- Oxydation de Corey-Kim
-
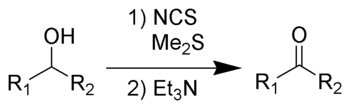
L'oxydation de Corey-Kim est une réaction d'oxydation organique utilisée pour la préparation des aldéhydes et des cétones à partir des alcools primaires et secondaires[1],[2],[3],[4],[5].
Elle est nommée d'après le chimiste américain Elias James Corey et le chimiste coréen-américain Choung Un Kim. Même si cette réaction possède l'avantage certain de pouvoir se dérouler à -25 °C contre -30 à -78 °C selon les cas pour l'oxydation de Swern, elle n'est pas employée de façon courante car elle utilise le sulfure de diméthyle (DMS), un liquide toxique, volatil et sentant particulièrement mauvais.
Notes et références
- E. J. Corey, C. U. Kim, « New and highly effective method for the oxidation of primary and secondary alcohols to carbonyl compounds », dans Journal of the American Chemical Society, vol. 94, no 21, 1972, p. 7586–7587 [lien DOI]
- E. J. Corey, C. U. Kim, « A method for the oxidation of sec,tert -1,2-diols to α-hydroxy ketones without carbon-carbon cleavage », dans Tetrahedron Letters, vol. 15, no 3, 1974, p. 287–290 [lien DOI]
- S. Katayama, K. Fukuda, T. Watanabe, M. Yamauchi, « Synthesis of 1,3-Dicarbonyl Compounds by the Oxidation of 3-Hydroxycarbonyl Compounds with Corey–Kim Reagent », dans Synthesis, 1988, p. 178–183 [lien DOI]
- T. T. Tidwell, « Oxidation of Alcohols by Activated Dimethyl Sulfoxide and Related Reactions: An Update », dans Synthesis, 1990, p. 857–870 [lien DOI]
- J. T. Pulkkinen, J. J. Vepsäläinen, « 3-Unsubstituted 1,5-Diaryl-2,4-pentanediones and -4-methoxy-2-pentanones: Synthesis via Corresponding 3-Hydroxy Ketones Generated from 2-Isoxazolines », dans Journal of Organic Chemistry, vol. 61, no 24, 1996, p. 8604–8609 [lien DOI]
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.