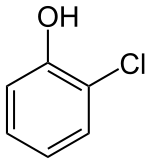
2-Chlorophénol
- 2-Chlorophénol
-
2-chlorophénol
| 2-chlorophénol |
 |
| Général |
| Nom IUPAC |
2-chlorophénol |
| Synonymes |
2-hydroxychlorobenzène
o-chlorophénol |
| No CAS |
95-57-8 |
| No EINECS |
202-433-2 |
| PubChem |
7245 |
| SMILES |
|
| InChI |
InChI=1S/C6H5ClO/c7-5-3-1-2-4-6(5)8/h1-4,8H
|
| Apparence |
liquide incolore, d'odeur caractéristique[1]. |
| Propriétés chimiques |
| Formule brute |
C6H5ClO [Isomères]
|
| Masse molaire |
128,556 g∙mol-1
C 56,06 %, H 3,92 %, Cl 27,58 %, O 12,45 %,
|
| pKa |
8,56[2] |
| Propriétés physiques |
| T° fusion |
9,8 °C[3]. |
| T° ébullition |
174 °C[4] |
| Solubilité |
28,5 g∙l-1 (eau, 20 °C)[4] |
| Masse volumique |
1,2573 g∙cm-3 à 25 °C[5]. |
| T° d’auto-inflammation |
550 °C[4] |
| Point d’éclair |
85 °C[4] |
| Pression de vapeur saturante |
1,32 mbar à 12 °C
2,3 mbar à 20 °C
4,0 mbar à 30 °C
15,0 mbar à 50 °C[4] |
| Thermochimie |
| ΔfusH° |
12,523 kJ∙mol-1 à 9,9 °C[3] |
| ΔvapH° |
52,4 kJ∙mol-1 à 24,14 °C[6]. |
| Cp |
188,7 J∙mol-1∙K-1 à 8,9 °C[3] |
| Précautions |
|
Directive 67/548/EEC
|

Xn
|

N
|
|
Numéro index :
604-008-00-0
Classification :
Xn; R20/21/22 - N; R51-53
Symboles :
Xn : Nocif
N : Dangereux pour l`environnement
Phrases R :
R20/21/22 : Nocif par inhalation, par contact avec la peau et par ingestion.
R51/53 : Toxique pour les organismes aquatiques, peut entraîner des effets néfastes à long terme pour l’environnement aquatique.
Phrases S :
(S2) : Conserver hors de portée des enfants.
S28 : Après contact avec la peau, se laver immédiatement et abondamment avec … (produits appropriés à indiquer par le fabricant).
S61 : Éviter le rejet dans l’environnement. Consulter les instructions spéciales/la fiche de données de sécurité.
|
| Phrases R : 20/21/22, 51/53, |
| Phrases S : (2), 28, 61, |
|
Transport
|
Code Kemler :
60 : matière toxique ou présentant un degré mineur de toxicité
Numéro ONU :
2021 : CHLOROPHÉNOLS LIQUIDES
Classe :
6.1
Étiquette :

