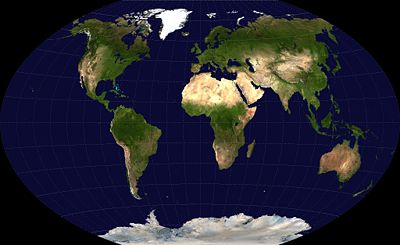
- Projection de Winkel-Tripel
-
La Projection de Winkel-Tripel est une projection cartographique créée par Oswald Winkel en 1921. Elle est définie comme la moyenne arithmétique de la projection cylindrique équidistante et de la projection d'Aitoff. Cette projection a été construite pour minimiser, pour une représentation complète du globe, les distorsions de surface, de direction et de distance, ce à quoi fait référence le terme allemand Tripel.
Sommaire
Expression
avec λ la différence de longitude avec le méridien central, ϕ la latitude, sinc le sinus cardinal non normalisé et régularisé en 0, ϕ1 la constante associée à la projection cylindrique équidistante, et
La transformation inverse ne peut pas être exprimée par une formule mathématique, et doit être calculée numériquement.
Caractéristiques
La projection de Winkel-Tripel n'est ni conforme, ni équivalente. Elle est un compromis entre les distorsions observées sur d'autres projections, et offre de manière générale peu de déformations. Elle est en fait la meilleure projection pour représenter l'intégralité du globe terrestre[1].
Utilisations
Depuis 1998, elle est utilisée par la National Geographic Society pour la réalisation des cartes mondiales.
Voir aussi
Références
- Flexion and Skewness in Map Projections of the Earth, 2007, David M. Goldberg & J. Richard Gott III, Cartographica, 2007, 42(4):297-318.
Liens externes
- Winkel Tripel projection (Denis J. Dean, Université du Colorado)
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.