- Réarrangement de Baker-Venkataraman
-
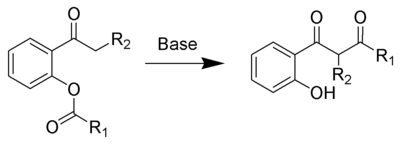
Le réarrangement de Baker-Venkataraman est la réaction chimique d'une 2-acétoxyacétophénone avec une base pour former une 1,3-dicétone substituée par un groupe phénol[1],[2].
La réaction a été nommée d'après les noms des chimistes Wilson Baker et Krishnaswamy Venkataraman.
Sommaire
Mécanisme
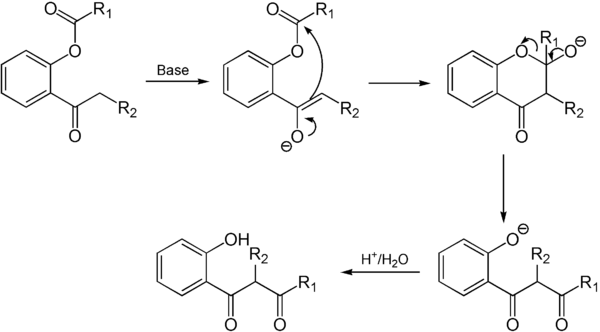
La base, qui ne fait que catalyser la réaction, s'attaque à l'hydrogène de la fonction acétophénone pour former un énolate. Ce groupe énolate attaque ensuite le carbone de la fonction ester de phénol, formant ainsi un alcoolate cyclique. Ce cycle finit par se rouvrir en dicétone et phénolate, qui est reprotoné en phénol.
Utilisation
Le réarrangement de Baker–Venkataraman est souvent utilisé dans la synthèse des chromones et des flavones[3],[4],[5],[6],[7],[8],[9],[10].
Notes et références
- W. Baker, « Molecular rearrangement of some o-acyloxyacetophenones and the mechanism of the production of 3-acylchromones », dans J. Chem. Soc., 1933, p. 1381–1389 [lien DOI]
- Mahal, H. S.; Venkataraman, K., « Synthetical experiments in the chromone. group. XIV. Action of sodamide on 1-acyloxy-2-acetonaphthones », dans J. Chem. Soc., 1934, p. 1767–1769 [lien DOI]
- T. S. Wheeler, « Flavone », dans Organic Syntheses, vol. 32, 1952, p. 72 [texte intégral] (also in the Collective Volume (1963) 4:478 (PDF)).
- P. K. Jain, « A Facile Baker-Venkataraman Synthesis of Flavones using Phase Transfer Catalysis », dans Synthesis, vol. 1982, 1982, p. 221–222 [lien DOI]
- Kalinin, A. V.;Da Silva, A. J. M.;Lopes, C. C.;Lopes, R. S. C.;Snieckus, V., « Directed ortho metalation - cross coupling links. Carbamoyl rendition of the baker-venkataraman rearrangement. Regiospecific route to substituted 4-hydroxycoumarins », dans Tetrahedron Lett., vol. 39, no 28, 9 July 1998, p. 4995–4998 [lien DOI]
- Kraus, G. A.; Fulton, B. S. Wood, S.H.J.Org.Chem. 1984, 49, 3212
- Reddy, B.P.; Krupadanam, G.L.D.J. Heterocycl. Chem 1996, 33, 1561
- Kalinin, A.V.; Sneckus, V. Tetrahedron Lett. 1998, 39 4999
- Thasana, N.; Ruchirawat, S. Tetrahedron Lett. 2002, 43, 4515
- Santo, C.M.M.;Sliva, A.M.S. Cavaleiro, J. A.S. Eur.J. Org. Chem. 2003, 4575
- (en) Cet article est partiellement ou en totalité issu de l’article de Wikipédia en anglais intitulé « Baker–Venkataraman rearrangement » (voir la liste des auteurs)
Voir aussi
- Réaction d'Allan-Robinson
- Acylation de Kostanecki
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.