6.1 : Matières toxiques
Emballage :
Groupe d'emballage III : matières faiblement dangereuses.
|
|
NFPA 704
|
|
|
|
SIMDUT[7]
|
   B3, D1A, D2A, E,
B3, D1A, D2A, E,
B3 : Liquide combustible
point d'éclair = 64 °C coupelle fermée (méthode non rapportée)
D1A : Matière très toxique ayant des effets immédiats graves
létalité aiguë : DL50 orale (rat) = 40 mg/kg
D2A : Matière très toxique ayant d'autres effets toxiques
embryotoxicité chez l'animal
E : Matière corrosive
nécrose de la peau chez l'animal
Divulgation à 0,1% selon les critères de classification
|
|
SGH[8]
|
Attention
H302, H312, H332, H411,
H302 : Nocif en cas d'ingestion
H312 : Nocif par contact cutané
H332 : Nocif par inhalation
H411 : Toxique pour les organismes aquatiques, entraîne des effets à long terme
|
| Écotoxicologie |
| DL50 |
345 mg/kg (souris, oral)
40 mg/kg (rat, oral)[2] |
| LogP |
2.15[1] |
|
Unités du SI & CNTP, sauf indication contraire.
|
Le 2-chlorophénol est un chlorophénol de formule brute C6H5Cl1O1. C'est un polluant des milieux aquatiques et un agent de désinfection.
Propriété physico-chimiques
Ce composé forme des azéotropes avec le toluène, l'acétophénone, le 2-bromotoluène, l'octan-2-ol et l'octan-2-one.
Production et synthèse
La voie de synthèse la plus utilisée est la chloration directe du phénol fondu avec du chlore gazeux[9]. Cette réaction donne des ortho- et para-chlorophénols dans un ratio qui dépend de la température. La formation du 2-chlorophénol est favorisée à haute température et dans un solvant aprotique non-polaire tel l'hexane, le tétrachlorure de carbone ou le dichloroéthane.
Notes et références
- ↑ a et b o - CHLOROPHENOL, fiche de sécurité du Programme International sur la Sécurité des Substances Chimiques, consultée le 9 mai 2009
- ↑ a et b (en) « 2-Chlorophenol » sur ChemIDplus, consulté le 24 février 2009
- ↑ a , b et c 2-Chlorophenol sur http://www.nist.gov/. Consulté le 24 février 2009
- ↑ a , b , c , d et e Entrée de « 2-Chlorophenol » dans la base de données de produits chimiques GESTIS de la BGIA (organisme allemand responsable de la sécurité et de la santé au travail) (allemand, anglais), accès le 24 février 2009 (JavaScript nécessaire)
- ↑ (en) W. F. Anzilotti et B. Columba Curran, « Electric Moments of Ortho-substituted Phenols and Anisoles. I. Halogen Derivatives », dans Journal of the American Society, vol. 65, no 4, avril 1943, p. 607-611 (ISSN 0002-7863)
- ↑ (en) Sergey P. Verevkin, Vladimir N. Emel'yanenko et Andreas Klamt, « Thermochemistry of Chlorobenzenes and Chlorophenols: Ambient Temperature Vapor Pressures and Enthalpies of Phase Transitions », dans Journal of Chemical and Engineering Data, vol. 52, no 2, 30 décembre 2007, p. 499-510 (ISSN 0021-9568)
- ↑ « Chlorophénol (ortho-) » dans la base de données de produits chimiques Reptox de la CSST (organisme canadien responsable de la sécurité et de la santé au travail), consulté le 24 avril 2009
- ↑ Numéro index 604-008-00-0 dans le tableau 3.1 de l'annexe VI du règlement CE N° 1272/2008 (16 décembre 2008)
- ↑ François Muller, Liliane Caillard, Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, Chlorophenols, Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co, 2002
 Portail de la chimie
Portail de la chimie
Catégories : Produit chimique nocif | Produit chimique dangereux pour l'environnement | Produit chimique corrosif | Chlorobenzène | Phénol
Wikimedia Foundation.
2010.
Contenu soumis à la licence CC-BY-SA. Source : Article 2-Chlorophénol de Wikipédia en français (auteurs)
Regardez d'autres dictionnaires:
Chlorophenol — Chlorophénol 2,4 dichlorophénol Les phénols sont halogénés très facilement à sec aux positions ortho et para non occupées dans le cycle benzénique. Le phénol lui même est transformé par le chlore, d abord en un mélange d ortho chlorophénol et de… … Wikipédia en Français
Chlorophenol red — IUPAC name 2 chloro 4 [3 (3 chloro 4 hydroxyphenyl) 1,1 dioxobenzo[c]oxathiol 3 yl]phenol … Wikipedia
Chlorophenol O-methyltransferase — Identifiers EC number 2.1.1.136 Databases IntEnz IntEnz view … Wikipedia
chlorophénol — ● chlorophénol nom masculin Dérivé chloré du phénol, Cl―C6H4―OH … Encyclopédie Universelle
Chlorophénol — Un exemple de chlorophénol : le 2,4 dichlorophénol Un chlorophénol est un isomère d un phénol avec un ou plusieurs atomes de chlore liés au cycle benzénique portant l alcool phénylique. Les phénols sont chlorés très facilement à sec aux… … Wikipédia en Français
Chlorophenol — 2 Chlorophenol A chlorophenol is any organochloride of phenol that contains one or more covalently bonded chlorine atoms. Chlorophenols are produced by electrophilic halogenation of phenol with chlorine. Most chlorophenols have a number of… … Wikipedia
chlorophenol — /klawr euh fee nawl, nol, klohr /, n. Chem. 1. any of three isomers having the formula C6H5ClO, derived from chlorine and phenol, used chiefly as intermediates in the manufacture of dyes. 2. any derivative of phenol of which one or more hydrogen… … Universalium
chlorophenol — chlorfenolis statusas T sritis chemija formulė ClC₆H₄OH atitikmenys: angl. chlorophenol rus. хлорфенол … Chemijos terminų aiškinamasis žodynas
chlorophenol red — Chem. an acid base indicator, C19H12Cl2O5S, that changes color from yellow to red as the acidity of a solution decreases. * * * … Universalium
chlorophenol — noun Any of several chlorinated derivatives of phenol, some of which are used as antiseptics or disinfectants … Wiktionary
chlorophenol — One of several substitution products obtained by the action of chlorine on phenol; used as antiseptics. * * * chlo·ro·phe·nol .klōr ō fē .nōl, .nȯl, .klȯr , fi also chlor·phe·nol ( )klōr , ( )klȯr n any of three derivatives C6H5ClO of phenol… … Medical dictionary










