5-méthylcytosine
- 5-méthylcytosine
-
| 5-méthylcytosine |
 |
| Général |
| Nom IUPAC |
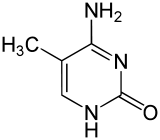
4-amino-5-méthylpyrimidin-2(1H)-one |
| No CAS |
554-01-8 |
| PubChem |
65040 |
| SMILES |
|
| InChI |
InChI : Vue 3D
InChI=1/C5H7N3O/c1-3-2-7-5(9)8-4(3)6/h2H,1H3,(H3,6,7,8,9)
|
| Propriétés chimiques |
| Formule brute |
C5H7N3O
|
| Masse molaire[1] |
125,1286 ± 0,0054 g·mol-1
C 47,99 %, H 5,64 %, N 33,58 %, O 12,79 %,
|
|
Unités du SI & CNTP, sauf indication contraire.
|
La 5-méthylcytosine est une forme méthylée de la cytosine, sur laquelle un groupement méthyle est attaché au carbone 5. Ceci altère sa structure sans cependant altérer ses propriétés de complémentarité des bases.
Notes et références
Wikimedia Foundation.
2010.
Contenu soumis à la licence CC-BY-SA. Source : Article 5-méthylcytosine de Wikipédia en français (auteurs)
Regardez d'autres dictionnaires:
methylcytosine — noun Any methyl derivative of cytosine, but especially 5 methylcytosine formed by methylation of DNA … Wiktionary
methylcytosine — meth·yl·cyt·o·sine .meth əl sīt ə .sēn n a methylated pyrimidine base C5H7N3O found in the nucleic acids (as some DNAs and transfer RNAs) of some organisms * * * meth·yl·cy·to·sine (meth″əl siґto sēn) a pyrimidine occurring in… … Medical dictionary
5-Methylcytosine — IUPAC name 4 amino 5 methyl 3H pyrimidin 2 one … Wikipedia
5-methylcytosine — A minor base that is present in both bacterial and human DNA … Medical dictionary
nucleic acid — /nooh klee ik, klay , nyooh /, Biochem. any of a group of long, linear macromolecules, either DNA or various types of RNA, that carry genetic information directing all cellular functions: composed of linked nucleotides. [1890 95; NUCLE(US) + IC;… … Universalium
DNA — For a non technical introduction to the topic, see Introduction to genetics. For other uses, see DNA (disambiguation). The structure of the DNA double helix. The atoms in the structure are colour coded by element and the detailed structure of two … Wikipedia
Epigenetics — In biology, the term epigenetics refers to changes in gene expression caused by mechanisms other than changes in the underlying DNA sequence. These changes may remain through cell divisions for the remainder of the cell s life and may also last… … Wikipedia
DNA demethylation — is a process of removal of methyl group from nucleotide in DNA. DNA demethylation could be passive and active. Passive process takes place in the absence of methylation of newly synthesised DNA strands by DNMT1 during several replication rounds… … Wikipedia
Deamination — is the removal of an amine group from a molecule. Enzymes which catalyse this reaction are called deaminases. In the human body, deamination takes place primarily in the liver, however glutamate is also deaminated in the kidneys. Deamination is… … Wikipedia
DNA methyltransferase — N 6 DNA Methylase crystal structure of type i restriction enzyme ecoki m protein (ec 2.1.1.72) (m.ecoki) Identifiers Symbol N6 Mtase Pfam … Wikipedia

