| S0liquide, 1 bar |
329,32 J·K-1·mol-1 |
| ΔfH0gaz |
-217,4 kJ·mol-1 |
| ΔfH0liquide |
-255,2 kJ·mol-1 |
| ΔfusH° |
9,27 kJ·mol-1 |
| ΔvapH° |
32,36 kJ·mol-1 |
| Cp |
équation[4] : 
Capacité thermique du gaz en J·mol-1·K-1 et température en kelvins, de 200 à 1 500 K.
Valeurs calculées :
190,764 J·mol-1·K-1 à 25 °C.
T
(K) |
T
(°C) |
Cp
 |
Cp
 |
| 200 |
-73,15 |
124 618 |
1 091 |
| 286 |
12,85 |
183 209 |
1 604 |
| 330 |
56,85 |
209 792 |
1 837 |
| 373 |
99,85 |
233 797 |
2 047 |
| 416 |
142,85 |
256 023 |
2 241 |
| 460 |
186,85 |
277 089 |
2 426 |
| 503 |
229,85 |
296 190 |
2 593 |
| 546 |
272,85 |
313 961 |
2 749 |
| 590 |
316,85 |
330 903 |
2 897 |
| 633 |
359,85 |
346 368 |
3 032 |
| 676 |
402,85 |
360 863 |
3 159 |
| 720 |
446,85 |
374 794 |
3 281 |
| 763 |
489,85 |
387 617 |
3 393 |
| 806 |
532,85 |
399 739 |
3 499 |
| 850 |
576,85 |
411 487 |
3 602 |
|
T
(K) |
T
(°C) |
Cp
 |
Cp
 |
| 893 |
619,85 |
422 388 |
3 698 |
| 936 |
662,85 |
432 764 |
3 789 |
| 980 |
706,85 |
442 878 |
3 877 |
| 1 023 |
749,85 |
452 299 |
3 960 |
| 1 066 |
792,85 |
461 281 |
4 038 |
| 1 110 |
836,85 |
470 026 |
4 115 |
| 1 153 |
879,85 |
478 135 |
4 186 |
| 1 196 |
922,85 |
485 800 |
4 253 |
| 1 240 |
966,85 |
493 161 |
4 317 |
| 1 283 |
1 009,85 |
499 851 |
4 376 |
| 1 326 |
1 052,85 |
506 000 |
4 430 |
| 1 370 |
1 096,85 |
511 679 |
4 479 |
| 1 413 |
1 139,85 |
516 566 |
4 522 |
| 1 456 |
1 182,85 |
520 725 |
4 559 |
| 1 500 |
1 226,85 |
524 142 |
4 589 |
|
|
| Précautions |
|
Directive 67/548/EEC
|
|
|
Numéro index :
601-009-00-8
Classification :
F; R11 - Xn; R65 - Xi; R38 - R67 - N; R50- 53
Symboles :
Xn : Nocif
F : Facilement inflammable
N : Dangereux pour l’environnement
Phrases R :
R11 : Facilement inflammable.
R38 : Irritant pour la peau.
R65 : Nocif : peut provoquer une atteinte des poumons en cas d’ ingestion.
R67 : L’ inhalation de vapeurs peut provoquer somnolence et vertiges.
R50/53 : Très toxique pour les organismes aquatiques, peut entraîner des effets néfastes à long terme pour l’ environnement aquatique.
Phrases S :
S2 : Conserver hors de portée des enfants.
S9 : Conserver le récipient dans un endroit bien ventilé.
S16 : Conserver à l’ écart de toute flamme ou source d’ étincelles - Ne pas fumer.
S29 : Ne pas jeter les résidus à l’ égout.
S33 : Éviter l’ accumulation de charges électrostatiques.
S60 : Éliminer le produit et son récipient comme un déchet dangereux.
S61 : Éviter le rejet dans l’ environnement. Consulter les instructions spéciales/ la fiche de données de sécurité.
