- Adonirubine
-
Adonirubine 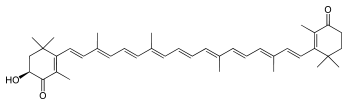
Général Nom IUPAC (6S)-6-hydroxy-2,4,4-triméthyl-3-[(1E,3E,5E,7E,9E,11E,13E,15E,17E)-3,7,12,16-tétraméthyl-18-(2,6,6-triméthyl-3-oxo-1-cyclohexényl)octadéca-1,3,5,7,9,11,13,15,17-nonaényl]cyclohex-2-én-1-one Synonymes 3-hydroxy-β,β-carotène-4,4'-dione
3-hydroxycanthaxanthineNo CAS PubChem SMILES InChI Propriétés chimiques Formule brute C40H52O3 [Isomères] Masse molaire[1] 580,8391 ± 0,0365 g·mol-1
C 82,71 %, H 9,02 %, O 8,26 %,Propriétés physiques T° fusion 214 à 216 °C [2] Unités du SI & CNTP, sauf indication contraire. L'adonirubine ou phoénicoxanthine est un composé de la famille des caroténoïdes. C'est un précurseur pour la formation de l'astaxanthine[3].
Notes et références
- Masse molaire calculée d’après Atomic weights of the elements 2007 sur www.chem.qmul.ac.uk.
- (de) K. Bernhard, G. Englert, H. Mayer, R. K. Müller, A. Rüttimann, M. Vecchi, E. Widmer et R. Zell, « Synthese von optisch aktiven, natürlichen Carotinoiden und strukturell verwandten Naturprodukten. IX. Synthese von (3R)-Hydroxyechinenon, (3R,3'R)- und (3R,3'S)-Adonixanthin, (3R)-Adonirubin, deren optischen Antipoden und verwandten Verbindungen », dans Helv. Chim. Acta, vol. 41, no 7, 4 novembre 1981, p. 407-2484 (ISSN 0018-019X) [lien DOI (page consultée le 23 mai 2011)]
- (en) B.-H. Liu et Y.-K. Lee, « Composition and biosynthetic pathways of carotenoids in the astaxanthin-producing green alga Chlorococcum sp. », dans Biotechnol. Lett., vol. 21, no 11, 1999, p. 1007-1010 (ISSN 0141-5492) [lien DOI (page consultée le 23 mai 2011)]
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
