- Eastern Interconnection
-
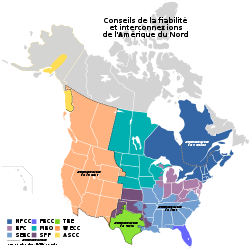 Carte montrant les deux réseaux électriques majeurs d'Amérique du Nord, ainsi que les trois réseaux mineurs. Les zones colorées indiquent les aires contrôlées par les neuf réseaux de la North American Electric Reliability Corporation.
Carte montrant les deux réseaux électriques majeurs d'Amérique du Nord, ainsi que les trois réseaux mineurs. Les zones colorées indiquent les aires contrôlées par les neuf réseaux de la North American Electric Reliability Corporation.
L’Eastern Interconnection est l'un des deux réseaux électriques à courant alternatif majeurs d'Amérique du Nord. L'autre réseau majeur est le Western Interconnection, alors que les trois interconnexions mineures sont l'Interconnexion du Québec, l'Alaska Interconnection et le Texas Interconnection.
Toutes les installations électriques du Eastern Interconnection sont électriquement reliées lors de l'exploitation normale du réseau, dans lequel l'électricité circule à une fréquence moyenne de 60 Hz. Ce réseau connecte les provinces maritimes, l'Ontario, le Manitoba et la Saskatchewan (mais pas le Québec), le sud des États-Unis et l'ouest des États-Unis jusqu'aux montagnes rocheuses (à l'exception de la plus grande partie du Texas).
Les interconnexions peuvent être effectuées à l'aide de lignes équipées de HVDC (pour le courant continu - DC) ou à l'aide de transformateurs à fréquence variable (TFV), lesquels permettent de contrôler le flux de l'énergie électrique tout en isolant le courant alternatif de chaque sous-réseau. En 2009, l'Eastern Interconnection est reliée au Western Interconnection avec six lignes DC, au Texas Interconnection avec deux lignes DC et à l'Interconnexion du Québec avec quatre lignes DC et un TFV.
Demande électrique
Le North American Electric Reliability Corporation (NERC) a publié les consommations courantes et projetées dans les régions connectées au Eastern Interconnection[1] :
Estimations de la demande future en électricité
pour les réseau de l'Eastern Interconnection (GW)Été Hiver Région 2007 2017 Croissance 2007 2017 Croissance Florida Reliability Coordinating Council (FRCC) 47 57 21,3 % 42 60 42,9 % Midwest Reliability Organization
(MRO pour les États-Unis)42 52 23,8 % 35 42 20,0 % Northeast Power Coordinating Council
(NPCC pour les États-Unis)61 69 13,1 % 48 53 10,4 % Reliabilityfirst (RFC) 180 209 16,1 % 141 164 16,3 % SERC Reliability Corporation (SERC) 209 243 16,3 % 179 209 16,8 % Southwest Power Pool (SPP) 43 51 18,6 % 31 38 22,6 % East Interconnection
(pour les États-Unis)582 681 17,0 % 476 566 18,9 % Midwest Reliability Organization
(Manitoba et Saskatchewan)6,2 6,9 11,3 % 7,3 8,2 12,3 % Northeast Power Coordinating Council
(Provinces maritimes, Québec et Ontario)50,3 50,7 0,8 % 65,0 66,7 2,6 % East Interconnection
(Canada)56,5 57,6 2,0 % 72,3 74,9 3,6 % Eastern Interconnection 638,5 738,6 15,7 % 548,3 640,9 16,9 % Notes et références
- Load Forecasting Working Group of the Reliability Assessment Subcommittee, 2008-2017 Regional and National Peak Demand and Energy Forecasts Bandwidths, North American Electric Reliability Corporation, août 2008, pdf [lire en ligne (page consultée le 2008-12-15)], p. 7-12
Articles connexes
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
