- Méthoxyoctane
-
Méthoxyoctane 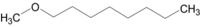
Général Nom IUPAC 1-méthoxyoctane Synonymes méthyloctyléther
oxyde de méthyle et d'octyleNo CAS No EINECS PubChem SMILES InChI Propriétés chimiques Formule brute C9H20O [Isomères] Masse molaire[1] 144,2545 ± 0,0089 g·mol-1
C 74,93 %, H 13,97 %, O 11,09 %,Propriétés physiques T° fusion -52,5 °C [2] T° ébullition 172,0 °C [2] Masse volumique 0,7830 g·cm-3 à 25 °C [3] Unités du SI & CNTP, sauf indication contraire. Le méthoxyoctane est un éther.
Production et synthèse
Le méthoxyoctane peut être synthétisé par réaction entre le octylate de sodium et le bromure de méthyle. L'octylate de sodium est préparé par addition de sodium dans de l'octan-1-ol[2]. La réaction a un rendement d'environ 50%[2]. Cette voie de synthèse s'appelle synthèse de Williamson.
- Na + CH3(CH2)6-CH2-OH
 CH3(CH2)6-CH2-ONa + 0,5 H2
CH3(CH2)6-CH2-ONa + 0,5 H2 - CH3(CH2)6-CH2-ONa + CH3Br
 CH3(CH2)6-CH2-O-CH3 + NaBr
CH3(CH2)6-CH2-O-CH3 + NaBr
Notes et références
- Masse molaire calculée d’après Atomic weights of the elements 2007 sur www.chem.qmul.ac.uk.
- (en) Lawrence W. Devaney et George W. Panian, « Preparation and Properties of Some Octyl Ethers », dans J. Am. Chem. Soc., vol. 75, no 19, 1953, p. 4836-4837 [lien DOI (page consultée le 16 septembre 2010)]
- (en) Misako Obama, Yuichiro Oodera, Nobuyuki Kohana, Tomitaka Yanase, Yoshihiro Saito et Kazuhito Kusano, « Densities, molar volumes, and cubic expansion coefficients of 78 aliphatic ethers », dans J. Chem. Eng. Data, vol. 30, no 1, 1985, p. 1-5 [lien DOI (page consultée le 16 septembre 2010)]
Catégorie :- Éther de méthyle
- Na + CH3(CH2)6-CH2-OH
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
