tz database
- tz database
-
La tz database, aussi appelée la zoneinfo database, est une base de données qui contient différentes informations sur les fuseaux horaires du monde. Tenue à jour par plusieurs personnes, elle est surtout utile aux logiciels et aux systèmes d'exploitation[1]. Elle est parfois appelée la Olson database en l'honneur d'Arthur David Olson, son créateur[2]. En 2011, Paul Eggert est l'éditeur de la tz database[3]. Elle se distingue par sa convention de nommage, mis au point par Eggert, pour désigner les fuseaux horaires, par exemple « America/New_York » et « Europe/Paris »[4]. Cette base de données contient une grande quantité d'informations à propos des fuseaux horaires historiques, dont les anciens fuseaux et tous les changements apportés depuis 1970, début de l’epoch de l'heure UNIX[5] Elle tient compte des changements horaires, telle l'heure d’été et les secondes intercalaires[6]
Le 6 octobre 2011, suite à des poursuites judiciaires, la base est fermée. Le 14 octobre 2011, l'ICANN prend en charge l'hébergement de la base et s'engage à faire face à toutes les poursuites[7].
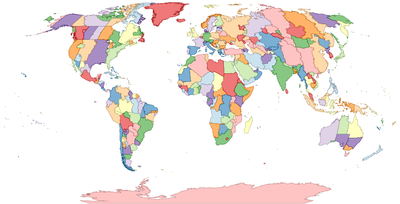
La
tz database divise le monde en régions où toutes les horloges officielles régionales sont actives depuis 1970. Cette carte, générée à partir de la version 2009r de la base de données, montre toutes les régions,
Antarctique exceptée
[8].
Notes et références
- ↑ (en) Sources for time zone and daylight saving time data, 2007-11-29. Consulté le 2007-12-03
- ↑ (en) Arthur David Olson, Resolved timezone issue? Other issues. New ctime manual page, tz mailing list, 1986-12-16
- ↑ (en) Re: FW: IANA time zone registration - proposal, mailing list time.tz, 2005-01
- ↑ (en) Paul Eggert, proposal for time zone names, tz mailing list, 1993-10-20
- ↑ (en) Arthur David Olson, Re: ist of issues, tz mailing list, 1987-03-18
- ↑ (en) Bob Devine, leap seconds; [0-60] is ok, tz mailing list, 1988-06-02
- ↑ (en) http://www.icann.org/en/news/releases/release-14oct11-en.pdf
- ↑ (en) A map of the TZ timezones of the world Mise à jour le 2009-11-23.
Liens externes
Wikimedia Foundation.
2010.
Contenu soumis à la licence CC-BY-SA. Source : Article tz database de Wikipédia en français (auteurs)
Regardez d'autres dictionnaires:
Database design — is the process of producing a detailed data model of a database. This logical data model contains all the needed logical and physical design choices and physical storage parameters needed to generate a design in a Data Definition Language, which… … Wikipedia
Database audit — Database auditing involves observing a database so as to be aware of the actions of database users. Database administrators and consultants often set up auditing for security purposes, for example, to ensure that those without the permission to… … Wikipedia
Database security — concerns the use of a broad range of information security controls to protect databases (potentially including the data, the database applications or stored functions, the database systems, the database servers and the associated network links)… … Wikipedia
Database administration and automation — Database administration is the function of managing and maintaining database management systems (DBMS) software. Mainstream DBMS software such as Oracle, IBM DB2 and Microsoft SQL Server need ongoing management. As such, corporations that use… … Wikipedia
Database activity monitoring — (DAM) is a database security technology for monitoring and analyzing database activity that operates independently of the database management system (DBMS) and does not rely on any form of native (DBMS resident) auditing or native logs such as… … Wikipedia
Database marketing — is a form of direct marketing using databases of customers or potential customers to generate personalized communications in order to promote a product or service for marketing purposes. The method of communication can be any addressable medium,… … Wikipedia
Database tuning — describes a group of activities used to optimize and homogenize the performance of a database. It usually overlaps with query tuning, but refers to design of the database files, selection of the database management system (DBMS), operating system … Wikipedia
Database journalism — or structured journalism is a principle in information management whereby news content is organized around structured pieces of data, as opposed to news stories. Communication scholar Wiebke Loosen defines database journalism as supplying… … Wikipedia
Database storage structures — Database tables/indexes are typically stored on hard disk in one of many forms, ordered/unordered Flat files, ISAM, Heaps, Hash buckets or B+ Trees. These have various advantages and disadvantages discussed in this topic. The most commonly used… … Wikipedia
Database virtualization — is the decoupling of the database layer, which lies between the storage and application layers within the application stack. Virtualization at the database layer allows hardware resources to be extended to allow for better sharing resources… … Wikipedia
database — da‧ta‧base [ˈdeɪtəˌbeɪs] noun [countable] COMPUTING a large amount of information on a particular subject that is stored on a computer in an organized way so that you can find and use it easily: • a database of all the UK clearing houses •… … Financial and business terms
 La tz database divise le monde en régions où toutes les horloges officielles régionales sont actives depuis 1970. Cette carte, générée à partir de la version 2009r de la base de données, montre toutes les régions, Antarctique exceptée[8].
La tz database divise le monde en régions où toutes les horloges officielles régionales sont actives depuis 1970. Cette carte, générée à partir de la version 2009r de la base de données, montre toutes les régions, Antarctique exceptée[8].
