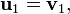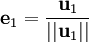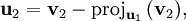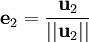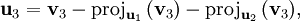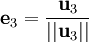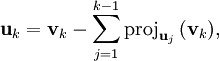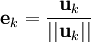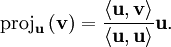Gram-Schmidt
- Gram-Schmidt
-
Procédé de Gram-Schmidt
En algèbre linéaire, dans un espace vectoriel muni d'un produit scalaire, le procédé de Gram-Schmidt[1], en notant ![N= [0,p]\,](/pictures/frwiki/50/2f6bce44984c0ebf193ada154043c3e6.png) ou
ou 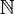 est un algorithme pour construire de proche en proche une base orthonormée à partir d'une base donnée.
est un algorithme pour construire de proche en proche une base orthonormée à partir d'une base donnée.
Précisément :
On oublie souvent la condition d'unicité. Elle permet de parler de l 'orthonormalisée de Gram-Schmidt.
L'étape générale de l'algorithme consiste à soustraire au vecteur vj + 1 sa projection orthogonale sur l'espace Fj. On s'appuie sur la famille orthonormale déjà construite pour le calcul de projection.
Cette méthode a été nommée en hommage à Jørgen Pedersen Gram et Erhard Schmidt, mais elle est plus ancienne et est retrouvée dans des travaux de Laplace et Cauchy.
Applications.
- Le procédé d'orthonormalisation de Gram-Schmidt donne (constructivement !) l'existence de bases orthonormées pour tout espace euclidien ou hermitien.
- On peut aussi orthonormaliser la base canonique (1,X,...)de R[X] et obtenir ainsi une famille de polynômes orthogonaux.
Procédé de Gram-Schmidt
Nous définissons l'opérateur de projection sur une droite vectorielle par :
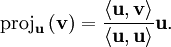
Le procédé de Gram-Schmidt est alors :
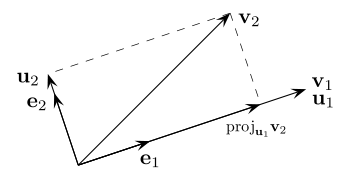
Les deux premières étapes du procédé de Gram–Schmidt.
Notes et références
- ↑ Mathématiques Tout-en-un . 2e année MP, Dunod, 2004, 2e éd. (ISBN 2-10-007576-4), p. 569
 Portail des mathématiques
Portail des mathématiques
Catégories : Algèbre bilinéaire | Algorithme
Wikimedia Foundation.
2010.
Contenu soumis à la licence CC-BY-SA. Source : Article Gram-Schmidt de Wikipédia en français (auteurs)
Regardez d'autres dictionnaires:
Gram-Schmidt — Das Gram Schmidtsche Orthogonalisierungsverfahren ist ein Algorithmus aus dem mathematischen Teilgebiet der linearen Algebra. Er erzeugt zu jedem System linear unabhängiger Vektoren aus einem Prähilbertraum, d. h. einem Vektorraum mit… … Deutsch Wikipedia
Gram Schmidt — Das Gram Schmidtsche Orthogonalisierungsverfahren ist ein Algorithmus aus dem mathematischen Teilgebiet der linearen Algebra. Er erzeugt zu jedem System linear unabhängiger Vektoren aus einem Prähilbertraum, d. h. einem Vektorraum mit… … Deutsch Wikipedia
Gram–Schmidt process — In mathematics, particularly linear algebra and numerical analysis, the Gram–Schmidt process is a method for orthogonalizing a set of vectors in an inner product space, most commonly the Euclidean space R n . The Gram–Schmidt process takes a… … Wikipedia
Gram-Schmidt-Orthogonalisierung — Das Gram Schmidtsche Orthogonalisierungsverfahren ist ein Algorithmus aus dem mathematischen Teilgebiet der linearen Algebra. Er erzeugt zu jedem System linear unabhängiger Vektoren aus einem Prähilbertraum, d. h. einem Vektorraum mit… … Deutsch Wikipedia
Gram-Schmidt-Prozess — Das Gram Schmidtsche Orthogonalisierungsverfahren ist ein Algorithmus aus dem mathematischen Teilgebiet der linearen Algebra. Er erzeugt zu jedem System linear unabhängiger Vektoren aus einem Prähilbertraum, d. h. einem Vektorraum mit… … Deutsch Wikipedia
Gram-Schmidt-Verfahren — Das Gram Schmidtsche Orthogonalisierungsverfahren ist ein Algorithmus aus dem mathematischen Teilgebiet der linearen Algebra. Er erzeugt zu jedem System linear unabhängiger Vektoren aus einem Prähilbertraum, d. h. einem Vektorraum mit… … Deutsch Wikipedia
Gram-Schmidt orthogonalization — /gram shmit /, Math. a process for constructing an orthogonal basis for a Euclidean space, given any basis for the space. [named after Jörgen Pedersen Gram (1850 1916), Danish mathematician, and Erhard Schmidt (1876 1959), German mathematician] * … Universalium
Gram-Schmidt orthogonalization — /gram shmit /, Math. a process for constructing an orthogonal basis for a Euclidean space, given any basis for the space. [named after Jörgen Pedersen Gram (1850 1916), Danish mathematician, and Erhard Schmidt (1876 1959), German mathematician] … Useful english dictionary
Procédé de Gram-Schmidt — En algèbre linéaire, dans un espace préhilbertien (c est à dire un espace vectoriel sur le corps des réels ou celui des complexes, muni d un produit scalaire), le procédé de Gram Schmidt[1] est un algorithme pour construire, à partir d une… … Wikipédia en Français
Lemme d'orthonormation de Gram-Schmidt — Procédé de Gram Schmidt En algèbre linéaire, dans un espace vectoriel muni d un produit scalaire, le procédé de Gram Schmidt[1], en notant ou est un algorithme pour construire de proche en proche une base orthonormée à partir d une base donnée.… … Wikipédia en Français
![N= [0,p]\,](/pictures/frwiki/50/2f6bce44984c0ebf193ada154043c3e6.png) ou
ou 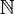 est un algorithme pour construire de proche en proche une base orthonormée à partir d'une base donnée.
est un algorithme pour construire de proche en proche une base orthonormée à partir d'une base donnée. est une famille libre d'un espace préhilbertien, il existe une et une seule famille orthonormée
est une famille libre d'un espace préhilbertien, il existe une et une seule famille orthonormée 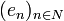 telle que :
telle que :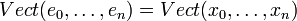 pour tout
pour tout 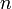
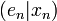 est strictement positif
est strictement positif