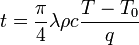Température d'autoignition
- Température d'autoignition
-
Point d’auto-inflammation
Le point d’auto-inflammation (ou d’auto-ignition) est la température à partir de laquelle un gaz ou une vapeur s’enflamme spontanément en l’absence de flamme pilote. On peut aussi dire (point d’allumage spontané) et en anglais on dit self-ignition point ou Spontaneous combustion.
À ne pas confondre avec le point d’inflammation qui est la température pour laquelle la combustion une fois amorcée peut continuer, et avec le point d’éclair qui est la température pour laquelle un liquide produit suffisamment de vapeurs pour qu’elles s’enflamment momentanément en présence d’une source d’énergie calorifique conventionnelle.
Quelques points d'auto-inflammation
Équation
Le temps  nécessaire à une substance exposée à une densité de flux thermique
nécessaire à une substance exposée à une densité de flux thermique  pour atteindre son point d’auto-inflammation
pour atteindre son point d’auto-inflammation  est donné par l’équation[1] :
est donné par l’équation[1] :
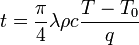
avec
Anecdote
L’écrivain Ray Bradbury a nommé son livre Fahrenheit 451 d’après le point d’auto-inflammation du papier, en référence au travail des « pompiers » de son histoire, qui ont pour devoir de brûler les livres.
Référence
- ↑ Principles of Fire Behavior, 1998, (ISBN 0-8273-7732-0).
Voir aussi
Articles connexes
 Portail de la chimie
Portail de la chimie
Catégories : Feu | Réaction chimique | Propriété chimique
Wikimedia Foundation.
2010.
Contenu soumis à la licence CC-BY-SA. Source : Article Température d'autoignition de Wikipédia en français (auteurs)
Regardez d'autres dictionnaires:
Autoignition temperature — The autoignition temperature or kindling point of a substance is the lowest temperature at which it will spontaneously ignite in a normal atmosphere without an external source of ignition, such as a flame or spark. This temperature is required to … Wikipedia
autoignition point — Chem. the minimum temperature at which a substance will undergo spontaneous combustion. Also called ignition point, ignition temperature. * * * … Universalium
autoignition point — Chem. the minimum temperature at which a substance will undergo spontaneous combustion. Also called ignition point, ignition temperature … Useful english dictionary
Engine knocking — Pinging redirects here. For other uses, see Ping (disambiguation). Knocking (also called knock, detonation, spark knock, pinging or pinking) in spark ignition internal combustion engines occurs when combustion of the air/fuel mixture in the… … Wikipedia
Homogeneous charge compression ignition — Thermodynamics … Wikipedia
Flash point — The flash point of a flammable liquid is the lowest temperature at which it can form an ignitable mixture in air. At this temperature the vapor may cease to burn when the source of ignition is removed. A slightly higher temperature, the fire… … Wikipedia
Ammonia — For other uses, see Ammonia (disambiguation). Ammonia … Wikipedia
Diethyl ether — Diethyl ether … Wikipedia
Homogeneous Charge Compression Ignition — Homogeneous Charge Compression Ignition, or HCCI, is a form of internal combustion in which well mixed fuel and oxidizer (typically air) are compressed to the point of auto ignition. As in other forms of combustion, this exothermic reaction… … Wikipedia
Oxyhydrogen — Knallgas redirects here. For bacteria which oxidize hydrogen, see Knallgas bacteria. Nineteenth century electrolytic cell for producing oxyhydrogen. Oxyhydrogen is a mixture of hydrogen (H2) and oxygen (O2) gases, typically in a 2:1 molar ratio,… … Wikipedia
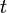 nécessaire à une substance exposée à une densité de flux thermique
nécessaire à une substance exposée à une densité de flux thermique 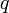 pour atteindre son point d’auto-inflammation
pour atteindre son point d’auto-inflammation 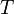 est donné par l’équation[1] :
est donné par l’équation[1] :