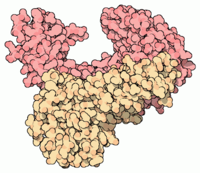
Reverse-transcriptases
- Reverse-transcriptases
-
Transcriptase inverse
La transcriptase inverse ou rétrotranscriptase (en anglais reverse transcriptase ou encore RT) est une enzyme utilisée par les rétrovirus et les rétrotransposons qui transcrivent l'information génétique des virus ou rétrotransposons de l'ARN en ADN, qui peut s'intégrer dans le génome de l'hôte. Les eucaryotes à ADN linéaire utilisent la télomérase, une variante de la transcriptase inverse, avec le modèle d'ARN contenu dans l'enzyme elle-même. L'enzyme que l'on mentionne collectivement sous le nom de transcriptase inverse comprend en général une polymérase de l'ADN ARN-dépendante et une polymérase de l'ADN ADN-dépendante, lesquelles travaillent en synergie pour réaliser la transcription en sens inverse de la direction standard. Cette transcription inverse ou rétrotranscription permet comme son nom l'indique de transcrire à l'envers c’est-à-dire d'obtenir de l'ADN à partir d'ARN.
La transcriptase inverse est utilisé dans le cadre d'une RT-PCR pour quantifier par exemple de l'ARN. En effet, la réaction en chaîne par polymérase (PCR) amplifie de l'ADN qui diffère de l'ARN par une différence de sucre (Désoxyribose pour l'ADN, Ribose pour l'ARN), ainsi que par une différence de base azotée (l'uracile (U) de l'ARN correspond à la thymine (T) de l'ADN), la RT effectue ce changement de base pour ainsi donner de l'ADN exploitable en PCR.
Lien externe
 Portail de la biologie
Portail de la biologie Portail de la chimie
Portail de la chimie Portail de la médecine
Portail de la médecine
Catégories : EC 2.7.7 | Enzyme de biologie moléculaire | Enzyme virale
Wikimedia Foundation.
2010.
Contenu soumis à la licence CC-BY-SA. Source : Article Reverse-transcriptases de Wikipédia en français (auteurs)
Regardez d'autres dictionnaires:
Reverse transcriptase — Protbox Name=Reverse Transcriptase Photo=1HMV.png|250px Caption=3D model of HIV reverse transcriptase HGNCid = Symbol = AltSymbols = Chromosome = Arm = Band = LocusSupplementaryData = Gene= Gene type= Protein length= Molecular weight= Structure=… … Wikipedia
Discovery and development of nucleoside and nucleotide reverse-transcriptase inhibitors — (NRTIs and NtRTIs) began in the 1980s when the AIDS epidemic hit Western societies. NRTIs inhibit the reverse transcriptase (RT), an enzyme that controls the replication of the genetic material of the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). The first … Wikipedia
Multicopy single-stranded DNA — An example of an RNA stem loop, similar to what is seen in the RNA region of msDNA Multicopy single stranded DNA (msDNA) is a type of extrachromosomal satellite DNA that consists of a single stranded DNA molecule linked via a phosphodiester bond… … Wikipedia
Murine leukemia virus — MMLV redirects here. It is also the Roman numeral for 2055. Murine leukemia virus Virus classification Group: Group VI (ssRNA RT) Family: Retroviridae Subfamily … Wikipedia
Transcriptasa inversa — La estructura cristalográfica de la transcriptasa inversa del VIH invertir en la subunidad P51 es de color verde y la subunidad P66 es de color azul.[1] … Wikipedia Español
Telomere — [ chromosomes (grey) capped by telomeres (white)] A telomere is a region of repetitive DNA at the end of chromosomes, which protects the end of the chromosome from destruction. Its name is derived from the Greek nouns telos ( τἐλος ) end and… … Wikipedia
TRT — (= telomerase reverse transcriptase; hEST2) The protein subunit (123 kD) that catalyses telomeric DNA extension has sequence and functional characteristics of a reverse transcriptase related to retrotransposon and retroviral reverse… … Dictionary of molecular biology
Flavonoid — The term flavonoid (or bioflavonoid) refers to a class of plant secondary metabolites. According to the IUPAC nomenclature, [http://www.iupac.org/goldbook/F02424.pdf Flavonoids (isoflavonoids and neoflavonoids).] , IUPAC Compendium of Chemical… … Wikipedia
Oncovirinae — Term formerly used to designate a now obsolete subfamily of viruses (family Retroviridae) composed of the RNA tumor viruses that contain two identical plus stranded RNA molecules. Subgroups are based on antigenicity, host range, and kind of… … Medical dictionary
Manganese — Not to be confused with Magnesium. This article is about the chemical element. For the ghost town, see Manganese, Minnesota. For the steamship, see SS Manganese. chromium ← manganese → iron ↑ Mn ↓ Tc … Wikipedia