C13H14N2O
- C13H14N2O
-
Harmaline
| Harmaline |
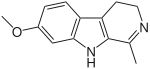 |
| Structure du harmaline |
| Général |
| Nom IUPAC |
7-méthoxy-1-méthyl-4,9-dihydro-3H-β-carboline |
| No CAS |
304-21-2 |
| No EINECS |
206-152-6 |
| SMILES |
|
| InChI |
InChI=1/C13H14N2O/c1-8-13-11(5-6-14-8)10-4-3-9(16-2)7-12(10)15-13/h3-4,7,15H,5-6H2,1-2H3
|
| Propriétés chimiques |
| Formule brute |
C13H14N2O [Isomères]
|
| Masse molaire |
214,2631 g∙mol-1
C 72,87 %, H 6,59 %, N 13,07 %, O 7,47 %,
|
|
Unités du SI & CNTP, sauf indication contraire.
|
L'harmaline au même titre que l'harmine est un alcaloïde végétal du groupe des harmanes. Il provient notamment des plantes du genre banisteriopsis et possède des propriétés d'antagonistes sérotoninergiques[1]. Combiné à la diméthyltryptamine d'autres plantes, il confère à l'ayahuasca sa propriété hallucinogène.
L'harmaline est également le principal alcaloïde du Peganum harmala une plante de la famille des Zygophyllaceae. C'est à partir de cette espèce qu'il fut isolé en 1841.
Pharmacologie
L'harmaline est un IMAO (inhibiteur des monoamine oxydases) légèrement psychodysleptique et analgésique.
Notes et références de l'article
- ↑ Denis Richards Dictionnaire des drogues des toxicomanies et des dépendances, 1999
Voir aussi
Articles connexes
 Portail de la chimie
Portail de la chimie Portail de la pharmacie
Portail de la pharmacie
Catégories : Alcaloïde | Dérivé hallucinogène de la tryptamine | Dihydroazine | Composé indolé
Wikimedia Foundation.
2010.
Contenu soumis à la licence CC-BY-SA. Source : Article C13H14N2O de Wikipédia en français (auteurs)
Regardez d'autres dictionnaires:
304-21-2 — Harmaline Harmaline Structure du harmaline Général Nom IUPAC 7 méthoxy 1 méthyl 4,9 dihydro 3H β carboline … Wikipédia en Français
Harmaline — Structure du harmaline Général Nom IUPAC 7 méthoxy 1 méthyl 4,9 dihydro 3H β carboline … Wikipédia en Français
Harmala alkaloid — Peganum harmala, commonly known as Syrian Rue Several alkaloids that function as monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) are found in the seeds of Peganum harmala (also known as Harmal or Syrian Rue), including harmine, harmaline, and harmalol,… … Wikipedia
Harmaline — Chembox new Name = Harmaline ImageFile = Harmaline.png ImageName = Harmaline IUPACName = 7 methoxy 1 methyl 3,4 dihydro 2H pyrido [3,4 b] indole [http://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/summary/summary.cgi?cid=5280951 PubChem] ] Section1 = Chembox… … Wikipedia
Moly (herb) — Moly (Greek: μῶλυ) is a magic herb mentioned in book 10 of Homer s Odyssey.[1] In the story, Hermes gave this herb to Odysseus to protect him from Circe s magic when he went to her home to rescue his friends.[2] These friends came together with… … Wikipedia
Harmalin — Strukturformel Allgemeines Name Harmalin Andere Namen 4,9 … Deutsch Wikipedia
Liste des composés organiques C13 — Liste des composés organiques C C2 C3 C4 C5 C6 C7 C8 C9 C10 C11 C12 C13 C14 C15 C16 C17 C18 C19 C2 … Wikipédia en Français
Гармалин — Гармалин … Википедия
Хармин — Химическое соединение ИЮПАК 4,9 дигидро 7 метокси 1 метил 3H пиридо[3,4 b]индол … Википедия
harmaline — An amine oxidase inhibitor and a central nervous system stimulant; obtained from the seeds of Peganum harmala (family Zygophyllaceae) and from Banisteria caapi (family Malpighiaceae); has been used in parkinsonism. SYN: harmidine. * * *… … Medical dictionary

