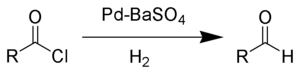Réduction de Rosenmund
- Réduction de Rosenmund
-
La réduction de Rosenmund est une réaction chimique dans laquelle un chlorure d'acyle est réduit par du dihydrogène en l'aldéhyde correspondant. Cette réaction porte le nom de Karl Wilhelm Rosenmund qui l'a découverte en 1918[1].
Formellement, cette réaction revient à une hydrogénolyse de la liaison C-Cl. Pour éviter la sur-réduction, il est a priori nécessaire d'empoisonner le catalyseur, ce qui peut être réaliser avec une amine tertiaire, qui éliminera également l'acide chlorhydrique formé[2].
Alternatives
L'action de certains hydrures est généralement préférée en laboratoire à cette réaction[1].
La synthèse des aldéhydes de Grundmann est une alternative à la réduction de Grundmann, mais reste très peu utilisée.
Notes et références
- ↑ a et b Jacques Drouin, Introduction à la chimie organique : Les molécules organiques dans votre environnement. Usages, toxicité, synthèse et réactivité, vol. 2005, Librairie du Cèdre, 1re éd. (ISBN 2-916346-00-7), p. 703
- ↑ (en) Jonathan Clayden, Nick Greeves, Stuart Warren et Peter Wothers, Organic chemistry, Oxford university press (ISBN 0-19-850346-6), p. 623
Catégorie : - Réaction d'oxydo-réduction organique
Wikimedia Foundation.
2010.
Contenu soumis à la licence CC-BY-SA. Source : Article Réduction de Rosenmund de Wikipédia en français (auteurs)
Regardez d'autres dictionnaires:
Rosenmund reduction — The Rosenmund reduction is a chemical reaction that reduces an acid halide to an aldehyde using hydrogen gas over palladium on carbon poisoned with barium sulfate. [cite journal author = Rosenmund, K. W. title = Über eine neue Methode zur… … Wikipedia
Rosenmund-Reaktion — Die Rosenmund Reduktion ist eine Namensreaktion in der Organischen Chemie, die nach dem deutschen Chemiker Karl Wilhelm Rosenmund benannt ist. Inhaltsverzeichnis 1 Reaktion 2 Nebenreaktionen 3 Literatur 4 Quellen … Deutsch Wikipedia
Rosenmund-Reduktion — Die Rosenmund Reduktion ist eine Namensreaktion in der Organischen Chemie, die nach dem deutschen Chemiker Karl Wilhelm Rosenmund benannt ist. Inhaltsverzeichnis 1 Reaktion 2 Nebenreaktionen 3 Literatur 4 … Deutsch Wikipedia
Karl Wilhelm Rosenmund — Infobox Scientist name = Karl Wilhelm Rosenmund image width = caption = Karl Wilhelm Rosenmund birth date = birth date|1884|12|15 birth place = Berlin, Germany residence = nationality = death date = death date and age|1965|2|8|1884|12|15 death… … Wikipedia
List of organic reactions — Well known reactions and reagents in organic chemistry include Contents: A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z See also Ext … Wikipedia
Organic redox reaction — Organic redox reactions: The Birch reduction Organic reductions or organic oxidations or organic redox reactions are redox reactions that take place with organic compounds. In organic chemistry oxidations and reductions are different from… … Wikipedia
CARBONYLÉS (DÉRIVÉS) — Le terme d’alcool déshydrogéné, dit par contraction aldéhyde , a tout d’abord été employé pour nommer un liquide très volatil et d’une odeur pénétrante provenant de l’oxydation ménagée de l’alcool éthylique et se différenciant de celui ci par un… … Encyclopédie Universelle
Aldehyde — An aldehyde. Formaldehyde, the simplest aldehyde … Wikipedia
Именные реакции в органической химии — В органической химии существует огромное число реакций, носящих имя исследователя, открывшего или исследовавшего данную реакцию. Часто в названии реакции фигурируют имена нескольких ученых: это могут быть авторы первой публикации (например,… … Википедия
Nitrile — This article is about the group of organic compounds. For the synthetic rubber product, see Nitrile rubber. The structure of the nitrile group A nitrile is any organic compound that has a C≡N functional group.[1] … Wikipedia