Réaction de Hill
- Réaction de Hill
-
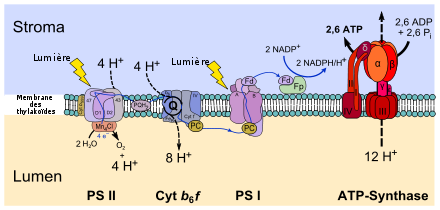
La réaction de Hill est une réaction d'oxydo-réduction se déroulant lors de la photosynthèse, mise en évidence expérimentalement par le biochimiste anglais Robert Hill en 1937 et 1939. Il a montré que la réaction de photosynthèse pouvait être découplée en deux réactions formant un système d'oxydoréduction. La réaction de Hill est représenté par l'équation suivante:
- 2 H2O + 2 A + (lumière, chloroplastes) → 2 AH2 + O2[1]
Hill réalise son expérience sur une suspension de chloroplastes et utilise, en absence de CO2, un oxydant artificiel : le ferricyanure de potassium. La réaction de Hill peut être définie par le transfert d'électron via le photosystème II (PSII) et la chaîne de transfert d'électrons jusqu'à un accepteur d'électrons artificiel.
Références
- ↑ A étant un accepteur d'électrons artificiel
Wikimedia Foundation.
2010.
Contenu soumis à la licence CC-BY-SA. Source : Article Réaction de Hill de Wikipédia en français (auteurs)
Regardez d'autres dictionnaires:
Réaction de Jarisch-Herxheimer — (ou réaction de Herxheimer) Classification et ressources externes CIM 10 T78.2 CIM 9 995.0 DiseasesDB … Wikipédia en Français
Hill reaction — hil n the light dependent transfer of electrons by chloroplasts in photosynthesis that results in the cleavage of water molecules and liberation of oxygen Hill Robin (fl 1937) British biochemist. Hill discovered the reaction that now bears his na … Medical dictionary
Hill reaction — Reaction, first demonstrated by Robert Hill in 1939, in which illuminated chloroplasts evolve oxygen when incubated in the presence of an artificial electron acceptor (eg. ferricyanide). The reaction is a property of photosystem II … Dictionary of molecular biology
Hill equation — The Hill equation is an equation used in biochemical characterization, which should not be confused with the Hill differential equation that is also sometimes referred to as simply the Hill equation or Hill s equation .In biochemistry, the… … Wikipedia
Réaction aldol — Aldolisation L aldolisation (appelée aussi cétolisation dans le cadre des cétones) est une réaction de formation de liaisons carbone carbone importante en chimie organique[1],[2],[3]. Elle implique généralement l addition nucléop … Wikipédia en Français
Réaction d'aldolisation — Aldolisation L aldolisation (appelée aussi cétolisation dans le cadre des cétones) est une réaction de formation de liaisons carbone carbone importante en chimie organique[1],[2],[3]. Elle implique généralement l addition nucléop … Wikipédia en Français
Réaction du cation de l'argent — Composés de l ion argent Le cation Ag+ fait partie du premier groupe de cations dans le schéma d analyse qualitative. Sa réaction la plus caractéristique est la suivante : cation Ag+ + anion Cl → précipité de chlorure d argent (solution… … Wikipédia en Français
Hill reagent — Discovered in 1937 by Robin Hill , these reagents allowed the discovery of electron transport chains during photosynthesis.These are dyes that act as artificial electron acceptors, changing color when they are reduced.Ex : 2,6… … Wikipedia
reaction — 1. The response of a muscle or other living tissue or organism to a stimulus. 2. The color change effected in litmus and certain other organic pigments by contact with substances such as acids or alkalies; also the property that such substances… … Medical dictionary
Hill reaction — noun Etymology: Robert Hill died 1991 British biochemist Date: 1950 the light dependent transfer of electrons by chloroplasts in photosynthesis that results in the cleavage of water molecules and liberation of oxygen … New Collegiate Dictionary