- Planum temporale
-
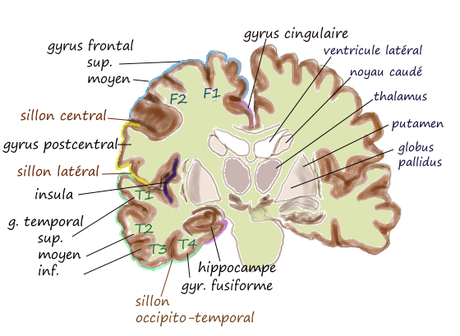
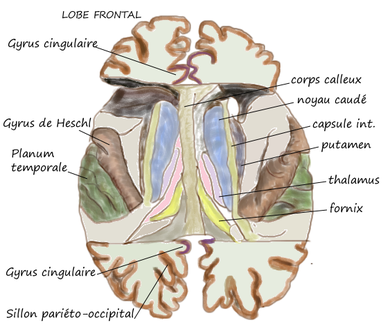
Le planum temporale PT est un gyrus du lobe temporal du cortex cérébral. Il est situé sur la face supérieure du gyrus temporal supérieur, à l'intérieur de la scissure de Sylvius, postérieurement au gyrus de Heschl et en s'enfonçant dans le cerveau jusqu'à l'insula.
Il a une forme plus ou moins triangulaire, limitée en avant par le sillon postérieur du premier gyrus temporal transverse (gyrus de Heschl), et en arrière par un sillon correspondant à la terminaison horizontale de la scissure de Sylvius.
Le PT correspond sur le plan cytoarchitectonique à du cortex auditif associatif. Dans l'hémisphère dominant pour le langage (le gauche en général), il comprend l'aire de Wernicke, impliquée dans le langage. L'examen de 100 cerveaux postmortem, a montré que l'aire du PT du côté gauche était plus grande dans 65% des cas[1]. Par contre, une analyse volumétrique (prenant en compte aussi l'épaisseur du cortex) faite par IRM sur 42 enfants de 4 à 15 ans n'a pas décelé d'asymétrie hémisphérique des PT significative[2].
Liens internes
Références
- Geschwind N, Levitsky W., « Human brain: left-right asymmetries in temporal speech region », dans Science, vol. 161, 1968, p. 186-7
- L.Vadlamudi, R.Hatton, K.Byth, J.Harasty, S.Vogrin, M.J.Cook, A.F.Bleasel, « Volumetric analysis of a specific language region – the planum temporale », dans Journal of Clinical Neuroscience, vol. 13, 2006
Olivier Houdé, Bernard Mazoyer, Nathalie Tzourio-Mazoyet, Cerveau et psychologie Introduction à l'imagerie cérébrale anatomique et fonctionnelle, puf, 2002
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.