- C16H25NO
-
Alpha sanshool
Alpha sanshool 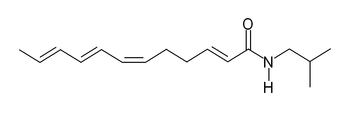
Général Nom IUPAC (2Z,6E,8E,10E)-N-
(2-methylpropyl)dodeca-
2,6,8,10-tetraenamideNo CAS PubChem SMILES Propriétés chimiques Formule brute C16H25NO [Isomères] Masse molaire 247,3758 g∙mol-1
C 77,68 %, H 10,19 %, N 5,66 %, O 6,47 %,Composés apparentés Autres composés alpha hydroxy sanshool Unités du SI & CNTP, sauf indication contraire. L’alpha sanshool est un amide à la saveur unique qui est à la fois irritante (pseudo-chaleur) comme le piment mais qui picote aussi (paresthésie)[1].
Origine
Elle a été identifié dans le poivre du Sichuan (Zanthoxylum piperitum) et définie, avec l’alpha hydroxy sanshool, comme étant la source principale de son goût caractéristique[1],[2].
Goût
Le pouvoir irritant de l'alpha sanshool, sur l'échelle de Scoville, est situé entre celui de la pipérine et celui du [6]-gingerol[2].
-
Composés Échelle de Scoville
(Unité SHU)Capsaïcine 16 000 000[3] [6]-Shogaol 160 000[4],[5] Pipérine 100 000[4],[5] Alpha sanshool 80,000-110,000[2] [6]-gingerol 60 000 [4],[5] Alpha hydroxy sanshool 16,000-22,000[2]
Notes et références de l'article
- ↑ a et b (en) [pdf] E Sugai, Y Morimitsu and K Kubota (2005) Quantitative Analysis of Sanshool Compounds in Japanese Pepper (Xanthoxylum piperitum DC.) and Their Pungent Characteristics Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem., Vol. 69, 1958-1962 DOI:10.1271/bbb.69.1958
- ↑ a , b , c et d (en) E Sugai, Y Morimitsu, Y Iwasaki, A Morita, T Wanatabe and K Kubota (2005) Pungent qualities of sanshool-related compounds evaluated by a sensory test and activation of rat TRPV1. Bioscience, biotechnology, and biochemistry, vol. 69, no10, pp. 1951-1957. DOI:10.1271/bbb.69.1951
- ↑ MA Cliff and H Heymann (1992) Time–intensity evaluation of oral burn. J. Sens. Stud., 8, 201–211. DOI:10.1111/j.1745-459X.1992.tb00195.x
- ↑ a , b et c (en) S Narasimhan and VS Govindarajan (1978) Evaluation of spices and oleoresin-VI-pungency of ginger components, gingerols and shogoals and quality. International Journal of Food Science & Technology 13 (1), 1–36. DOI:10.1111/j.1365-2621.1978.tb00773.x
- ↑ a , b et c (en) VS Govindarajan, S Narasimhan, B Rajalakshmi and D Rajalakshmi (1980) Evaluation of spices and oleoresins - Correlation of pungency stimuli and pungency in ginger.Zeitschrift für Lebensmitteluntersuchung und -Forschung A, Volume 170(3), p200-203 DOI:10.1007/BF01042540
Voir aussi
Articles connexes
Liens et documents externes
- (en) Alkyldienamides exhibiting taste and sensory effect in flavor compositions United States Patent 7361376
- Portail de la chimie
- Portail de l’alimentation et de la gastronomie
Catégories : Goût piquant | Amide | Alcène -
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