S62 : En cas d’ ingestion, ne pas faire vomir. Consulter immédiatement un médecin et lui montrer l’ emballage ou l’ étiquette.
|
| Phrases R : 11, 38, 50/53, 65, 67, |
| Phrases S : 2, 9, 16, 29, 33, 60, 61, 62, |
|
Transport
|
Code Kemler :
33 : matière liquide très inflammable ( point d' éclair inférieur à 21° C)
Numéro ONU :
1262 : OCTANES
Classe :
3
Étiquette :
 3 : Liquides inflammables
3 : Liquides inflammables
|
|
Unités du SI & CNTP, sauf indication contraire.
|
Le 2,3,4-triméthylpentane, de la famille des hydrocarbures et de formule brute C8H18. C'est un des isomères de l'octane. C'est un liquide très inflammable
Notes et références
- ↑ Masse molaire calculée d’après Atomic weights of the elements 2007 sur www.chem.qmul.ac.uk.
- ↑ a et b (en) Iwona Owczarek et Krystyna Blazej, « Recommended Critical Temperatures. Part I. Aliphatic Hydrocarbons », dans J. Phys. Chem. Ref. Data, vol. 32, no 4, 4 août 2003, p. 1411 [lien DOI]
- ↑ (en) Iwona Owczarek et Krystyna Blazej, « Recommended Critical Pressures. Part I. Aliphatic Hydrocarbons », dans J. Phys. Chem. Ref. Data, vol. 35, no 4, 18 septembre 2006, p. 1461 [lien DOI]
- ↑ (en) Carl L. Yaws, Handbook of Thermodynamic Diagrams, vol. 3, Huston, Texas, Gulf Pub. Co. (ISBN 0-88415-859-4)
Catégories : - Produit chimique nocif
- Produit chimique facilement inflammable
- Produit chimique dangereux pour l'environnement
- Alcane ramifié
- Isomère de l'octane
Wikimedia Foundation.
2010.
Contenu soumis à la licence CC-BY-SA. Source : Article 2,3,4-triméthylpentane de Wikipédia en français (auteurs)
Regardez d'autres dictionnaires:
trimethylpentane — noun Any of several isomers of octane having three methyl groups attached to a pentane chain; but especially to isooctane, used as a standard for octane number … Wiktionary
2,2,3-triméthylpentane — Représentations du 2 … Wikipédia en Français
2,2,4-Trimethylpentane — Chembox new Name = 2,2,4 Trimethylpentane ImageFile1=2,2,4 Trimethylpentane.svg ImageName1=Skeletal formula of 2,2,4 trimethylpentane ImageFile2 = Isooctane 3D balls.png ImageName2 = 2,2,4 Trimethylpentane IUPACName = 2,2,4 Trimethylpentane… … Wikipedia
2,3,3-triméthylpentane — Général … Wikipédia en Français
2,2,4-triméthylpentane — Isooctane Isooctane Général Nom IUPAC … Wikipédia en Français
2.2.4-triméthylpentane — Isooctane Isooctane Général Nom IUPAC … Wikipédia en Français
564-02-3 — 2,2,3 triméthylpentane 2,2,3 triméthylpentane Représentations du 2,2,3 triméthylpentane … Wikipédia en Français
560-21-4 — 2,3,3 triméthylpentane 2,3,3 triméthylpentane Génér … Wikipédia en Français
565-75-3 — 2,3,4 triméthylpentane 2,3,4 triméthylpentane Représentations du 2,3,4 triméthylpentane … Wikipédia en Français
Liste D'hydrocarbures Saturés Acycliques — Voici une compilation d’hydrocarbures saturés linéaires et quelques unes de leurs propriétés. Il s agit ici des alcanes et de leurs isomères ramifiés. Lecture du tableau PM : masse molaire moléculaire Tf : température de fusion en… … Wikipédia en Français









